|
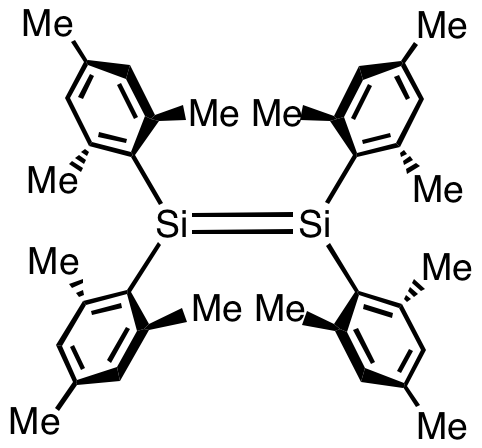
Disilyne
Disilyne is a silicon hydride with the formula . Several isomers are possible, but none are sufficiently stable to be of practical value. Substituted disilynes contain a formal silicon–silicon triple bond and as such are sometimes written R2Si2 (where R is a substituent group). They are the silicon analogues of alkynes. The term ''silyne'' has two diverse meanings. Some chemists use it to refer to compounds containing a silicon–silicon triple bond,Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) ''Inorganic Chemistry'', Elsevier whereas others use the term to refer to compounds containing a silicon–carbon triple bond by analogy to silene, which often refers to compounds containing silicon–carbon double bonds. The term polysilyne can refer to the layer polymer (SiH)n or substituted derivatives. Substituted disilynes The first example isolated and characterised by X-ray crystallography is an emerald green crystalline compound reported in 2004. This molecule has the formu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disilene
Disilene is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . The name ''disilene'', referring to the structure of a particular prototropic tautomer of the molecule. It is the simplest silene. Properties and bonding Disilene is a molecule with one Si=Si bond, and four equivalent Si-H bonds. Unlike ethylene, disilene is kinetically unstable with respect to tautomerisation. Disilene has two other tautomers, that are very close in energy: (μ2-''H'')disilene, and disilanylidene. Organodisilenes Disilenes bearing sterically bulky substituents are isolable and have been well characterized although they remain mainly of academic interest. The first stabilised disilene was tetramesityldisilene, (C6Me3H2)4Si2. The Si=Si distance in this molecule is 2.15 Å, about 10% shorter than a typical Si–Si single bond. The Si2C4 core is roughly planar. Such species are typically prepared by reduction of organosilicon halides: :2 R2SiCl2 + 4 Na → R2Si=SiR2 + 4 NaCl. An alternative synthesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digermyne
Digermynes are a class of compounds that are regarded as the heavier digermanium analogues of alkynes. The parent member of this entire class is HGeGeH, which has only been characterized computationally, but has revealed key features of the whole class. Because of the large interatomic repulsion between two Ge atoms, only kinetically stabilized digermyne molecules can be synthesized and characterized by utilizing bulky protecting groups and appropriate synthetic methods, for example, reductive coupling of germanium(II) halides. The bonding between two Ge atoms in digermyne is different from C≡C bond in alkynes, which results in the ''trans''-bent structure of digermyne. ''Trans''-bent structure is quite common in heavier Group 14 element analogues of alkynes. The second order Jahn-Teller (SOJT) effect of digermynes gives rise to slipped π-bond and large molecular geometrical distortion. Because of the multibonded feature of digermynes and the large interatomic repulsion of tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylene
Acetylene ( systematic name: ethyne) is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in its pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution. Pure acetylene is odorless, but commercial grades usually have a marked odor due to impurities such as divinyl sulfide and phosphine.Compressed Gas Association (1995Material Safety and Data Sheet – Acetylene As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because its two carbon atoms are bonded together in a triple bond. The carbon–carbon triple bond places all four atoms in the same straight line, with CCH bond angles of 180°. Discovery Acetylene was discovered in 1836 by Edmund Davy, who identified it as a "new carburet of hydrogen". It was an accidental discovery while attempting to isolate potassium metal. By heating potassium carbonate with carbon at very high temperatures, he pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-bonding Orbital
A non-bonding orbital, also known as ''non-bonding molecular orbital'' (NBMO), is a molecular orbital whose occupation by electrons neither increases nor decreases the bond order between the involved atoms. Non-bonding orbitals are often designated by the letter n in molecular orbital diagrams and electron transition notations. Non-bonding orbitals are the equivalent in molecular orbital theory of the lone pairs in Lewis structures. The energy level of a non-bonding orbital is typically in between the lower energy of a valence shell bonding orbital and the higher energy of a corresponding antibonding orbital. As such, a non-bonding orbital with electrons would commonly be a HOMO (highest occupied molecular orbital). According to molecular orbital theory, molecular orbitals are often modeled by the linear combination of atomic orbitals. In a simple diatomic molecule such as hydrogen fluoride (chemical formula: HF), one atom may have many more electrons than the other. A sigma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disilane
Disilane is a chemical compound with chemical formula Si2H6 that was identified in 1902 by Henri Moissan and Samuel Smiles (1877–1953). Moissan and Smiles reported disilane as being among the products formed by the action of dilute acids on metal silicides. Although these reactions had been previously investigated by Friedrich Woehler and Heinrich Buff between 1857 and 1858, Moissan and Smiles were the first to explicitly identify disilane. They referred to disilane as ''silicoethane''. Higher members of the homologous series SinH2n+2 formed in these reactions were subsequently identified by Carl Somiesky (sometimes spelled "Karl Somieski") and Alfred Stock. At standard temperature and pressure, disilane is a colourless, acrid gas. Disilane and ethane have similar structures, although disilane is much more reactive. Other compounds of the general formula Si2X6 (X = hydride, halide, alkyl, aryl, and mixtures of these groups) are called disilanes. Disilane is a group 14 hydr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanium
Germanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ge and atomic number 32. It is lustrous, hard-brittle, grayish-white and similar in appearance to silicon. It is a metalloid in the carbon group that is chemically similar to its group neighbors silicon and tin. Like silicon, germanium naturally reacts and forms complexes with oxygen in nature. Because it seldom appears in high concentration, germanium was discovered comparatively late in the discovery of the elements. Germanium ranks near fiftieth in relative abundance of the elements in the Earth's crust. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev predicted its existence and some of its properties from its position on his periodic table, and called the element ekasilicon. In 1886, Clemens Winkler at Freiberg University found the new element, along with silver and sulfur, in the mineral argyrodite. Winkler named the element after his country, Germany. Germanium is mined primarily from sphalerite (the primary ore of zinc), though ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead
Lead is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metals, heavy metal that is density, denser than most common materials. Lead is Mohs scale of mineral hardness#Intermediate hardness, soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, lead is a shiny gray with a hint of blue. It tarnishes to a dull gray color when exposed to air. Lead has the highest atomic number of any stable nuclide, stable element and three of its isotopes are endpoints of major nuclear decay chains of heavier elements. Lead is toxic, even in small amounts, especially to children. Lead is a relatively unreactive post-transition metal. Its weak metallic character is illustrated by its amphoteric nature; lead and lead oxides react with acids and base (chemistry), bases, and it tends to form covalent bonds. Compounds of lead are usually found in the +2 oxidation state rather than the +4 state common with lighte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Group 14
The carbon group is a periodic table group consisting of carbon (C), silicon (Si), germanium (Ge), tin (Sn), lead (Pb), and flerovium (Fl). It lies within the p-block. In modern IUPAC notation, it is called group 14. In the field of semiconductor physics, it is still universally called group IV. The group was once also known as the tetrels (from the Greek word ''tetra'', which means four), stemming from the Roman numeral IV in the group names, or (not coincidentally) from the fact that these elements have four valence electrons (see below). They are also known as the crystallogens or adamantogens. Characteristics Chemical Like other groups, the members of this family show patterns in electron configuration, especially in the outermost shells, resulting in trends in chemical behavior: Each of the elements in this group has 4 electrons in its outer shell. An isolated, neutral group 14 atom has the s2 p2 configuration in the ground state. These elements, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzene
Benzene is an organic chemical compound with the molecular formula C6H6. The benzene molecule is composed of six carbon atoms joined in a planar ring with one hydrogen atom attached to each. Because it contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms, benzene is classed as a hydrocarbon. Benzene is a natural constituent of petroleum and is one of the elementary petrochemicals. Due to the cyclic continuous pi bonds between the carbon atoms, benzene is classed as an aromatic hydrocarbon. Benzene is a colorless and highly flammable liquid with a sweet smell, and is partially responsible for the aroma of gasoline. It is used primarily as a precursor to the manufacture of chemicals with more complex structure, such as ethylbenzene and cumene, of which billions of kilograms are produced annually. Although benzene is a major industrial chemical, it finds limited use in consumer items because of its toxicity. History Discovery The word "''benzene''" derives from "''gum benzoin''" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylacetylene
Phenylacetylene is an alkyne hydrocarbon containing a phenyl group. It exists as a colorless, viscous liquid. In research, it is sometimes used as an analog for acetylene; being a liquid, it is easier to handle than acetylene gas. Preparation In the laboratory, phenylacetylene can be prepared by elimination of hydrogen bromide from styrene dibromide using sodium amide in ammonia: : It can also be prepared by the elimination of hydrogen bromide from bromostyrene using molten potassium hydroxide. Reactions Phenylacetylene is a prototypical terminal acetylene, undergoing many reactions expected of that functional group. It undergoes semihydrogenated over Lindlar catalyst to give styrene. In the presence of base and copper(II) salts, it undergoes oxidative coupling to give diphenylbutadiyne. In the presence of metal catalysts, it undergoes oligomerization, trimerization, and even polymerization. : In the presence of gold or mercury reagents, phenylacetylene hydrates to give a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bond Order
In chemistry, bond order, as introduced by Linus Pauling, is defined as the difference between the number of bonds and anti-bonds. The bond order itself is the number of electron pairs ( covalent bonds) between two atoms. For example, in diatomic nitrogen N≡N, the bond order between the two nitrogen atoms is 3 ( triple bond). In acetylene H–C≡C–H, the bond order between the two carbon atoms is also 3, and the C–H bond order is 1 (single bond). In carbon monoxide , the bond order between carbon and oxygen is 3. In thiazyl trifluoride , the bond order between sulfur and nitrogen is 3, and between sulfur and fluorine is 1. In diatomic oxygen O=O the bond order is 2 ( double bond). In ethylene the bond order between the two carbon atoms is also 2. The bond order between carbon and oxygen in carbon dioxide O=C=O is also 2. In phosgene , the bond order between carbon and oxygen is 2, and between carbon and chlorine is 1. In some molecules, bond orders can be 4 ( q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylacetylene
Propyne (methylacetylene) is an alkyne with the chemical formula . It is a component of MAPD gas—along with its isomer propadiene (allene), which was commonly used in gas welding. Unlike acetylene, propyne can be safely condensed.Peter Pässler, Werner Hefner, Klaus Buckl, Helmut Meinass, Andreas Meiswinkel, Hans-Jürgen Wernicke, Günter Ebersberg, Richard Müller, Jürgen Bässler, Hartmut Behringer, Dieter Mayer, "Acetylene" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, Weinheim 2007 (). Production and equilibrium with propadiene Propyne exists in equilibrium with propadiene, the mixture of propyne and propadiene being called MAPD: :H3CC#CH H2C=C=CH2 The coefficient of equilibrium ''K''eq is 0.22 at 270 °C or 0.1 at 5 °C. MAPD is produced as a side product, often an undesirable one, by cracking propane to produce propene, an important feedstock in the chemical industry. MAPD interferes with the catalytic polymerization of propene. Laborat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




2.png)
