|
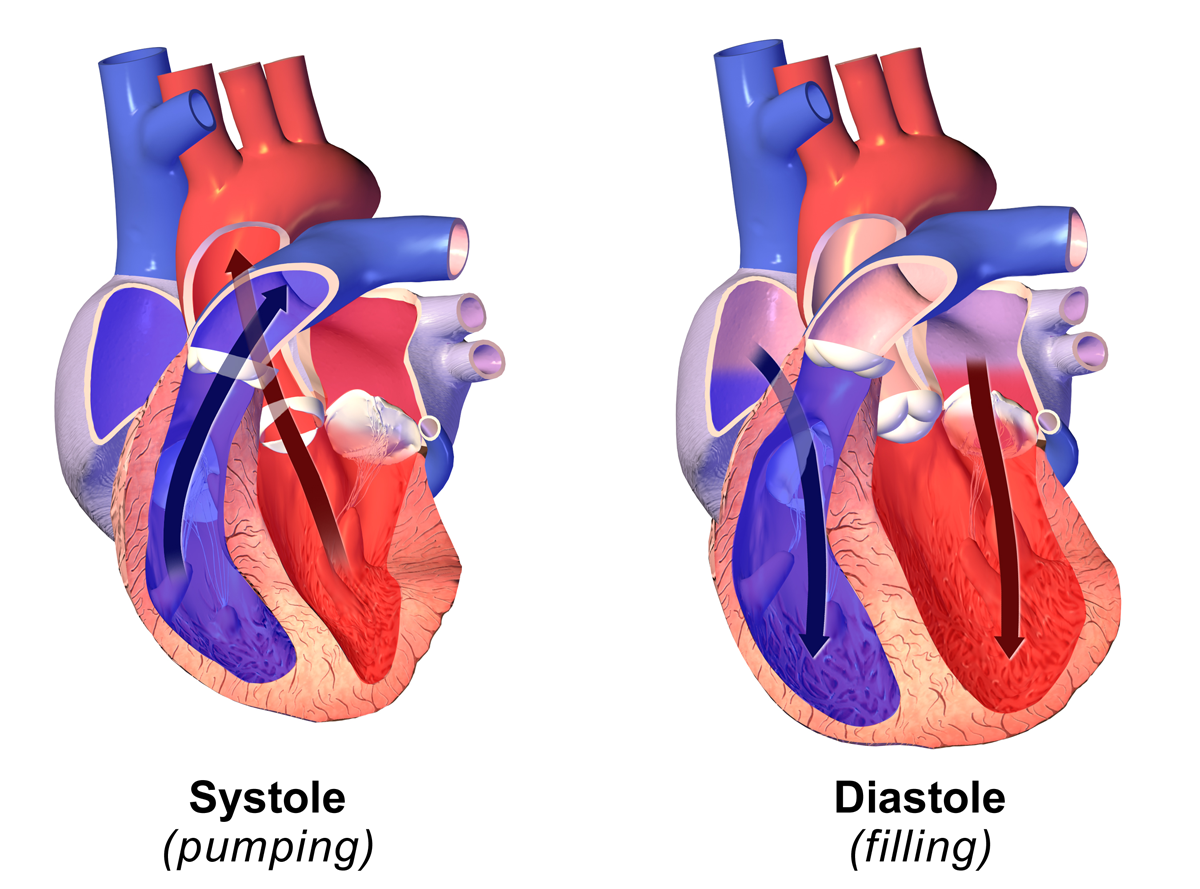
Diastolic
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during systole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the left ventricle is maximally filled – is normal, defined as greater than 50%; this may be measured by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. Approximately half of people with heart failure have preserved ejection fraction, while the other half have a reduction in ejection fraction, called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Risk factors for HFpEF include hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, and obstructive sleep apnea. Those with HFpEF have a higher prevalence of obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease than those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. The prevalence of HFpEF is expected to increase as more people develop obesity and other medic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastolic Dysfunction
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the left ventricle is maximally filled – is normal, defined as greater than 50%; this may be measured by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. Approximately half of people with heart failure have preserved ejection fraction, while the other half have a reduction in ejection fraction, called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Risk factors for HFpEF include hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, and obstructive sleep apnea. Those with HFpEF have a higher prevalence of obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease than those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. The prevalence of HFpEF is expected to increase as more people develop obesity and other medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastolic Function
In clinical cardiology the term "diastolic function" is most commonly referred as how the heart fills. Parallel to "diastolic function", the term " systolic function" is usually referenced in terms of the left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), which is the ratio of stroke volume and end-diastolic volume. Due to the epidemic of heart failure, particularly the cases determined as diastolic heart failure, it is increasingly urgent and crucial to understand the meaning of “diastolic function”. Unlike "systolic function", which can be simply evaluated by LVEF, there are no established dimensionless parameters for "diastolic function" assessment. Hence to further study "diastolic function" the complicated and speculative physiology must be taken into consideration. How the heart works during its filling period still has many misconceptions remaining. To better understand diastolic function, it is crucial to realize that the left ventricle is a mechanical suction pump at, and for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frank–Starling Law
The Frank–Starling law of the heart (also known as Starling's law and the Frank–Starling mechanism) represents the relationship between stroke volume and end diastolic volume.Widmaier, E. P., Hershel, R., & Strang, K. T. (2016).''Vander's Human Physiology: The Mechanisms of Body Function''(14th ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education. The law states that the stroke volume of the heart increases in response to an increase in the volume of blood in the ventricles, before contraction (the end diastolic volume), when all other factors remain constant. As a larger volume of blood flows into the ventricle, the blood stretches cardiac muscle, leading to an increase in the force of contraction. The Frank-Starling mechanism allows the cardiac output to be synchronized with the venous return, arterial blood supply and humoral length, without depending upon external regulation to make alterations. The physiological importance of the mechanism lies mainly in maintaining left and ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E/A Ratio
The E/A ratio is a marker of the function of the left ventricle of the heart. It represents the ratio of peak velocity blood flow from left ventricular relaxation in early diastole (the E wave) to peak velocity flow in late diastole caused by atrial contraction (the A wave). It is calculated using Doppler echocardiography, an ultrasound-based cardiac imaging modality. Abnormalities in the E/A ratio suggest that the left ventricle, which pumps blood into the systemic circulation, cannot fill with blood properly in the period between contractions. This phenomenon is referred to as diastolic dysfunction and can eventually lead to the symptoms of heart failure. Physiology The heart is a biological pump designed to move blood through the brain and body. It has four chambers: two "upper" chambers called the atria, and two "lower" chambers called the ventricles. Anatomically, the atria are more posterior to the ventricles, but for ease of understanding, are often drawn "above" them. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Diastolic Volume
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is amount of blood present in ventricle at the end of diastole. Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, ''EDV'' is often used synonymously with '' preload'', which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in cardiac muscle prior to contraction (systole). An increase in EDV increases the preload on the heart and, through the Frank-Starling mechanism of the heart, increases the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle during systole (stroke volume). __TOC__ Sample values The right ventricular end-diastolic volume (RVEDV) ranges between 100 and 160 mL. The right ventricular end-diastolic volume index (RVEDVI) is calculated by RVEDV/ BSA and ranges between 60 and 100 mL/m2. See also * End-systolic volume * Stroke volume In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the ventr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Diasystole
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ found in humans and other animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels. The heart and blood vessels together make the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the tissue, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to the lungs. In humans, the heart is approximately the size of a closed fist and is located between the lungs, in the middle compartment of the thorax, chest, called the mediastinum. In humans, the heart is divided into four chambers: upper left and right Atrium (heart), atria and lower left and right Ventricle (heart), ventricles. Commonly, the right atrium and ventricle are referred together as the right heart and their left counterparts as the left heart. In a healthy heart, blood flows one way through the heart due to heart valves, which prevent cardiac regurgitation, backflow. The heart is enclosed in a protective sac, the pericardium, which also contains a sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Heart Sound
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stethoscope to listen for these unique and distinct sounds that provide important auditory data regarding the condition of the heart. In healthy adults, there are two normal heart sounds, often described as a ''lub'' and a ''dub'' that occur in sequence with each heartbeat. These are the first heart sound (S1) and second heart sound (S2), produced by the closing of the atrioventricular valves and semilunar valves, respectively. In addition to these normal sounds, a variety of other sounds may be present including heart murmurs, adventitious sounds, and gallop rhythms S3 and S4. Heart murmurs are generated by turbulent flow of blood and a murmur to be heard as turbulent flow must require pressure difference of at least 30 mm of Hg between ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. Its contrasting phase is diastole, the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. Etymology The term originates, via Neo-Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. Terminology, general explanation The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semilunar Valves
A heart valve is a biological Check valve, one-way valve that allows blood flow, blood to flow in one direction through the chambers of the heart. A mammalian heart usually has four valves. Together, the valves determine the direction of blood flow through the heart. Heart valves are opened or closed by a difference in blood pressure on each side. The mammalian heart has two atrioventricular valves separating the upper Atrium (heart), atria from the lower Ventricle (heart), ventricles: the mitral valve in the left heart, and the tricuspid valve in the right heart. The two semilunar valves are at the entrance of the arteries leaving the heart. These are the aortic valve at the aorta, and the pulmonary valve at the pulmonary artery. The heart also has a coronary sinus valve and an inferior vena cava valve, not discussed here. Structure The heart valves and the heart chamber, chambers are lined with endocardium. Heart valves separate the Atrium (heart), atria from the Ventricle (he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |