|
Dilophosaurus
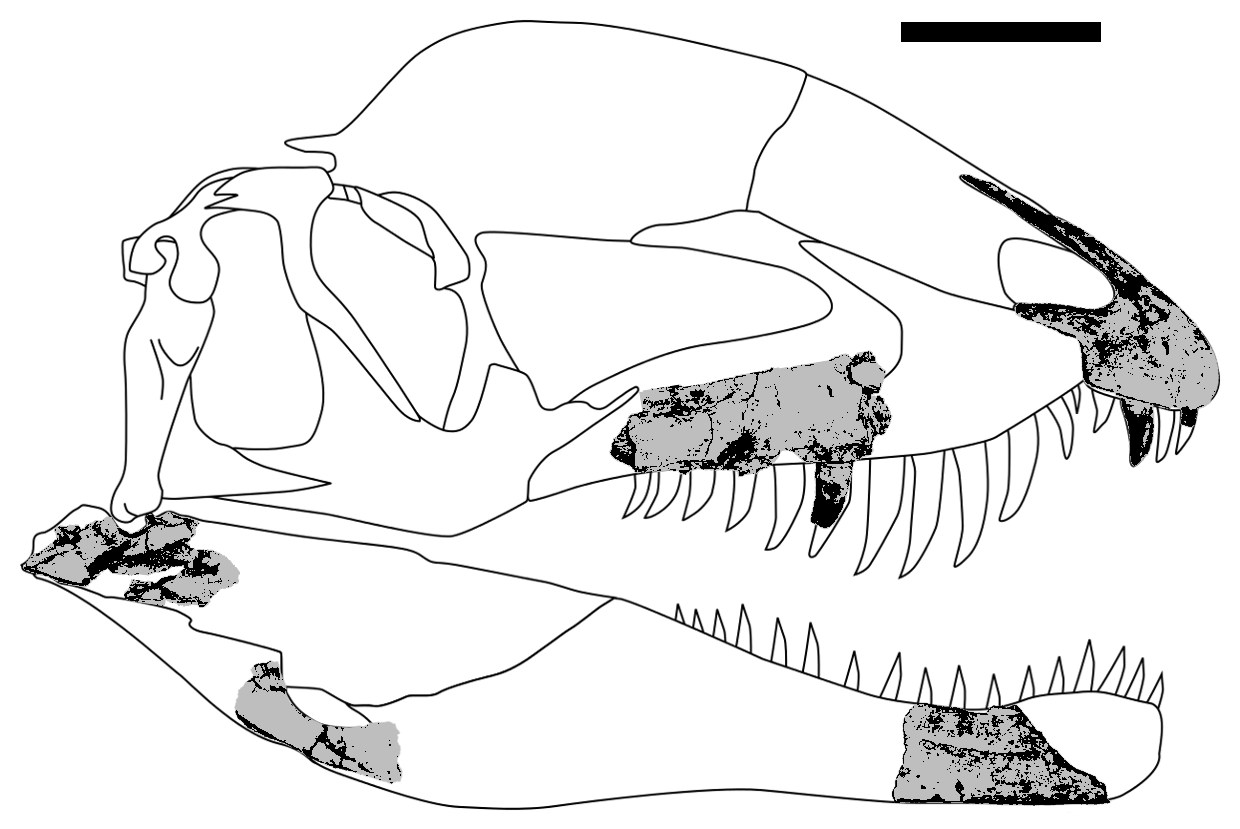
''Dilophosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of theropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now North America during the Early Jurassic, about 186 million years ago. Three skeletons were discovered in northern Arizona in 1940, and the two best preserved were collected in 1942. The most complete specimen became the holotype of a new species in the genus ''Megalosaurus'', named ''M. wetherilli'' by Samuel P. Welles in 1954. Welles found a larger skeleton belonging to the same species in 1964. Realizing it bore crests on its skull, he assigned the species to the new genus ''Dilophosaurus'' in 1970, as ''Dilophosaurus wetherilli''. The genus name means "two-crested lizard", and the species name honors John Wetherill, a Navajo councilor. Further specimens have since been found, including an infant. Fossil footprints have also been attributed to the animal, including resting traces. Another species, ''Dilophosaurus sinensis'' from China, was named in 1993, but was later found to belon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dilophosauridae
''Dilophosaurus'' ( ) is a genus of theropod dinosaurs that lived in what is now North America during the Early Jurassic, about 186 million years ago. Three skeletons were discovered in northern Arizona in 1940, and the two best preserved were collected in 1942. The most complete specimen became the holotype of a new species in the genus ''Megalosaurus'', named ''M. wetherilli'' by Samuel P. Welles in 1954. Welles found a larger skeleton belonging to the same species in 1964. Realizing it bore crests on its skull, he assigned the species to the new genus ''Dilophosaurus'' in 1970, as ''Dilophosaurus wetherilli''. The genus name means "two-crested lizard", and the species name honors John Wetherill, a Navajo councilor. Further specimens have since been found, including an infant. Fossil footprints have also been attributed to the animal, including resting traces. Another species, ''Dilophosaurus sinensis'' from China, was named in 1993, but was later found to belong t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic Epoch (geology), Epoch (in chronostratigraphy corresponding to the Lower Jurassic series (stratigraphy), Series) is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma (million years ago), and ends at the start of the Middle Jurassic 174.7 ±0.8 Ma. Certain rocks of marine origin of this age in Europe are called "Lias Group, Lias" and that name was used for the period, as well, in 19th-century geology. In southern Germany rocks of this age are called Black Jurassic. Origin of the name Lias There are two possible origins for the name Lias: the first reason is it was taken by a geologist from an England, English quarryman's dialect pronunciation of the word "layers"; secondly, sloops from north Cornwall, Cornish ports such as Bude would sail across the Bristol Channel to the Vale of Glamorgan to load up with rock from coastal limestone quarries (lias and Carbonif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Footprints
A fossil track or ichnite (Greek "''ιχνιον''" (''ichnion'') – a track, trace or footstep) is a fossilized footprint. This is a type of trace fossil. A fossil trackway is a sequence of fossil tracks left by a single organism. Over the years, many ichnites have been found, around the world, giving important clues about the behaviour (and foot structure and stride) of the animals that made them. For instance, multiple ichnites of a single species, close together, suggest 'herd' or 'pack' behaviour of that species. Combinations of footprints of different species provide clues about the interactions of those species. Even a set of footprints of a single animal gives important clues, as to whether it was bipedal or quadrupedal. In this way, it has been suggested that some pterosaurs, when on the ground, used their forelimbs in an unexpected quadrupedal action. Special conditions are required, in order to preserve a footprint made in soft ground (such as an alluvial plain or a f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayenta Formation
The Kayenta Formation is a geological formation in the Glen Canyon Group that is spread across the Colorado Plateau area of the United States, including northern Arizona, northwest Colorado, Nevada, and Utah. Originally suggested as being Sinemurian-Pliensbachian, but more recent Detrital zircon geochronology, dating of detrital zircons has yielded a depositional age of 183.7 ± 2.7 Ma, thus a Pliensbachian-Toarcian age is more likely. A previous depth work recovered a solid "Carixian" (Lower-Middle Pliensbachian) age from measurements done in the Tenney Canyon. More recent works have provided varied datations for the layers, with samples from Colorado and Arizona suggesting 197.0±1.5-195.2±5.5 Ma (Middle Sinemurian), while the topmost section is likely Toarcian or close in age, maybe even recovering terrestrial deposits coeval with the Toarcian Oceanic Anoxic Event. This last age assignation also correlated the Toarcian Vulcanism on the west Cordilleran Magmatic Arc, as the num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleopathologies
Paleopathology, also spelled palaeopathology, is the study of ancient diseases and injuries in organisms through the examination of fossils, mummified tissue, skeletal remains, and analysis of coprolites. Specific sources in the study of ancient human diseases may include early documents, illustrations from early books, painting and sculpture from the past. All these objects provide information on the evolution of diseases as well as how past civilizations treated conditions. Studies have historically focused on humans, although there is no evidence that humans are more prone to pathologies than any other animal. The word paleopathology is derived from the Ancient Greek roots of ''palaios'' meaning "old", ''pathos'' () meaning "experience" or "suffering", and ''-logia'' (), "study". Paleopathology is an interdisciplinary science, meaning it involves knowledge from many sectors including (but not limited to) "clinical pathology, human osteology, epidemiology, social anthropology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Selection
Sexual selection is a mechanism of evolution in which members of one sex mate choice, choose mates of the other sex to mating, mate with (intersexual selection), and compete with members of the same sex for access to members of the opposite sex (intrasexual selection). These two forms of selection mean that some individuals have greater reproductive success than others within a population, for example because they are more Animal sexual behaviour, attractive or prefer more attractive partners to produce offspring. Successful males benefit from frequent mating and monopolizing access to one or more fertile females. Females can maximise the return on the energy they invest in reproduction by selecting and mating with the best males. The concept was first articulated by Charles Darwin who wrote of a "second agency" other than natural selection, in which competition between mate candidates could lead to speciation. The theory was given a mathematical basis by Ronald Fisher in the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Species Recognition
Intra-species recognition is the recognition by a member of an animal species of a conspecific (another member of the same species). In many species, such recognition is necessary for procreation. Different species may employ different methods, but all of them are based on one or more senses. The recognition may happen by the chemical signature ( smell), by having a distinctive shape or color (sight), by emitting certain sounds (hearing), or even by behaviour patterns. Often a combination of these is used. Among human beings, the sense of sight is usually in charge of recognizing other members of the same species, with maybe the subconscious help of smell. In particular, the human brain has a disproportionate amount of processing power dedicated to finely analyze the features of a human face. This is why most humans are able to distinguish human beings from one other (barring look-alikes), and a human being from a similar species like some anthropomorphic ape, with only a quick g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Display
Display behaviour is a set of ritualized behaviours that enable an animal to communicate to other animals (typically of the same species) about specific stimuli. Such ritualized behaviours can be visual, but many animals depend on a mixture of visual, audio, tactical and chemical signals. Evolution has tailored these stereotyped behaviours to allow animals to communicate both conspecifically and interspecifically which allows for a broader connection in different niches in an ecosystem. It is connected to sexual selection and survival of the species in various ways. Typically, display behaviour is used for courtship between two animals and to signal to the female that a viable male is ready to mate. In other instances, species may make territorial displays, in order to preserve a foraging or hunting territory for its family or group. A third form is exhibited by tournament species in which males will fight in order to gain the 'right' to breed. Animals from a broad range of evolut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelophysidae
Coelophysoidea is an extinct clade of theropod dinosaurs common during the Late Triassic and Early Jurassic periods. They were widespread geographically, probably living on all continents. Coelophysoids were all slender, carnivorous forms with a superficial similarity to the coelurosaurs, with which they were formerly classified, and some species had delicate cranial crests. Sizes range from about 1 to 6 m in length. It is unknown what kind of external covering coelophysoids had, and various artists have portrayed them as either scaly or feathered. Some species may have lived in packs, as inferred from sites where numerous individuals have been found together. Examples of coelophysoids include ''Coelophysis'', ''Procompsognathus'' and '' Liliensternus''. Most dinosaurs formerly referred to as being in the dubious taxon "Podokesauridae" are now classified as coelophysoids. The family Coelophysidae, which is contained within Coelophysoidea, flourished in the Late Triassic and Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dracovenator
''Dracovenator'' () is a genus of neotheropod dinosaur that lived approximately 201 to 199 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic period in what is now South Africa. ''Dracovenator'' was a medium-sized, moderately built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to an estimated in length and in body mass. Its type specimen was based on only a partial skull that was recovered. Discovery The type material BP/1/5243 for ''Dracovenator'' was discovered at the "Upper Drumbo Farm" locality in the upper Elliot Formation which is part of the Stormberg Group in Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. It was collected by James Kitching and Regent "Lucas" Huma in sandstone that was deposited during the Hettangian stage of the Jurassic period, approximately 201 to 199 million years ago. The paratype material BP/1/5278 (originally assigned to ''Syntarsus rhodesiensis'') was discovered in 1981, also at the Elliot Formation in pinkish-maroon silty mudstone that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestigial
Vestigiality is the retention, during the process of evolution, of genetically determined structures or attributes that have lost some or all of the ancestral function in a given species. Assessment of the vestigiality must generally rely on comparison with homologous features in related species. The emergence of vestigiality occurs by normal evolutionary processes, typically by loss of function of a feature that is no longer subject to positive selection pressures when it loses its value in a changing environment. The feature may be selected against more urgently when its function becomes definitively harmful, but if the lack of the feature provides no advantage, and its presence provides no disadvantage, the feature may not be phased out by natural selection and persist across species. Examples of vestigial structures (also called degenerate, atrophied, or rudimentary organs) are the loss of functional wings in island-dwelling birds; the human vomeronasal organ; and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
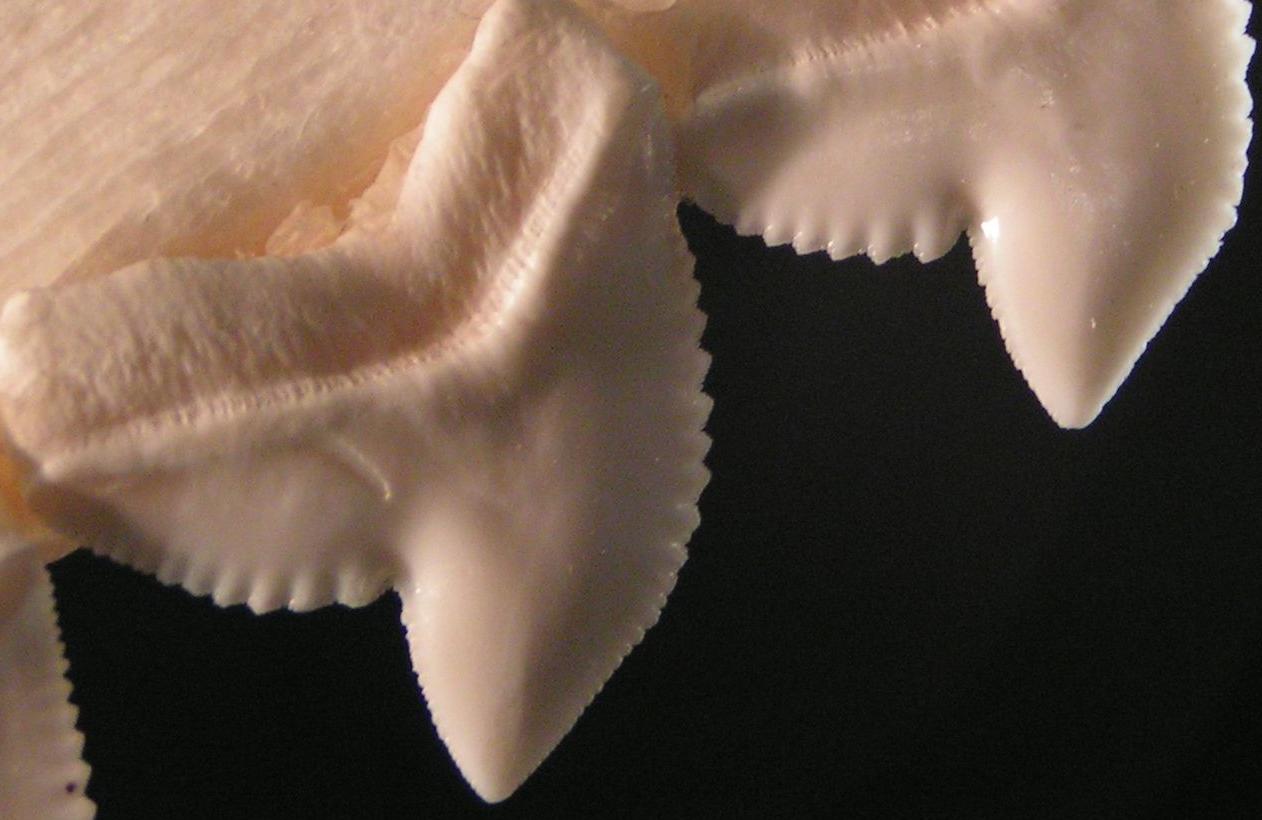
Serration
Serration is a saw-like appearance or a row of sharp or tooth-like projections. A serrated cutting edge has many small points of contact with the material being cut. By having less contact area than a smooth blade or other edge, the applied pressure at each point of contact is greater, and the points of contact are at a sharper angle to the material being cut. This causes a cutting action that involves many small splits in the surface of the material being cut, which cumulatively serve to cut the material along the line of the blade. Serration in nature In nature, serration is commonly seen in the cutting edge on the teeth of some species, usually sharks. However, it also appears on non-cutting surfaces, for example, in botany where a toothed leaf margin or other plant part, such as the edge of a carnation petal, is described as being serrated. A serrated leaf edge may reduce the force of wind and other natural elements. Probably the largest serrations on Earth occur on the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |