|
Diaschisma
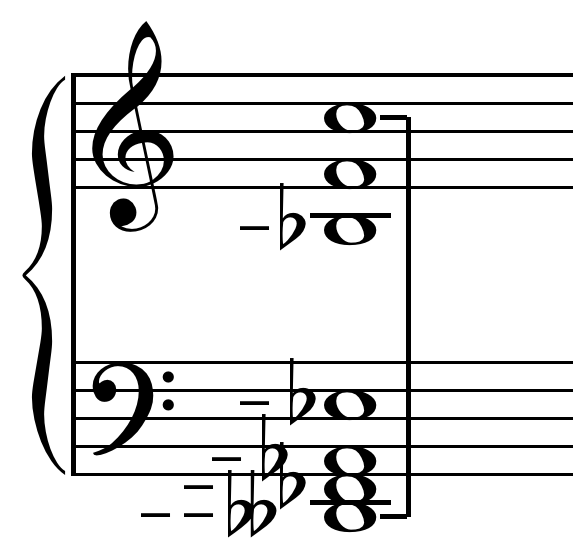
The diaschisma (or diacisma) is a small interval (music), musical interval defined as the difference between three octaves and four perfect fifths plus two just major third, major thirds (in just intonation). It can be represented by the ratio 2048:2025 and is about 19.5 cent (music), cents. The use of the name diaschisma for this interval is due to Hermann Helmholtz, Helmholtz; earlier Jean-Philippe Rameau, Rameau had called that interval a "diminished comma" or comma minor. A diaschisma is the difference between a schisma and a syntonic comma, as well as the difference between the greater chromatic semitone (135:128 = 92.18 cents) and the just minor second (16:15 = 111.73 cents).(1897). Columbian cyclopedia, Volume 9', np. Garretson, Cox & Company. pre-ISBN. Medieval theorists Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, Boethius and Tinctoris described the diaschisma as one-half of the Pythagorean minor second, or 256/243, which would make the other half either 25/24 (70.67 cents) or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaschisma Cuisenaire Rods Just
The diaschisma (or diacisma) is a small musical interval defined as the difference between three octaves and four perfect fifths plus two major thirds (in just intonation). It can be represented by the ratio 2048:2025 and is about 19.5 cents. The use of the name diaschisma for this interval is due to Helmholtz; earlier Rameau had called that interval a "diminished comma" or comma minor. A diaschisma is the difference between a schisma and a syntonic comma, as well as the difference between the greater chromatic semitone (135:128 = 92.18 cents) and the just minor second (16:15 = 111.73 cents).(1897). Columbian cyclopedia, Volume 9', np. Garretson, Cox & Company. pre-ISBN. Medieval theorists Boethius and Tinctoris described the diaschisma as one-half of the Pythagorean minor second, or 256/243, which would make the other half either 25/24 (70.67 cents) or about 45 cents. The diaschisma may be approximated by 89/88, 19.56 cents. Tempering out the diaschisma, in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaschisma
The diaschisma (or diacisma) is a small interval (music), musical interval defined as the difference between three octaves and four perfect fifths plus two just major third, major thirds (in just intonation). It can be represented by the ratio 2048:2025 and is about 19.5 cent (music), cents. The use of the name diaschisma for this interval is due to Hermann Helmholtz, Helmholtz; earlier Jean-Philippe Rameau, Rameau had called that interval a "diminished comma" or comma minor. A diaschisma is the difference between a schisma and a syntonic comma, as well as the difference between the greater chromatic semitone (135:128 = 92.18 cents) and the just minor second (16:15 = 111.73 cents).(1897). Columbian cyclopedia, Volume 9', np. Garretson, Cox & Company. pre-ISBN. Medieval theorists Anicius Manlius Severinus Boethius, Boethius and Tinctoris described the diaschisma as one-half of the Pythagorean minor second, or 256/243, which would make the other half either 25/24 (70.67 cents) or a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schisma
In music, the schisma (also spelled ''skhisma'') is the interval between the syntonic comma (81:80) and the Pythagorean comma which is slightly larger. It equals or ≈ 1.00113, which corresponds to 1.9537 cents (). It may also be defined as: * the difference (in cents) between 8 justly tuned perfect fifths plus a justly tuned major third and 5 octaves; * the ratio of major limma to the Pythagorean limma; * the ratio of the syntonic comma and the diaschisma. ''Schisma'' is a Greek word meaning a split or crack (see schism) whose musical sense was introduced by Boethius at the beginning of the 6th century in the 3rd book of his ''De institutione musica''. Boethius was also the first to define the diaschisma. Andreas Werckmeister defined the ''grad'' as the twelfth root of the Pythagorean comma, or equivalently the difference between the justly tuned fifth (3:2) and the equally tempered fifth of 700 cents (2). This value, 1.955 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comma (music)
In music theory, a comma is a very small interval (music), interval, the difference resulting from Musical tuning, tuning one note (music), note two different ways. Traditionally, there are two most common commata; the syntonic comma (80:81), "the difference between a just intonation, just major 3rd and four just perfect 5ths less two octaves", and the Pythagorean comma (524288:531441, approximately 73:74), "the difference between twelve 5ths and seven octaves". The word ''comma'' used without qualification refers to the syntonic comma, which can be defined, for instance, as the difference between an F tuned using the D-based Pythagorean tuning system, and another F tuned using the D-based quarter-comma meantone tuning system. Pitches separated by either comma are considered the same note because conventional notation does not distinguish Pythagorean intervals from 5-limit intervals. Other intervals are considered commas because of the enharmonic equivalences of a tuning system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-limit Tuning And Intervals
Five-limit tuning, 5-limit tuning, or 5-prime-limit tuning (not to be confused with 5-odd-limit tuning), is any system for tuning a musical instrument that obtains the frequency of each note by multiplying the frequency of a given reference note (the base note) by products of integer powers of 2, 3, or 5 (prime numbers limited to 5 or lower), such as . Powers of 2 represent intervallic movements by octaves. Powers of 3 represent movements by intervals of perfect fifths (plus one octave, which can be removed by multiplying by 1/2, i.e., 2−1). Powers of 5 represent intervals of major thirds (plus two octaves, removable by multiplying by 1/4, i.e., 2−2). Thus, 5-limit tunings are constructed entirely from stacking of three basic purely-tuned intervals (octaves, thirds and fifths). Since the perception of consonance seems related to low numbers in the harmonic series, and 5-limit tuning relies on the three lowest primes, 5-limit tuning should be capable of producing very conson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval (music)
In music theory, an interval is a difference in pitch between two sounds. An interval may be described as horizontal, linear, or melodic if it refers to successively sounding tones, such as two adjacent pitches in a melody, and vertical or harmonic if it pertains to simultaneously sounding tones, such as in a chord. In Western music, intervals are most commonly differences between notes of a diatonic scale. Intervals between successive notes of a scale are also known as scale steps. The smallest of these intervals is a semitone. Intervals smaller than a semitone are called microtones. They can be formed using the notes of various kinds of non-diatonic scales. Some of the very smallest ones are called commas, and describe small discrepancies, observed in some tuning systems, between enharmonically equivalent notes such as C and D. Intervals can be arbitrarily small, and even imperceptible to the human ear. In physical terms, an interval is the ratio between two sonic fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Just Minor Second
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a 12-tone scale (or half of a whole step), visually seen on a keyboard as the distance between two keys that are adjacent to each other. For example, C is adjacent to C; the interval between them is a semitone. In a 12-note approximately equally divided scale, any interval can be defined in terms of an appropriate number of semitones (e.g. a whole tone or major second is 2 semitones wide, a major third 4 semitones, and a perfect fifth 7 semitones). In music theory, a distinction is made between a diatonic semitone, or minor second (an interval encompassing two different staff positions, e.g. from C to D) and a chromatic semitone or augmented unison (an interval between two notes at the same staff position, e.g. f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Chromatic Semitone
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a 12-tone scale (or half of a whole step), visually seen on a keyboard as the distance between two keys that are adjacent to each other. For example, C is adjacent to C; the interval between them is a semitone. In a 12-note approximately equally divided scale, any interval can be defined in terms of an appropriate number of semitones (e.g. a whole tone or major second is 2 semitones wide, a major third 4 semitones, and a perfect fifth 7 semitones). In music theory, a distinction is made between a diatonic semitone, or minor second (an interval encompassing two different staff positions, e.g. from C to D) and a chromatic semitone or augmented unison (an interval between two notes at the same staff position, e.g. from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Minor Second
A semitone, also called a minor second, half step, or a half tone, is the smallest interval (music), musical interval commonly used in Western tonal music, and it is considered the most Consonance and dissonance#Dissonance, dissonant when sounded harmonically. It is defined as the interval between two adjacent notes in a chromatic scale, 12-tone scale (or half of a whole step), visually seen on a keyboard as the distance between two keys that are adjacent to each other. For example, C is adjacent to C; the interval between them is a semitone. In a 12-note approximately equally divided scale, any interval can be defined in terms of an appropriate number of semitones (e.g. a whole tone or major second is 2 semitones wide, a major third 4 semitones, and a perfect fifth 7 semitones). In music theory, a distinction is made between a diatonic semitone, or minor second (an interval encompassing two different staff positions, e.g. from C to D) and a chromatic semitone or augmented uniso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Just Major Third
Just or JUST may refer to: Arts and entertainment * "Just" (song), 1995, by Radiohead * ''Just!'', Australian author Andy Griffiths' children's story collections * ''Just'', a 1998 album by Dave Lindholm * "Just", a 2005 song on ''Lost and Found'' by Mudvayne * "Just", a 2016 song on ''Melting'' by Mamamoo Businesses * JUST, Inc., an American food manufacturing company * Just Group, an Australian owner and operator of seven retail brands * Just Group plc, a British company specialising in retirement products and services Education * Jashore University of Science and Technology, Bangladesh * Jinwen University of Science and Technology, Taiwan * Jordan University of Science and Technology, Jordan People * Just (surname) * Just (given name) * List of people known as the Just See also * * Jus (other) Jus or JUS may refer to: Language * Jussive mood, in grammar * Yus, two early Cyrillic letters * Jumla Sign Language, of Nepal (ISO 639-3:jus) Law * Jus (law), a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntonic Comma
In music theory Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "Elements of music, ..., the syntonic comma, also known as the chromatic diesis, the Didymean comma, the Ptolemy, Ptolemaic comma, or the diatonic comma is a small Comma (music), comma type interval (music), interval between two musical notes, equal to the frequency ratio (= 1.0125) (around 21.51 cent (music), cents). Two notes that differ by this interval would sound different from each other even to untrained ears, but would be close enough that they would be more likely interpreted as out-of-tune versions of the same note than as different notes. The comma is also referred to as a ''Didymean comma'' because it is the amount by which Didymus the Musician, Didymus corrected the Pythagorean interval, Pythagorean major thir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |