|
Diphyodonty
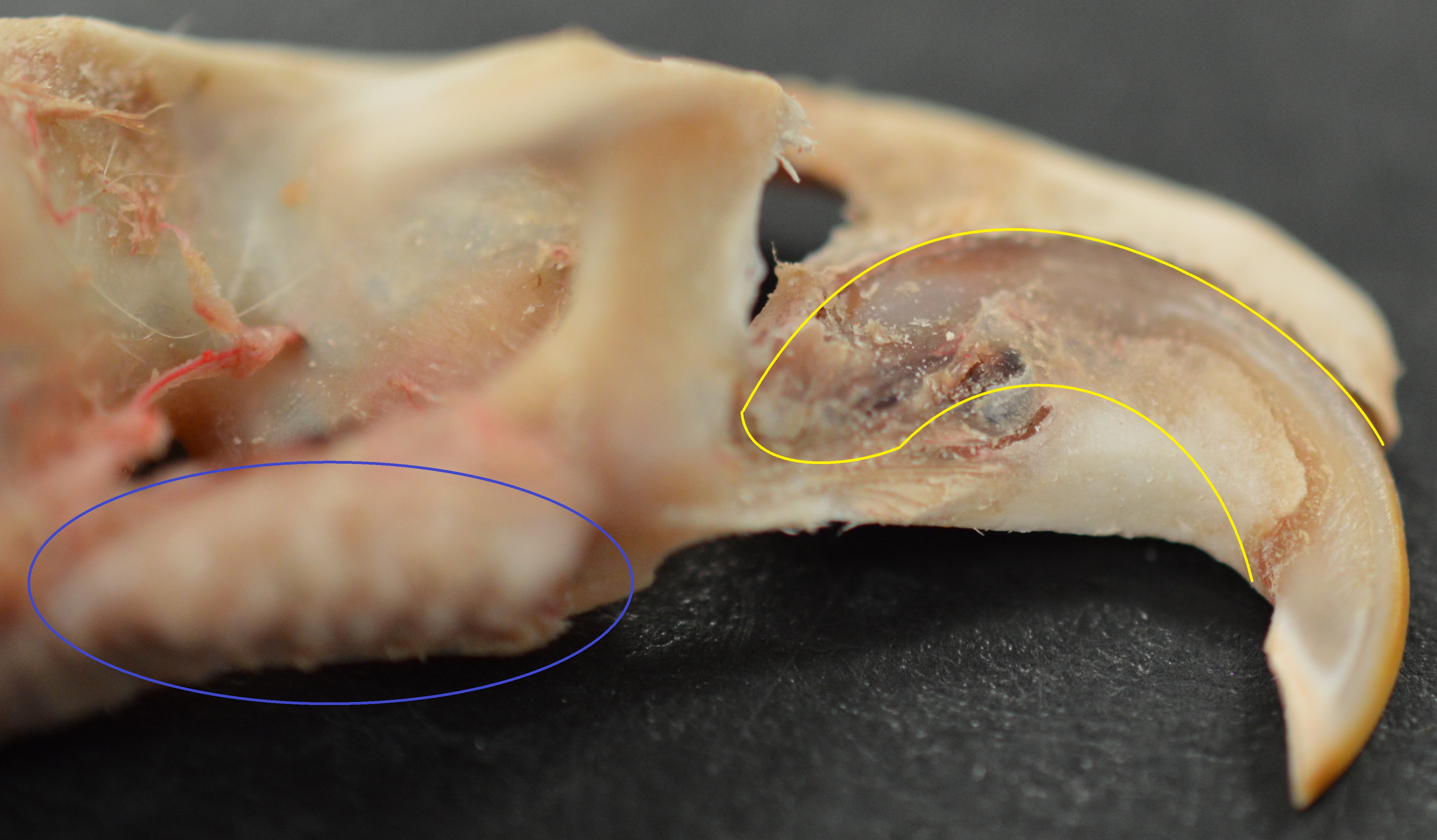
A diphyodont is any animal with two sets of teeth, initially the ''deciduous'' set and consecutively the '' permanent'' set. Most mammals are diphyodonts—as to chew their food they need a strong, durable and complete set of teeth. Diphyodonts contrast with ''polyphyodonts'', whose teeth are constantly replaced. Diphyodonts also differ from '' monophyodonts'', which are animals who have only one set of teeth that does not change over a long period of growth. In diphyodonts, the number of teeth that are replaced varies from species to species. In humans, a set of twenty deciduous teeth, or "milk teeth", are replaced by a completely new set of thirty-two adult teeth. In some cases hypodontia or hyperdontia occurs, the latter in cleidocranial dysostosis and Gardner's syndrome. In the hare the anterior incisors are not replaced but the posterior smaller incisors are replaced. Not much is known about the developmental mechanisms regulating diphyodont replacement. The house shrew, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth (animal)
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferret
The ferret (''Mustela furo'') is a small, domesticated species belonging to the family Mustelidae. The ferret is most likely a domesticated form of the wild European polecat (''Mustela putorius''), as evidenced by the ferret's ability to interbreed with European polecats and produce hybrid offspring. Physically, ferrets resemble other mustelids because of their long, slender bodies. Including their tail, the average length of a ferret is about ; they weigh between ; and their fur can be black, brown, white, or a mixture of those colours. The species is sexually dimorphic, with males being considerably larger than females. Ferrets may have been domesticated since ancient times, but there is widespread disagreement because of the sparseness of written accounts and the inconsistency of those which survive. Contemporary scholarship agrees that ferrets were bred for sport, hunting rabbits in a practice known as rabbiting. In North America, the ferret has become an increasingly pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thecodont Dentition
Thecodont dentition is a morphological arrangement in which the base of the tooth is completely enclosed in a deep socket of bone, as seen in crocodilians, dinosaurs and mammals, and opposed to acrodont and pleurodont dentition seen in squamate reptiles. Notably, this appears to be the ancestral tooth condition in Amniota Amniotes are tetrapod vertebrate animals belonging to the clade Amniota, a large group that comprises the vast majority of living terrestrial and semiaquatic vertebrates. Amniotes evolved from amphibious stem tetrapod ancestors during the C .... This morphology was once used as a basis for the now-defunct taxonomic group Thecodontia. References Dentition types Archosaurs {{Vertebrate anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schultz's Rule
Schultz's rule is a rule developed by Adolph Hans Schultz, declaring a relationship between the first tooth eruption of the molar versus the permanent teeth and the progress or aging of its carrier. It states that species that live longer have more wear on deciduous teeth and as a result start replacing them relatively early in life. Which is an indicator for examining fossil data. According to research, '' Myotragus balearicus'' follows Schultz's Rule. See also * Diphyodont * Polyphyodont * Tooth development A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, teari ... References Further reading * * Tooth development Animal anatomy Paleontological concepts and hypotheses {{dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyphyodont
A polyphyodont is any animal whose tooth (animal), teeth are continually replaced. In contrast, diphyodonts are characterized by having only two successive sets of teeth. Polyphyodonts include most toothed fishes (most notably sharks), many reptiles such as crocodiles and geckos, and most other vertebrates, with mammals being the main exception (though Polyphyodont#Evolution in mammals, not absolute). Growth New, permanent teeth grow in the jaws, usually under or just behind the old tooth, from stem cells in the dental lamina. Young animals typically have a full set of teeth when they hatch; there is no tooth change in the egg. Within days, tooth replacement begins, usually in the back of the jaw continuing forward like a wave. On average a tooth is replaced every few months. Crocodilia Crocodilia are the only non-mammalian vertebrates with tooth sockets. Alligators grow a successional tooth (a small replacement tooth) under each mature functional tooth for replacement once a y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monophyodont
A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the outermost embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterodont
In anatomy, a heterodont (from Greek, meaning 'different teeth') is an animal which possesses more than a single tooth morphology. Human dentition is heterodont and diphyodont as an example. In vertebrates, heterodont pertains to animals where teeth are differentiated into different forms. For example, members of the Synapsida generally possess incisors, canines ("dogteeth"), premolars, and molars. The presence of heterodont dentition is evidence of some degree of feeding and or hunting specialization in a species. In contrast, homodont or isodont dentition refers to a set of teeth that possess the same tooth morphology. In invertebrates, the term heterodont refers to a condition where teeth of differing sizes occur in the hinge plate, a part of the Bivalvia Bivalvia () or bivalves, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class (biology), class of aquatic animal, aquatic molluscs (marine and freshwater) that have laterally co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kangaroo
Kangaroos are marsupials from the family Macropodidae (macropods, meaning "large foot"). In common use, the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, the red kangaroo, as well as the antilopine kangaroo, eastern grey kangaroo, and western grey kangaroo. Kangaroos are indigenous to Australia and New Guinea. The Australian government estimates that 42.8 million kangaroos lived within the commercial harvest areas of Australia in 2019, down from 53.2 million in 2013. As with the terms " wallaroo" and "wallaby", "kangaroo" refers to a paraphyletic grouping of species. All three terms refer to members of the same taxonomic family, Macropodidae, and are distinguished according to size. The largest species in the family are called "kangaroos" and the smallest are generally called "wallabies". The term "wallaroos" refers to species of an intermediate size. There are also the tree-kangaroos, another type of macropod which inhabit the upper branches ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elephant
Elephants are the largest living land animals. Three living species are currently recognised: the African bush elephant ('' Loxodonta africana''), the African forest elephant (''L. cyclotis''), and the Asian elephant ('' Elephas maximus''). They are the only surviving members of the family Elephantidae and the order Proboscidea; extinct relatives include mammoths and mastodons. Distinctive features of elephants include a long proboscis called a trunk, tusks, large ear flaps, pillar-like legs, and tough but sensitive grey skin. The trunk is prehensile, bringing food and water to the mouth and grasping objects. Tusks, which are derived from the incisor teeth, serve both as weapons and as tools for moving objects and digging. The large ear flaps assist in maintaining a constant body temperature as well as in communication. African elephants have larger ears and concave backs, whereas Asian elephants have smaller ears and convex or level backs. Elephants are scatter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
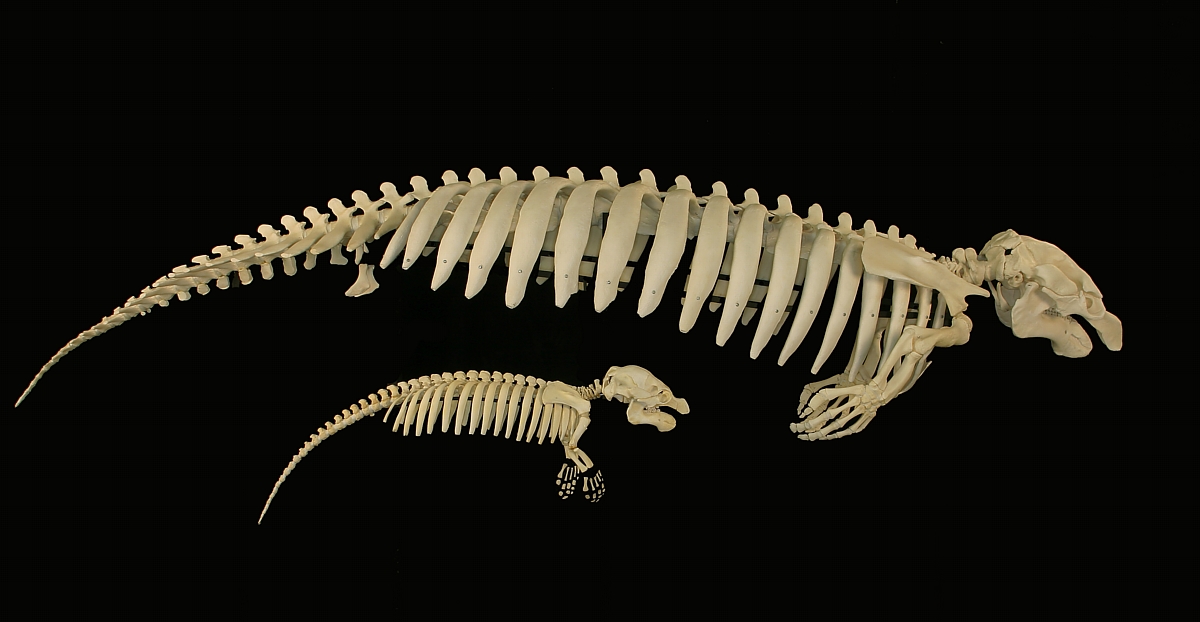
Manatees
Manatees (, family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species in the order Sirenia: the Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis''), the West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), and the West African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''). They measure up to long, weigh as much as , and have paddle-like tails. Manatees are herbivores and eat over 60 different freshwater and saltwater plants. Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the Amazon basin, and West Africa. The main causes of death for manatees are human-related issues, such as habitat destruction and human objects. Their slow-moving, curious nature has led to violent collisions with propeller-driven boats and ships. Some manatees have been found with over 50 scars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Mainichi
The is one of the major newspapers in Japan, published by In addition to the ''Mainichi Shimbun'', which is printed twice a day in several local editions, Mainichi also operates an English-language news website called , and publishes a bilingual news magazine, ''Mainichi Weekly''. It also publishes paperbacks, books and other magazines, including a weekly news magazine, ''Sunday Mainichi''. It is one of the four national newspapers in Japan; the other three are ''The Asahi Shimbun'', the ''Yomiuri Shimbun'' and the ''Nihon Keizai Shimbun''. The ''Sankei Shimbun'' and the ''Chunichi Shimbun'' are not currently in the position of a national newspaper despite a large circulation for both. History The history of the ''Mainichi Shimbun'' began with the founding of two papers during the Meiji period. The ''Tokyo Nichi Nichi Shimbun'' was founded first, in 1872. The ''Mainichi'' claims that it is the oldest existing Japanese daily newspaper with its 136-year history. The Osaka ''Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miniature Pig
A miniature pig, minipig or micro-pig is a type of domestic pig characterised by its unusually small size but has no formal definition and can cover a variety of breeds. Some miniature pigs – such as the Cerdo Cuino of Mexico, the Lon I of Vietnam, the Ras-n-Lansa of Guam in the Marianas Islands and the Wuzhishan of Hainan Island in China – are traditional breeds of those areas. Many others have been selectively bred since the mid-twentieth century specifically for laboratory use in biomedical research; among these are the Clawn and the Ohmini of Japan, the Czech Minipig, the German Göttingen Minipig, the Lao-Sung of Taiwan, the Russian Minisib, the extinct Minnesota Miniature of the United States and the Westran of Australia. Some minipigs have been bred to be marketed as companion animals. Miniature pigs generally reach their full size in about four years, and may live for up to fifteen. Some may reach a height of at the shoulder and a body length of . Young ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |