|
Draft (hull)
The draft or draught of a ship is a determined depth of the vessel below the waterline, measured vertically to its hull's lowest—its propellers, or keel, or other reference point. Draft varies according to the loaded condition of the ship. A deeper draft means the ship will have greater vertical depth below the waterline. Draft is used in under keel clearance calculations, where the draft is calculated with the available depth of water (from Electronic navigational charts) to ensure the ship can navigate safely, without grounding. Navigators can determine their draught by calculation or by visual observation (of the ship's painted load lines). Related terminology A ship's draft/draught is the "depth of the vessel below the waterline measured vertically to the lowest part of the hull, propellers, or other reference point". That is, the draft or draught is the maximum depth of any part of the vessel, including appendages such as rudders, propellers and drop keels if de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Ship Length Measurements
A ship is a large watercraft, vessel that travels the world's oceans and other Waterway, navigable waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity and purpose. Ships have supported Geographic exploration, exploration, Global trade, trade, Naval warfare, warfare, Human migration, migration, colonization, and science. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a Full-rigged ship, ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is Square rig, square-rigged. The earliest historical evidence of boats is found in Egypt during the 4th millennium BCE. In 2024, ships had a global cargo capacity of 2.4 billion tons, with the three largest classes being ships carrying dry bulk (43%), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
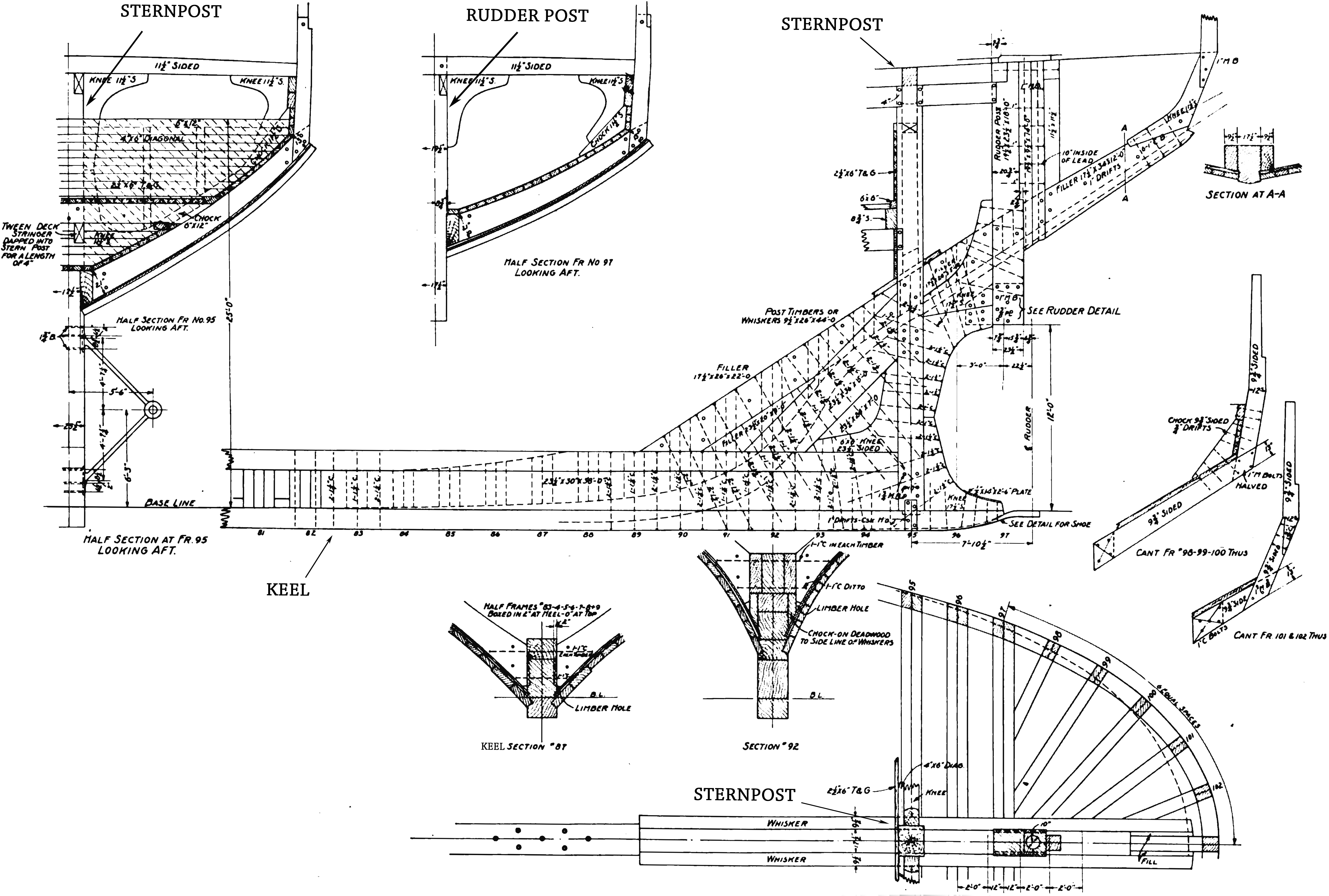 |
Stern
The stern is the back or aft-most part of a ship or boat, technically defined as the area built up over the sternpost, extending upwards from the counter rail to the taffrail. The stern lies opposite the bow, the foremost part of a ship. Originally, the term only referred to the aft port section of the ship, but eventually came to refer to the entire back of a vessel. The stern end of a ship is indicated with a white navigation light at night. Sterns on European and American wooden sailing ships began with two principal forms: the ''square'' or ''transom'' stern and the ''elliptical'', ''fantail'', or ''merchant'' stern, and were developed in that order. The hull sections of a sailing ship located before the stern were composed of a series of U-shaped rib-like frames set in a sloped or "cant" arrangement, with the last frame before the stern being called the ''fashion timber(s)'' or ''fashion piece(s)'', so called for "fashioning" the after part of the ship. This frame i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Decimeters
The decimetre (or in American English; symbol: dm), is a unit of length in the International System of Units, equal to one tenth of a metre, ten centimetres, one hundred millimetres, and 3.937 inches. The common non- SI metric unit of volume, the litre, is defined as one cubic decimetre, although, from 1901 to 1964, there was a slight difference between the two due to the litre being defined using the kilogram rather than the metre. Markings of a ship's draft are shown in decimeters in most of the world. See also *Metric prefix *Deci- * *Conversion of units Conversion of units is the conversion of the unit of measurement in which a quantity is expressed, typically through a multiplicative conversion factor that changes the unit without changing the quantity. This is also often loosely taken to incl ..., for comparison with other units of length. References Metre -01 {{measurement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Metric System
The metric system is a system of measurement that standardization, standardizes a set of base units and a nomenclature for describing relatively large and small quantities via decimal-based multiplicative unit prefixes. Though the rules governing the metric system have changed over time, the modern definition, the International System of Units (SI), defines the metric prefixes and seven base units: metre (m), kilogram (kg), second (s), ampere (A), kelvin (K), Mole (unit), mole (mol), and candela (cd). An SI derived unit is a named combination of base units such as hertz (cycles per second), Newton (unit), newton (kg⋅m/s2), and tesla (unit), tesla (1 kg⋅s−2⋅A−1) and in the case of Celsius a shifted scale from Kelvin. Certain units have been Non-SI units mentioned in the SI#Units officially accepted for use with the SI, officially accepted for use with the SI. Some of these are decimalised, like the litre and electronvolt, and are considered "metric". Others, like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Imperial Units
The imperial system of units, imperial system or imperial units (also known as British Imperial or Exchequer Standards of 1826) is the system of units first defined in the British Weights and Measures Act 1824 and continued to be developed through a series of Weights and Measures Acts and amendments. The imperial system developed from earlier English units as did the Comparison of the imperial and US customary measurement systems, related but differing system of United States customary units, customary units of the United States. The imperial units replaced the Winchester measure, Winchester Standards, which were in effect from 1588 to 1825. The system came into official use across the British Empire in 1826. By the late 20th century, most nations of the former empire had metrication, officially adopted the metric system as their main system of measurement, but imperial units are still used alongside metric units in the United Kingdom and in some other parts of the former empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
International Load Line
The load line, also known as Plimsoll line, indicates the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures in order to safely maintain buoyancy, particularly with regard to the hazard of waves. The load line is a waterline that corresponds to the maximum draft of the ship, thus yet another name, load waterline. Varying water temperatures will affect a ship's draft, because warm water is less dense than cold water, providing less buoyancy. In the same way, fresh water is less dense than salinated or seawater, with a similar lessening effect upon buoyancy. The rules for international load lines are defined by the International Convention on Load Lines from 1966. For inland water transport regional, national or local rules apply. Load lines are indicated by special markings on the hull. The marking for the main load line, the summer load line, is called load line mark or Plimsoll mark (positioned amidships), the marks for other conditions are n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Bow (watercraft)
The bow () is the forward part of the hull of a ship or boat, the point that is usually most forward when the vessel is underway. The aft end of the boat is the stern. Prow may be used as a synonym for bow or it may mean the forward-most part of the bow above the waterline. Function A ship's bow should be designed to enable the hull to pass efficiently through the water. Bow shapes vary according to the speed of the boat, the seas or waterways being navigated, and the vessel's function. Where sea conditions are likely to promote pitching, it is useful if the bow provides reserve buoyancy; a flared bow (a raked stem with flared topsides) is ideal to reduce the amount of water shipped over the bow. Ideally, the bow should reduce the resistance and should be tall enough to prevent water from regularly washing over the top of it. Large commercial barges on inland waterways rarely meet big waves and may have remarkably little freeboard at the bow, whereas fast military ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
733 How-deep
__NOTOC__ Year 733 ( DCCXXXIII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 733 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Byzantine Empire * Emperor Leo III confiscates the papal territories in Sicily and Calabria (Southern Italy), from which Pope Gregory III derives most of his income tax. He transfers ecclesiastical jurisdiction in the former Praetorian prefecture of Illyricum to Anastasius, patriarch of Constantinople. Gregory begins his support of a revolt in Italy against iconoclasm. By now the break between the papacy and the Byzantine Empire is almost complete. * Arab-Byzantine Wars: Arab forces under Mu’awiya ibn Hisham penetrate deep into Anatolia and conquer the cities of Antalya, Doralyum and Afyonkarahisar. These conquests differ from previous ones, as Arab military settling occurs in them, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Draft Marks On A Ship's Bow, With Reflections
Draft, the draft, or draught may refer to: Watercraft dimensions * Draft (hull), the distance from waterline to keel of a vessel * Draft (sail), degree of curvature in a sail * Air draft, distance from waterline to the highest point on a vessel Selection processes * Draft (politics), groundswell of support to compel a candidate to run for office * Draft (sports), selection of players for professional sports teams * Conscription, selection for e.g. military service Entertainment * Draft (musician) (born 1986), electronic musician and DJ * ''Drafted'' (comics), a 2007 comic released by Devil's Due Publishing * ''The Draft'' (comics), a 1988 one-shot comic book from Marvel Comics * The Draft (band), an American punk rock band * ''The Draft!'' (film), a 2023 Indonesian science fiction horror film * WWE draft, a World Wrestling Entertainment program which drafts superstars to different WWE brands * Draughts, board game, a.k.a. checkers * The Draft (''The League''), t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Squat Effect
The squat effect is the hydrodynamic phenomenon by which a vessel moving through shallow water creates an area of reduced pressure that causes the ship to increase its draft (alternatively decrease the underkeel clearance of the vessel in marine terms) and thereby be closer to the seabed than would otherwise be expected. This phenomenon is caused by the water flow which accelerates as it passes between the hull and the seabed in confined waters, the increase in water velocity causing a resultant reduction in pressure. Squat effect from a combination of vertical sinkage and a change of trim may cause the vessel to dip towards the stern or towards the bow. This is understood to be a function of the Block coefficient of the vessel concerned, finer lined vessels Cb 0.7 squatting by the head or bow. Squat effect is approximately proportional to the square of the speed of the ship. Thus, by reducing speed by half, the squat effect is reduced by a factor of four. Squat effect is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
List (watercraft)
The angle of list is the degree to which a vessel heels (leans or tilts) to either port or starboard at equilibrium—with no external forces acting upon it. If a listing ship goes beyond the point where a righting moment will keep it afloat, it will capsize and potentially sink. Listing is caused by the off-centerline distribution of weight aboard due to uneven loading or to flooding. By contrast, ''roll'' is the dynamic movement from side to side caused by waves. See also * Angle of loll * Heeling (sailing) * Capsizing * Metacentric height *Ship stability Ship stability is an area of naval architecture and ship design that deals with how a ship behaves at sea, both in still water and in waves, whether intact or damaged. Stability calculations focus on center of mass#center of gravity, centers of ... * Ship motions References Engineering concepts Naval architecture Ship measurements Angle {{navy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |