|
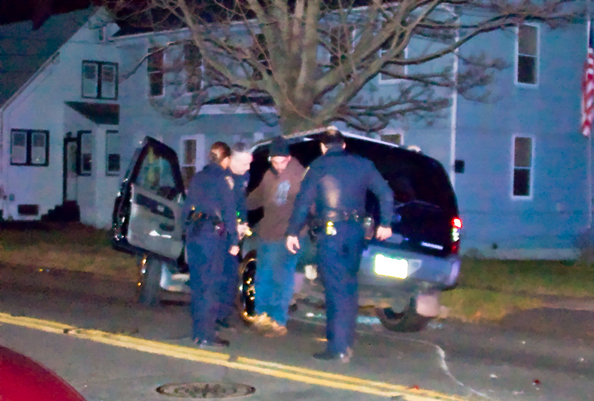
Drinking And Driving
Drunk driving (or drink-driving in British English) is the act of driving under the influence of alcohol. A small increase in the blood alcohol content increases the relative risk of a motor vehicle crash. In the United States, alcohol is involved in 32% of all traffic fatalities. Terminology United States In the United States, most states have generalized their criminal offense statutes to driving under the influence (DUI). These DUI statutes generally cover intoxication by any drug, including alcohol. Such laws may also apply to operating boats, aircraft, farm machinery, horse-drawn carriages, and bicycles. Specific terms used to describe alcohol-related driving offenses include "drinking and driving", "drunk driving", and "drunken driving". Most DUI offenses are alcohol-related so the terms are used interchangeably in common language, and "drug-related DUI" is used to distinguish. United Kingdom In the United Kingdom, there are two separate offences to do with alcohol a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breathalyzer
A breathalyzer or breathalyser (a portmanteau of ''breath'' and ''analyzer/analyser''), also called an alcohol meter, is a device for measuring breath alcohol (drug), alcohol content (BrAC). It is commonly utilized by law enforcement officers whenever they initiate traffic stops. The name is a genericized trademark of the Breathalyzer brand name of instruments developed by inventor Robert Frank Borkenstein in the 1950s. Origins Research into the possibilities of using breath to test for alcohol in a person's body dates as far back as 1874, when Francis E. Anstie made the observation that small amounts of alcohol were excreted in breath. In 1927, Emil Bogen produced a paper on breath analysis. He collected air in a football bladder and then tested this air for traces of alcohol, discovering that the alcohol content of 2 litres of expired air was a little greater than that of 1 cc of urine. Also in 1927, a Chicago chemist, William Duncan McNally, invented a breathalyz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Poisoning
Alcohol intoxication, commonly described in higher doses as drunkenness or inebriation, and known in overdose as alcohol poisoning, is the behavior and physical effects caused by recent consumption of alcohol. The technical term ''intoxication'' in common speech may suggest that a large amount of alcohol has been consumed, leading to accompanying physical symptoms and deleterious health effects. Mild intoxication is mostly referred to by slang terms such as ''tipsy'' or ''buzzed''. In addition to the toxicity of ethanol, the main psychoactive component of alcoholic beverages, other physiological symptoms may arise from the activity of acetaldehyde, a metabolite of alcohol. These effects may not arise until hours after ingestion and may contribute to a condition colloquially known as a hangover. Symptoms of intoxication at lower doses may include mild sedation and poor coordination. At higher doses, there may be slurred speech, trouble walking, impaired vision, mood swings an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to Nociception, respond normally to Pain, painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal Circadian rhythm, sleep-wake cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. The person may experience respiratory and circulatory problems due to the body's inability to maintain normal bodily functions. People in a coma often require extensive medical care to maintain their health and prevent complications such as pneumonia or blood clots. Coma patients exhibit a complete absence of wakefulness and are unable to consciously feel, speak or move. Comas can be the result of natural causes, or can be Induced coma, medically induced, for example, during General anaesthesia, general anesthesia. Clinically, a coma can be defined as the consistent inability to follow a one-step command. For a patient to maintain consciousness, the components of ''wakefulness'' and ''awareness'' must be maintained. Wak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Depression
Hypoventilation (also known as respiratory depression) occurs when ventilation is inadequate (''hypo'' meaning "below") to perform needed respiratory gas exchange. By definition it causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide (hypercapnia) and respiratory acidosis. Hypoventilation is not synonymous with respiratory arrest, in which breathing ceases entirely and death occurs within minutes due to hypoxia and leads rapidly into complete anoxia, although both are medical emergencies. Hypoventilation can be considered a precursor to hypoxia, and its lethality is attributed to hypoxia with carbon dioxide toxicity. Causes Hypoventilation may be caused by: *A medical condition such as stroke affecting the brainstem *Voluntary breath-holding or underbreathing, for example, hypoventilation training or the Buteyko method. *Medication or drugs, typically when taken in accidental or intentional overdose. Opioids are a well-known cause of drug-induced hypoventilation due to their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterograde Amnesia
In neurology, anterograde amnesia is the inability to create new memories after an event that caused amnesia, leading to a partial or complete inability to recall the recent past, while long-term memories from before the event remain intact. This is in contrast to retrograde amnesia, where memories created prior to the event are lost while new memories can still be created. Both can occur together in the same patient. To a large degree, anterograde amnesia remains a mysterious ailment because the precise mechanism of storing memories is not yet well understood, although it is known that the regions of the brain involved are certain sites in the temporal cortex, especially in the hippocampus and nearby subcortical regions. Signs and symptoms People with anterograde amnesic syndromes may present widely varying degrees of forgetfulness. Some with severe cases have a combined form of anterograde and retrograde amnesia, sometimes called global amnesia. In the case of drug-induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stupor
Stupor is the lack of critical mental function and a level of consciousness, in which an affected person is almost entirely unresponsive and responds only to intense stimuli such as pain. The word derives from the Latin '' stupor'' ("numbness, insensibility"). Signs and symptoms Stupor is characterized by impaired reaction to external stimuli. Those in a stuporous state are rigid, mute and only appear to be conscious, as the eyes are open and follow surrounding objects. If not stimulated externally, a patient with stupor will appear to be in a sleepy state most of the time. In some extreme cases of severe depressive disorders the patient can become motionless, lose their appetite and become mute. Short periods of restricted responsivity can be achieved by intense stimulation (e.g. pain, bright light, loud noise, shock). Causes Stupor is associated with infectious diseases, complicated toxic states (e.g. heavy metals), severe hypothermia, mental illnesses (e.g. schizophren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedation
Sedation is the reduction of irritability or agitation by administration of sedative drugs, generally to facilitate a medical procedure or diagnostic procedure. Examples of drugs which can be used for sedation include isoflurane, diethyl ether, propofol, etomidate, ketamine, pentobarbital, lorazepam and midazolam. Medical uses Sedation is typically used in minor surgical procedures such as endoscopy, vasectomy, or dentistry and for reconstructive surgery, some cosmetic surgeries, removal of wisdom teeth, or for high-anxiety patients. Sedation methods in dentistry include inhalation sedation (using nitrous oxide), oral sedation, and intravenous (IV) sedation. Inhalation sedation is also sometimes referred to as "relative analgesia". Sedation is also used extensively in the intensive care unit so that patients who are being mechanical ventilation, ventilated tolerate having an endotracheal tube in their vertebrate trachea, trachea. It can also be used during a long term brain EEG ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lethargy
Lethargy is a state of tiredness, sleepiness, weariness, fatigue, sluggishness, or lack of energy. It can be accompanied by depression, decreased motivation, or apathy. Lethargy can be a normal response to inadequate sleep, overexertion, overworking, stress, lack of exercise, improper nutrition, drug abuse, boredom, or a symptom of an underlying illness or disorder. It may also be a side effect of medication or caused by an interaction between medications or medication(s) and alcohol. It may also be an altered level of consciousness. When part of a normal response, lethargy often resolves with rest, adequate sleep, decreased stress, physical exercise, and good nutrition. Its symptoms, however, can last days or even months, so it can be a sign of a recent underlying illness or infection if it does not resolve normally. See also * Clinical depression * Disorders of diminished motivation * Encephalitis lethargica * Sleep apnea * Sleep deprivation * Somnolence Somnolence ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol Flush Reaction
Alcohol flush reaction is a condition in which a person develops flushes or blotches associated with erythema on the face, neck, shoulders, ears, and in some cases, the entire body after consuming alcoholic beverages. The reaction is the result of an accumulation of acetaldehyde, a metabolic byproduct of the catabolic metabolism of alcohol, and is caused by an aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 deficiency. This syndrome has been associated with lower than average rates of alcoholism, possibly due to its association with adverse effects after drinking alcohol. However, it has also been associated with an increased risk of esophageal cancer in those who do drink. The reaction is informally termed Asian flush due to its frequent occurrence in East Asians, with approximately 30 to 50% of Chinese, Japanese, and Koreans showing characteristic physiological responses to drinking alcohol that includes facial flushing, nausea, headaches and a fast heart rate. The condition may be also high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyl Alcohol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the pseudoelement symbol for ethyl. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and pungent taste. As a psychoactive depressant, it is the active ingredient in alcoholic beverages, and the second most consumed drug globally behind caffeine. Ethanol is naturally produced by the fermentation process of sugars by yeasts or via petrochemical processes such as ethylene hydration. Historically it was used as a general anesthetic, and has modern medical applications as an antiseptic, disinfectant, solvent for some medications, and antidote for methanol poisoning and ethylene glycol poisoning. It is used as a chemical solvent and in the synthesis of organic compounds, and as a fuel source for lamps, stoves, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Car Rams Through Security Gate At A House
A car, or an automobile, is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of cars state that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people rather than cargo. There are around one billion cars in use worldwide. The French inventor Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot built the first steam-powered road vehicle in 1769, while the Swiss inventor François Isaac de Rivaz designed and constructed the first internal combustion-powered automobile in 1808. The modern car—a practical, marketable automobile for everyday use—was invented in 1886, when the German inventor Carl Benz patented his Benz Patent-Motorwagen. Commercial cars became widely available during the 20th century. The 1901 Oldsmobile Curved Dash and the 1908 Ford Model T, both American cars, are widely considered the first mass-produced and mass-affordable cars, respectively. Cars were rapidly adopted in the US, where they replaced horse-drawn carriages. In Europe and other pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |