|
Diabetes In Cats
Feline diabetes mellitus is a chronic disease in cats whereby either insufficient insulin response or insulin resistance leads to persistently high blood glucose concentrations. Diabetes affects up to 1 in 230 cats, and may be becoming increasingly common. Diabetes is less common in cats than in dogs. The condition is treatable, and if treated properly the cat can experience a normal life expectancy. In cats with type2 diabetes, prompt effective treatment may lead to #Remission, diabetic remission, in which the cat no longer needs injected insulin. Untreated, the condition leads to increasingly weak legs in cats and eventually to malnutrition, diabetic ketoacidosis, ketoacidosis and/or dehydration, and death. Diabetes in cats can be classified into the following: * Type1 diabetes, in which the immune system attacks the pancreas, is "extremely rare" in cats, unlike in dogs and humans. * Type2 diabetes is responsible for 80–95% of diabetic cases. They are generally severely in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronic Disease
A chronic condition (also known as chronic disease or chronic illness) is a health condition or disease that is persistent or otherwise long-lasting in its effects or a disease that comes with time. The term ''chronic'' is often applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include diabetes, functional gastrointestinal disorder, eczema, arthritis, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, autoimmune diseases, genetic disorders and some viral diseases such as hepatitis C and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. An illness which is lifelong because it ends in death is a terminal illness. It is possible and not unexpected for an illness to change in definition from terminal to chronic as medicine progresses. Diabetes and HIV for example were once terminal yet are now considered chronic, due to the availability of insulin for diabetics and daily drug treatment for individuals with HIV, which allow these individuals to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantigrade
151px, Portion of a human skeleton, showing plantigrade habit In terrestrial animals, plantigrade locomotion means walking with the toes and metatarsals flat on the ground. It is one of three forms of locomotion adopted by terrestrial mammals. The other options are digitigrade, walking on the toes and fingers with the heel and wrist permanently raised, and unguligrade, walking on the nail or nails of the toes (the hoof) with the heel/wrist and the digits permanently raised. The leg of a plantigrade mammal includes the bones of the upper leg (femur/humerus) and lower leg (tibia and fibula/radius and ulna). The leg of a digitigrade mammal also includes the metatarsals/metacarpals, the bones that in a human compose the arch of the foot and the palm of the hand. The leg of an unguligrade mammal also includes the phalanges, the finger and toe bones. Among extinct animals, most early mammals such as pantodonts were plantigrade. A plantigrade foot is the primitive condition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Sugar
The blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, blood glucose level, or glycemia is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. For a 70 kg (154 lb) human, approximately four grams of dissolved glucose (also called "blood glucose") is maintained in the blood plasma at all times. Glucose that is not circulating in the blood is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level by releasing just enough glucose from these glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle in order to maintain homeostasis. Glucose can be transported from the intestines or liver to other tissues in the body via the bloodstream. Cellular glucose uptake is primarily regulated by insulin, a hormone produced in the pancreas. Once inside the cell, the glucose can now act as an energy source as it undergoes the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glargine
Insulin glargine sold under the brand name Lantus among others is a long-acting modified form of medical insulin, used in the management of type 1 and type 2 diabetes. It is injected just under the skin. Effects generally begin an hour after use. Common side effects include low blood sugar, problems at the site of injection, itchiness, and weight gain. Other serious side effects include low blood potassium. NPH insulin rather than insulin glargine is generally preferred in pregnancy. After injection, microcrystals slowly release insulin for about 24 hours. This insulin causes body tissues to absorb glucose from the blood and decreases glucose production by the liver. Insulin glargine was patented, but the patent expired in most jurisdictions in 2014. It was approved for medical use in the United States in 2000. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. In 2022, it was the 28th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fructosamine
Fructosamines are compounds that result from glycation reactions between glucose and a primary amine, followed by isomerization via the Amadori rearrangement. Biologically, fructosamines are recognized by fructosamine-3-kinase, which may trigger the degradation of advanced glycation end-products (though the true clinical significance of this pathway is unclear). Fructosamine can also refer to the specific compound 1-amino-1-deoxy-D-fructose ( isoglucosamine), first synthesized by Nobel laureate Hermann Emil Fischer in 1886. Most commonly, fructosamine refers to a laboratory test for diabetes management that is rarely used in human clinical practice (simple blood glucose monitoring or hemoglobin A1c testing are preferred). In small animal veterinary practice however it is part of the diabetic cat or dog diagnosis and monitoring giving an indication of blood glucose levels over the previous week. Many direct-to-consumer lab testing companies sell fructosamine tests. Use in med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insulin-like Growth Factor-1
Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), also called somatomedin C, is a hormone similar in molecular structure to insulin which plays an important role in childhood growth, and has anabolic effects in adults. In the 1950s IGF-1 was called " sulfation factor" because it stimulated sulfation of cartilage in vitro, and in the 1970s due to its effects it was termed "nonsuppressible insulin-like activity" (NSILA). IGF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IGF1'' gene. IGF-1 consists of 70 amino acids in a single chain with three intramolecular disulfide bridges. IGF-1 has a molecular weight of 7,649 daltons. In dogs, an ancient mutation in IGF1 is the primary cause of the toy phenotype. IGF-1 is produced primarily by the liver. Production is stimulated by growth hormone (GH). Most of IGF-1 is bound to one of 6 binding proteins (IGF-BP). IGFBP-1 is regulated by insulin. IGF-1 is produced throughout life; the highest rates of IGF-1 production occur during the pubertal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
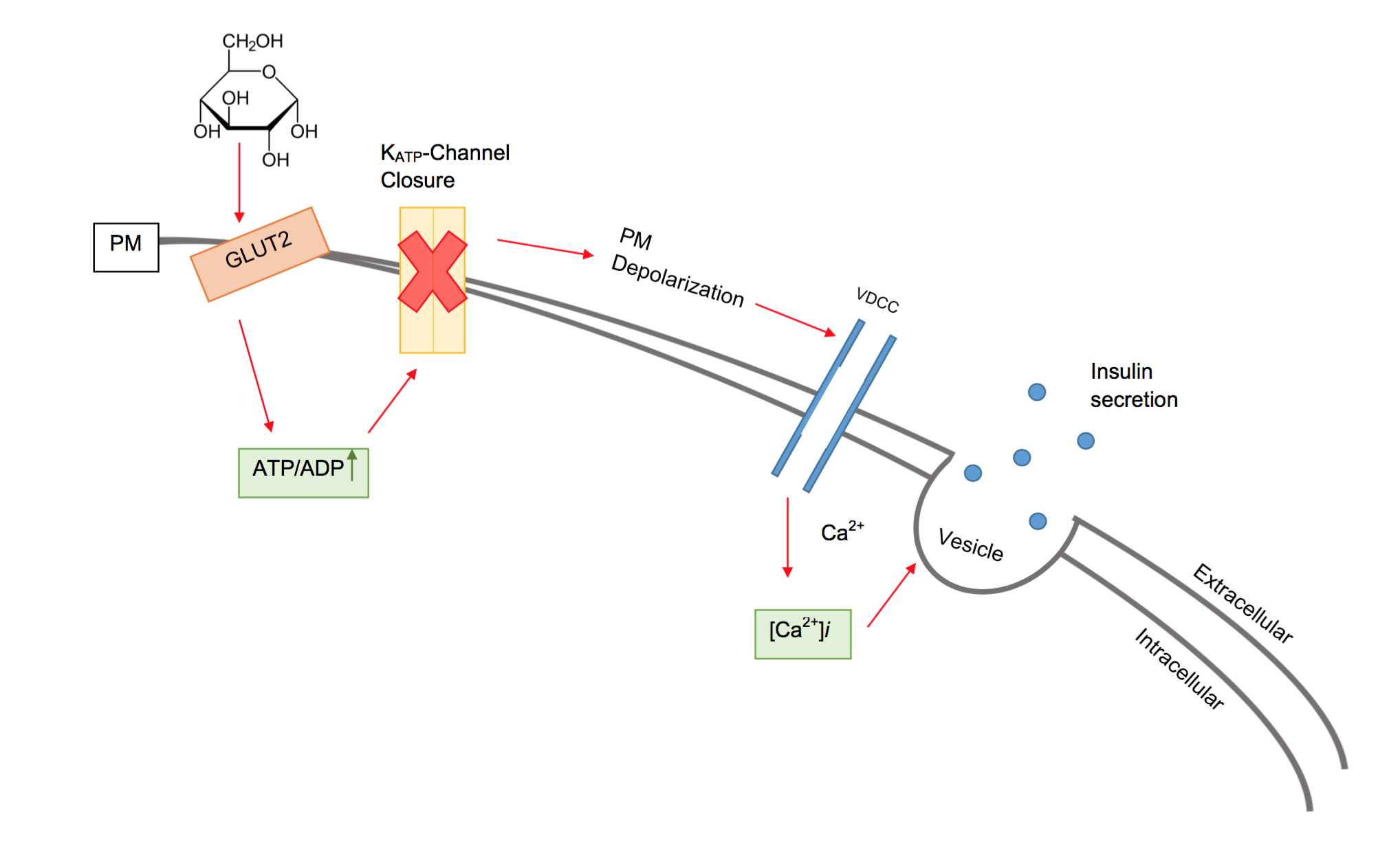
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes (T2D), formerly known as adult-onset diabetes, is a form of diabetes mellitus that is characterized by high blood sugar, insulin resistance, and relative lack of insulin. Common symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue and unexplained weight loss. Other symptoms include increased hunger, having a sensation of pins and needles, and sores (wounds) that heal slowly. Symptoms often develop slowly. Long-term complications from high blood sugar include heart disease, stroke, diabetic retinopathy, which can result in blindness, kidney failure, and poor blood flow in the lower limbs, which may lead to amputations. A sudden onset of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state may occur; however, ketoacidosis is uncommon. Type 2 diabetes primarily occurs as a result of obesity and lack of exercise. Some people are genetically more at risk than others. Type 2 diabetes makes up about 90% of cases of diabetes, with the other 10% due primar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition where unusually high amount of glucose is present in blood. It is defined as blood glucose level exceeding 6.9 mmol/L (125 mg/dL) after fasting for 8 hours or 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) 2 hours after eating. Blood glucose level indication Patients with diabetes are oriented to avoid exceeding the recommended postprandial threshold of 160 mg/dL (8.89 mmol/L) for optimal glycemic control. Values of blood glucose higher than 160 mg/dL are classified as 'very high' hyperglycemia, a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose (glucotoxicity) circulates in the blood plasma. These values are higher than the renal threshold of 10 mmol/L (180 mg/dL) up to which glucose reabsorption is preserved at physiological rates and insulin therapy is not necessary. Blood glucose values higher than the cutoff level of 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL) are used to diagnose T2DM and strongly associated with metabolic disturbances, although symp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin Sheath
Myelin Sheath ( ) is a lipid-rich material that in most vertebrates surrounds the axons of neurons to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) pass along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Myelin ensheaths part of an axon known as an internodal segment, in multiple myelin layers of a tightly regulated internodal length. The ensheathed segments are separated at regular short unmyelinated intervals, called nodes of Ranvier. Each node of Ranvier is around one micrometre long. Nodes of Ranvier enable a much faster rate of conduction known as saltatory conduction where the action potential recharges at each node to jump over to the next node, and so on till it reaches the axon terminal. At the terminal the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy includes various types of nerve damage associated with diabetes mellitus. The most common form, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, affects 30% of all diabetic patients. Studies suggests that cutaneous nerve branches, such as the sural nerve, are involved in more than half of patients with diabetes 10 years after the diagnosis and can be detected with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Symptoms depend on the site of nerve damage and can include motor changes such as weakness; sensory symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain; or autonomic changes such as urinary symptoms. These changes are thought to result from a microvascular disease, microvascular injury involving small blood vessels that supply nerves (vasa nervorum). Relatively common conditions which may be associated with diabetic neuropathy include distal symmetric polyneuropathy; Oculomotor nerve palsy, third, Fourth nerve palsy, fourth, or Sixth nerve palsy, sixth cranial nerve palsy; mononeuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a metabolic state caused by uncontrolled production of ketone bodies that cause a metabolic acidosis. While ketosis refers to any elevation of blood ketones, ketoacidosis is a specific pathologic condition that results in changes in blood pH and requires medical attention. The most common cause of ketoacidosis is diabetic ketoacidosis but it can also be caused by alcohol, medications, toxins, and rarely, starvation. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of ketoacidosis are variable depending on the underlying cause. The most common symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and weakness. Breath may also develop the smell of acetone as it is a volatile ketone that can be exhaled. Rapid deep breathing, or Kussmaul breathing, may be present to compensate for the metabolic acidosis. Altered mental status is more common in diabetic than alcoholic ketoacidosis. Causes Ketoacidosis is caused by the uncontrolled production of ketone bodies. Usually the production of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |