|
Disinfection By-products
A disinfectant is a chemical substance or compound used to inactivate or destroy microorganisms on inert surfaces. Disinfection does not necessarily kill all microorganisms, especially resistant bacterial spores; it is less effective than sterilization, which is an extreme physical or chemical process that kills all types of life. Disinfectants are generally distinguished from other antimicrobial agents such as antibiotics, which destroy microorganisms within the body, and antiseptics, which destroy microorganisms on living tissue. Disinfectants are also different from biocides—the latter are intended to destroy all forms of life, not just microorganisms. Disinfectants work by destroying the cell wall of microbes or interfering with their metabolism. It is also a form of decontamination, and can be defined as the process whereby physical or chemical methods are used to reduce the amount of pathogenic microorganisms on a surface. Disinfectants can also be used to destroy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidizing agent, oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and . However, the nature of fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycobacteria
''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') and leprosy ('' M. leprae'') in humans. The Greek prefix ''myco-'' means 'fungus', alluding to this genus' mold-like colony surfaces. Since this genus has cell walls with a waxy lipid-rich outer layer containing high concentrations of mycolic acid, acid-fast staining is used to emphasize their resistance to acids, compared to other cell types. Mycobacterial species are generally aerobic, non-motile, and capable of growing with minimal nutrition. The genus is divided based on each species' pigment production and growth rate. While most ''Mycobacterium'' species are non-pathogenic, the genus' characteristic complex cell wall contributes to evasion from host defenses. Microbiology Morphology Mycobacteria are aerobic with 0.2-0.6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacterial Endospores
An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by some bacteria in the phylum Bacillota. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form (''endo'' means 'within'), but it is not a true spore (i.e., not an offspring). It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in Gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of '' Bacillus marismortui'' in salt crystals approximately 25 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself into a vegetative state. Mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viral Envelope
A viral envelope is the outermost layer of many types of viruses. It protects the genetic material in their life cycle when traveling between host cells. Not all viruses have envelopes. A viral envelope protein or E protein is a protein in the envelope, which may be acquired by the capsid from an infected host cell. Host cell infection process Numerous human pathogenic viruses in circulation are encased in lipid bilayers, and they infect their target cells by causing the viral envelope and cell membrane to fuse. Although there are effective vaccines against some of these viruses, there is no preventative or curative medicine for the majority of them. In most cases, the known vaccines operate by inducing antibodies that prevent the pathogen from entering cells. This happens in the case of enveloped viruses when the antibodies bind to the viral envelope proteins. The membrane fusion event that triggers viral entrance is caused by the viral membrane fusion protein. Many envelo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetative Reproduction
Vegetative reproduction (also known as vegetative propagation, vegetative multiplication or cloning) is a form of asexual reproduction occurring in plants in which a new plant grows from a fragment or cutting of the parent plant or specialized reproductive structures, which are sometimes called vegetative propagules. Many plants naturally reproduce this way, but it can also be induced artificially. Horticulturists have developed asexual propagation techniques that use vegetative propagules to replicate plants. Success rates and difficulty of propagation vary greatly. Monocotyledons typically lack a vascular cambium, making them more challenging to propagate. Plant propagation Plant propagation is the process of plant reproduction of a species or cultivar, and it can be sexual or asexual. It can happen through the use of vegetative parts of the plants, such as leaves, stems, and roots to produce new plants or through growth from specialized vegetative plant parts. W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC-BY Icon
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by Creative Commons, a U.S. non-profit corporation founded in 2001. There have also been five versions of the suite of licenses, numbered 1.0 through 4.0. Released in November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Therapeutic Goods Act 1989
The Therapeutic Goods Act 1989 is an Act of the Commonwealth of Australia which regulates therapeutic goods. The Act is administered by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), which is part of the Commonwealth Department of Health. The statutory framework set out in the Act is supplemented by the Therapeutic Goods Regulations 1990 and the Therapeutic Goods (Medical Devices) Regulations 2002. The central mechanism through which therapeutic goods (being medicines, biologicals and medical devices) are regulated is the Australian Register of Therapeutic Goods (ARTG). Subject to the alternative supply/export pathways set out in the Act, all therapeutic goods must be "registered" (for prescription medicines), "listed" (for complementary and over-the-counter medicines) or "included" (for biologicals and medical devices A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American And British English Spelling Differences
Despite the various list of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of Comparison of American and British English, the differences between American English, American and British English, British or English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States. A "British standard" began to emerge following the 1755 publication of Samuel Johnson's ''A Dictionary of the English Language'', and an "American standard" started following the work of Noah Webster and, in particular, his ''Webster's Dictionary, An American Dictionary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
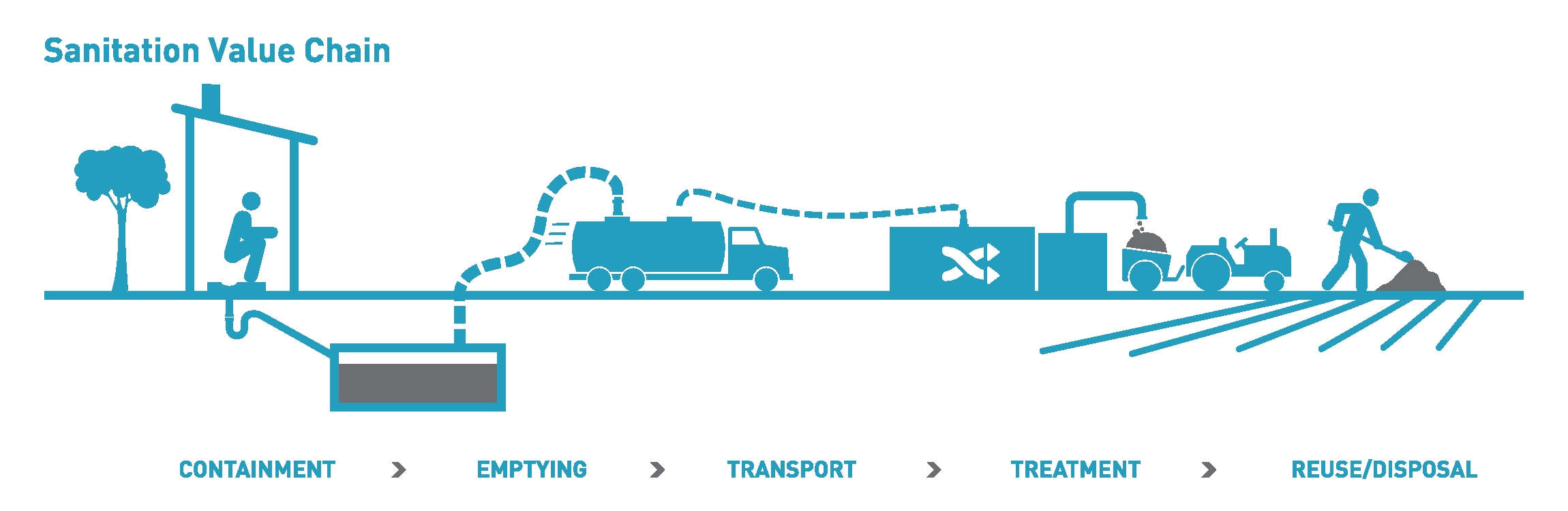
Septage
Fecal sludge management (FSM) (or faecal sludge management in British English) is the storage, collection, transport, treatment and safe end use or disposal of fecal sludge. Together, the collection, transport, treatment and end use of fecal sludge constitute the "value chain" or "service chain" of fecal sludge management. Fecal sludge is defined very broadly as what accumulates in onsite sanitation systems (e.g. pit latrines, septic tanks and Container-based sanitation, container-based solutions) and specifically is not transported through a Sanitary sewer, sewer. It is composed of Human waste, human excreta, but also anything else that may go into an onsite containment technology, such as flushwater, cleansing materials (e.g. toilet paper and Anal hygiene, anal cleansing materials), Feminine hygiene, menstrual hygiene products, grey water (i.e. bathing or kitchen water, including fats, oils and grease), and Municipal solid waste, solid waste. Fecal sludge that is removed from sep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sewage Sludge
Sewage sludge is the residual, semi-solid material that is produced as a by-product during sewage treatment of industrial or municipal wastewater. The term "septage" also refers to sludge from simple wastewater treatment but is connected to simple on-site sanitation systems, such as septic tanks. After treatment, and dependent upon the quality of sludge produced (for example with regards to heavy metal content), sewage sludge is most commonly either disposed of in landfills, dumped in the ocean or applied to land for its fertilizing properties, as pioneered by the product Milorganite. The term " Biosolids" is often used as an alternative to the term sewage sludge in the United States, particularly in conjunction with reuse of sewage sludge as fertilizer after sewage sludge treatment. Biosolids can be defined as organic wastewater solids that can be reused after stabilization processes such as anaerobic digestion and composting. Opponents of sewage sludge reuse reject this t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanitation
Sanitation refers to public health conditions related to clean drinking water and treatment and disposal of human excreta and sewage. Preventing human contact with feces is part of sanitation, as is hand washing with soap. Sanitation systems aim to protect human health by providing a clean environment that will stop the transmission of disease, especially through the fecal–oral route.SuSanA (2008)Towards more sustainable sanitation solutions . Sustainable Sanitation Alliance (SuSanA) For example, diarrhea, a main cause of malnutrition and stunted growth in children, can be reduced through adequate sanitation. There are many other diseases which are easily transmitted in communities that have low levels of sanitation, such as ascariasis (a type of intestinal worm infection or helminthiasis), cholera, hepatitis, polio, schistosomiasis, and trachoma, to name just a few. A range of sanitation technologies and approaches exists. Some examples are community-led total sanita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |