|
Domestication Of The Horse
It is not entirely clear how, when or where the domestication of the horse took place. Although horses appeared in Paleolithic cave art as early as 30,000 BCE, these were wild horses and were probably hunted for meat. The clearest evidence of early use of the horse as a means of transport is from chariot burials dated . However, an increasing amount of evidence began to support the hypothesis that horses were domesticated in the Eurasian Steppes in approximately 3500 BCE. Discoveries in the context of the Botai culture had suggested that Botai settlements in the Akmola Province of Kazakhstan are the location of the earliest domestication of the horse. However, Taylor and Barrón-Ortiz (2021) argue that Botai findings only reflect intensive exploitation of wild horses—possibly involving some level of management, herding, or seasonal capture—but not full domestication in the way we see in later horse-using societies. Warmuth et al. (2012) pointed to horses having been domes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic ( years ago) ( ), also called the Old Stone Age (), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone tools, and which represents almost the entire period of human prehistoric technology. It extends from the earliest known use of stone tools by Hominini, hominins, 3.3 million years ago, to the end of the Pleistocene, 11,650 Before Present#Radiocarbon calibration, cal Before Present, BP. The Paleolithic Age in Europe preceded the Mesolithic Age, although the date of the transition varies geographically by several thousand years. During the Paleolithic Age, hominins grouped together in small societies such as band society, bands and subsisted by gathering plants, fishing, and hunting or scavenging wild animals. The Paleolithic Age is characterized by the use of Knapping, knapped stone tools, although at the time humans also used wood and bone tools. Other organic commodities were adapted for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoke
A yoke is a wooden beam used between a pair of oxen or other animals to enable them to pull together on a load when working in pairs, as oxen usually do; some yokes are fitted to individual animals. There are several types of yoke, used in different cultures, and for different types of oxen. A pair of oxen may be called a ''yoke of oxen'', and yoke is also a verb, as in "to ''yoke'' a pair of oxen". Other animals that may be yoked include horses, mules, donkeys, and water buffalo. Etymology The word "yoke" is believed to derive from Proto-Indo-European *yugóm (yoke), from root *''yewg''- (join, unite), and is thus cognate with '' yoga''. This root has descendants in almost all known Indo-European languages including German ''Joch'', Latin ''iugum'', Ancient Greek ζυγόν (''zygon''), Persian یوغ (''yuğ''), Sanskrit युग (''yugá''), Hittite 𒄿𒌑𒃷 (iúkan), Old Church Slavonic иго (''igo''), Lithuanian ''jungas'', Old Irish ''cuing'', and Armenian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holarctic
The Holarctic realm is a biogeographic realm that comprises the majority of habitats found throughout the continents in the Northern Hemisphere. It corresponds to the floristic Boreal Kingdom. It includes both the Nearctic zoogeographical region (which covers most of North America), and Alfred Wallace's Palearctic zoogeographical region (which covers North Africa, and all of Eurasia except for Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, the southern Arabian Peninsula). These regions are further subdivided into a variety of ecoregions. Many ecosystems and the animal and plant communities that depend on them extend across a number of continents and cover large portions of the Holarctic realm. This continuity is the result of those regions’ shared glacial history. Major ecosystems Within the Holarctic realm, there are a variety of ecosystems. The type of ecosystem found in a given area depends on its latitude and the local geography. In the far north, a band of Arctic tun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
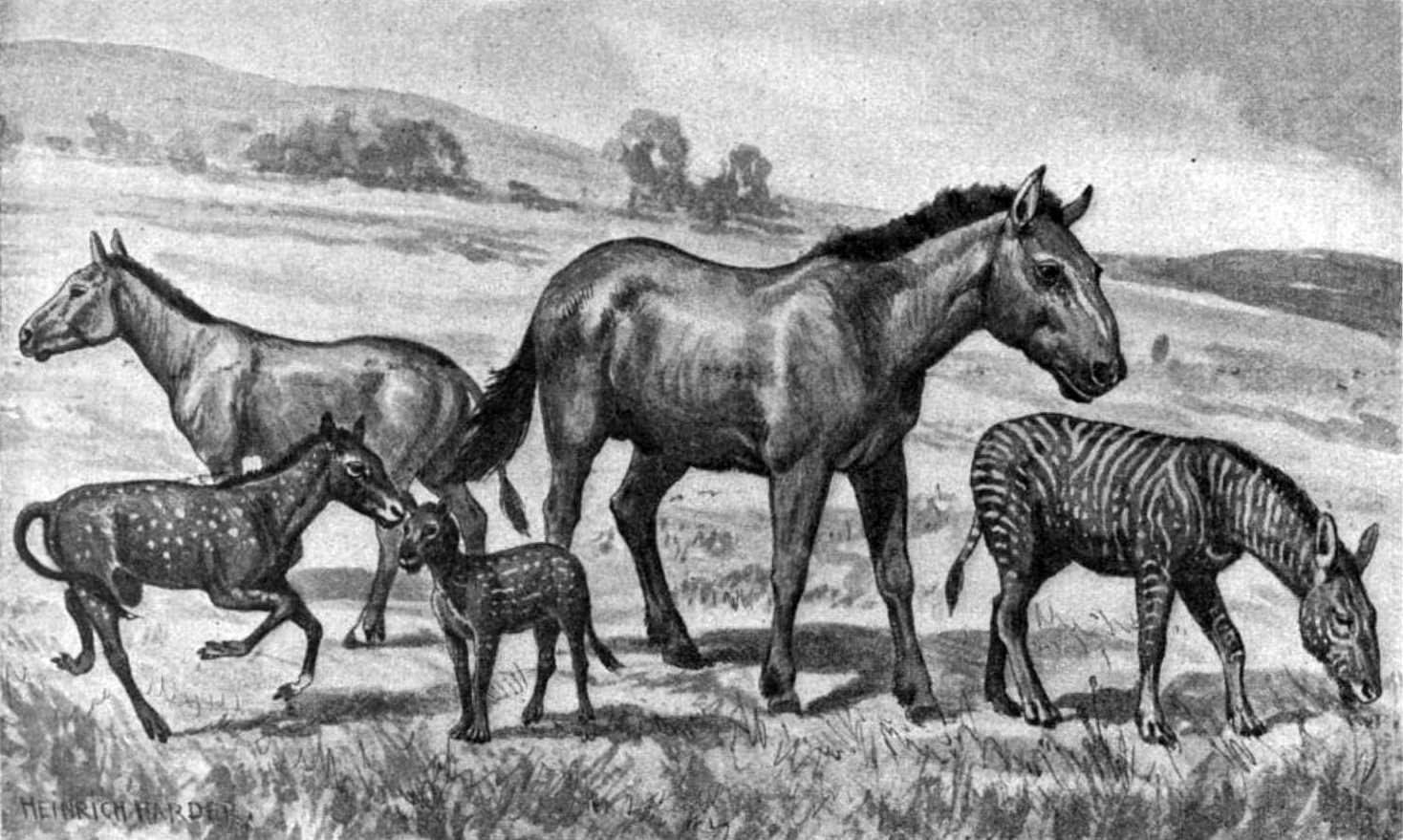
Przewalski's Horse
Przewalski's horse (''Equus ferus przewalskii'' or ''Equus przewalskii''), also called the takhi, Mongolian wild horse or Dzungarian horse, is a rare and endangered wild horse originally native to the steppes of Central Asia. It is named after the Russian geographer and explorer Nikolay Przhevalsky. Once extinct in the wild, since the 1990s it has been Reintroduction, reintroduced to its native habitat in Mongolia in the Khustain Nuruu National Park, Takhin Tal Nature Reserve, and Khomiin Tal, as well as several other locales in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Several genetic characteristics of Przewalski's horse differ from what is seen in modern domestic horses, indicating neither is an ancestor of the other. For example, Przewalski's horse has 33 chromosome pairs, compared to 32 for the domestic horse. Their ancestral lineages split from a common ancestor between 160,000 and 38,000 years ago, long before the domestication of the horse. Przewalski's horse was long considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equus (genus)
''Equus'' () is a genus of mammals in the perissodactyl family (biology), family Equidae, which includes wild horse, horses, Asinus, asses, and zebras. Within the Equidae, ''Equus'' is the only recognized Extant taxon, extant genus, comprising seven living species. Like Equidae more broadly, ''Equus'' has numerous extinct species known only from fossils. The genus originated in North America and dispersed into the Old World and South America during the Early and Middle Pleistocene. Equinae, Equines are odd-toed ungulates with slender legs, long heads, relatively long necks, manes (erect in most subspecies), and long tails. All species are herbivorous, and mostly grazers, with simpler digestive systems than Ruminantia, ruminants but able to subsist on lower-quality vegetation. While the domestic horse and donkey (along with their feral horse, feral descendants) exist worldwide, wild equine populations are limited to Africa and Asia. Wild equine social systems are in two forms; a H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World Stilt-legged Horse
''Haringtonhippus'' is an extinct genus of equine from the Pleistocene of North America The genus is monospecific, consisting of the species ''H. francisci'', initially described in 1915 by Oliver Perry Hay as ''Equus francisci''. Members of the genus are often referred to as stilt-legged horses, in reference to their slender distal limb bones, in contrast with those of contemporary "stout legged" caballine true horses. ''Haringtonhippus'' fossils have only been discovered in North America. Specimens have been found from southern Mexico to southern South Dakota and in Alberta, Canada, at sites such as Gypsum Cave and Natural Trap Cave, as well as eastern Beringia in Yukon A later study found that ''Equus cedralensis'' from the Late Pleistocene of Mexico also belonged to this species. The earliest species of the lineage appeared in North America during the Late Pliocene to Early Pleistocene, around 2 to 3 Ma. It became extinct at the end of the Late Pleistocene, around 12,000 ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippidion
''Hippidion'' (meaning ''little horse'') is an extinct genus of equine that lived in South America from the Late Pliocene to the end of the Late Pleistocene (Lujanian), between 2.5 million and 11,000 years ago. They were one of two lineages of equines native to South America during the Pleistocene epoch, alongside '' Equus (Amerhippus) neogeus''. Taxonomy Evolution Although early ancient DNA analysis studies suggested a close relationship with the wild horse, ''Equus ferus,'' this was later shown to be incorrect, with more complete sequences finding ''Hippidion'' as an outgroup to all living equines and less closely related to living equines than the North American "New World stilt legged horse", '' Haringtonhippus francisci.'' Cladogram shown below: ''Hippidion'' is part of a distinct lineage of equines belonging to the tribe Equini that are suggested to have diverged from the ancestors of living equines of the genus '' Equus'' at least 6 million years ago. The earliest mem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
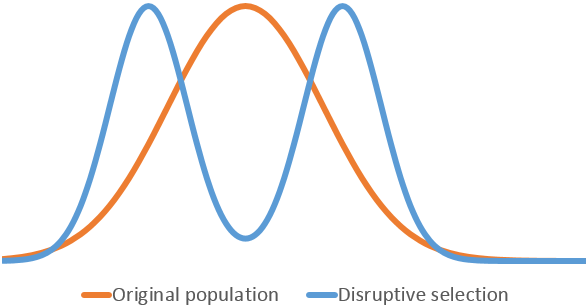
Genetic Divergence
Genetic divergence is the process in which two or more populations of an ancestral species accumulate independent genetic changes ( mutations) through time, often leading to reproductive isolation and continued mutation even after the populations have become reproductively isolated for some period of time, as there is not any genetic exchange anymore. In some cases, subpopulations cover living in ecologically distinct peripheral environments can exhibit genetic divergence from the remainder of a population, especially where the range of a population is very large (see parapatric speciation). The genetic differences among divergent populations can involve silent mutations (that have no effect on the phenotype) or give rise to significant morphological and/or physiological changes. Genetic divergence will always accompany reproductive isolation, either due to novel adaptations via selection and/or due to genetic drift, and is the principal mechanism underlying speciation. On a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Ancestor
Common descent is a concept in evolutionary biology applicable when one species is the ancestor of two or more species later in time. According to modern evolutionary biology, all living beings could be descendants of a unique ancestor commonly referred to as the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) of all life on Earth. Common descent is an effect of speciation, in which multiple species derive from a single ancestral population. The more recent the ancestral population two species have in common, the more closely they are related. The most recent common ancestor of all currently living organisms is the last universal ancestor, which lived about 3.9 billion years ago. The two earliest pieces of evidence for life on Earth are graphite found to be biogenic in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in western Greenland and microbial mat fossils found in 3.48 billion-year-old sandstone discovered in Western Australia. All currently living organisms on Earth sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clade
In biology, a clade (), also known as a Monophyly, monophyletic group or natural group, is a group of organisms that is composed of a common ancestor and all of its descendants. Clades are the fundamental unit of cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy adopted by most biological fields. The common ancestor may be an individual, a population, or a species (extinct or Extant taxon, extant). Clades are nested, one in another, as each branch in turn splits into smaller branches. These splits reflect evolutionary history as populations diverged and evolved independently. Clades are termed ''monophyletic'' (Greek: "one clan") groups. Over the last few decades, the cladistic approach has revolutionized biological classification and revealed surprising evolutionary relationships among organisms. Increasingly, taxonomists try to avoid naming Taxon, taxa that are not clades; that is, taxa that are not Monophyly, monophyletic. Some of the relationships between organisms that the molecul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PLOS Biology
''PLOS Biology'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering all aspects of biology. Publication began on October 13, 2003. It is the first journal published by the Public Library of Science. The editor-in-chief is Nonia Pariente. In addition to research articles, the journal publishes magazine content aimed to be accessible to a broad audience. Article types in this section are essays, "unsolved mysteries", editorials, and synopses. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * Biological Abstracts * BIOSIS Previews *''Current Contents''/Agriculture, Biology & Environmental Sciences *''Current Contents''/Life Sciences *Chemical Abstracts Service * Embase *''Index Medicus''/MEDLINE/PubMed *Science Citation Index *Scopus *'' The Zoological Record'' According to ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal had a 2023 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equidae
Equidae (commonly known as the horse family) is the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic Family (biology), family of Wild horse, horses and related animals, including Asinus, asses, zebra, zebras, and many extinct species known only from fossils. The family evolved more than 50 million years ago, in the Eocene epoch, from a small, multi-toed ungulate into larger, single-toed animals. All Extant taxon, extant species are in the genus ''Equus (genus), Equus'', which originated in North America. Equidae belongs to the order Perissodactyla, which includes the extant tapirs and rhinoceros, and several extinct families. It is more specifically grouped within the superfamily (taxonomy), superfamily Equoidea, the only other family being the extinct Palaeotheriidae. The term equid refers to any member of this family, including any equinae, equine. Evolution The oldest known fossils assigned to Equidae were found in North America, and date from the early Eocene epoch, 54 million years ago. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |