|
Deque
In computer science, a double-ended queue (abbreviated to deque, ) is an abstract data type that generalizes a queue, for which elements can be added to or removed from either the front (head) or back (tail). It is also often called a head-tail linked list, though properly this refers to a specific data structure ''implementation'' of a deque (see below). Naming conventions ''Deque'' is sometimes written ''dequeue'', but this use is generally deprecated in technical literature or technical writing because ''dequeue'' is also a verb meaning "to remove from a queue". Nevertheless, several libraries and some writers, such as Aho, Hopcroft, and Ullman in their textbook ''Data Structures and Algorithms'', spell it ''dequeue''. John Mitchell, author of ''Concepts in Programming Languages,'' also uses this terminology. Distinctions and sub-types This differs from the queue abstract data type or ''first in first out'' list ( FIFO), where elements can only be added to one end and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Queue (abstract Data Type)
In computer science, a queue is a collection of entities that are maintained in a sequence and can be modified by the addition of entities at one end of the sequence and the removal of entities from the other end of the sequence. By convention, the end of the sequence at which elements are added is called the back, tail, or rear of the queue, and the end at which elements are removed is called the head or front of the queue, analogously to the words used when people line up to wait for goods or services. The operation of adding an element to the rear of the queue is known as ''enqueue'', and the operation of removing an element from the front is known as ''dequeue''. Other operations may also be allowed, often including a '' peek'' or ''front'' operation that returns the value of the next element to be dequeued without dequeuing it. The operations of a queue make it a first-in-first-out (FIFO) data structure. In a FIFO data structure, the first element added to the queue will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peek (data Type Operation)
In computer science, peek is an operation on certain abstract data types, specifically sequential collection (abstract data type), collections such as Stack (abstract data type), stacks and Queue (abstract data type), queues, which returns the value of the top ("front") of the collection without removing the element from the collection. It thus returns the same value as operations such as "pop" or "dequeue", but does not modify the data. The name "peek" is similar to the basic "push" and "pop" operations on a stack, but the name for this operation varies depending on data type and language. Peek is generally considered an inessential operation, compared with the more basic operations of adding and removing data, and as such is not included in the basic definition of these data types. However, since it is a useful operation and generally easily implemented, it is frequently included in practices, and in some definitions peek is included as basic, with pop (or analog) defined in terms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FIFO (computing And Electronics)
Representation of a FIFO queue In computing and in systems theory, first in, first out (the first in is the first out), acronymized as FIFO, is a method for organizing the manipulation of a data structure (often, specifically a data buffer) where the oldest (first) entry, or "head" of the queue, is processed first. Such processing is analogous to servicing people in a queue area on a first-come, first-served (FCFS) basis, i.e. in the same sequence in which they arrive at the queue's tail. FCFS is also the jargon term for the FIFO operating system scheduling algorithm, which gives every process central processing unit (CPU) time in the order in which it is demanded. FIFO's opposite is LIFO, last-in-first-out, where the youngest entry or "top of the stack" is processed first. A priority queue is neither FIFO or LIFO but may adopt similar behaviour temporarily or by default. Queueing theory encompasses these methods for processing data structures, as well as interactions be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Data Structure
In computing, a persistent data structure or not ephemeral data structure is a data structure that always preserves the previous version of itself when it is modified. Such data structures are effectively immutable, as their operations do not (visibly) update the structure in-place, but instead always yield a new updated structure. The term was introduced in Driscoll, Sarnak, Sleator, and Tarjan's 1986 article. A data structure is partially persistent if all versions can be accessed but only the newest version can be modified. The data structure is fully persistent if every version can be both accessed and modified. If there is also a meld or merge operation that can create a new version from two previous versions, the data structure is called confluently persistent. Structures that are not persistent are called ''ephemeral''. These types of data structures are particularly common in logical and functional programming, as languages in those paradigms discourage (or fully forbid) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Array
In computer science, a dynamic array, growable array, resizable array, dynamic table, mutable array, or array list is a random access, variable-size list data structure that allows elements to be added or removed. It is supplied with standard libraries in many modern mainstream programming languages. Dynamic arrays overcome a limit of static arrays, which have a fixed capacity that needs to be specified at allocation. A dynamic array is not the same thing as a dynamically allocated array or variable-length array, either of which is an array whose size is fixed when the array is allocated, although a dynamic array may use such a fixed-size array as a back end.See, for example, thsource code of java.util.ArrayList class from OpenJDK 6 Bounded-size dynamic arrays and capacity A simple dynamic array can be constructed by allocating an array of fixed-size, typically larger than the number of elements immediately required. The elements of the dynamic array are stored contiguous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Art Of Computer Programming
''The Art of Computer Programming'' (''TAOCP'') is a comprehensive multi-volume monograph written by the computer scientist Donald Knuth presenting programming algorithms and their analysis. it consists of published volumes 1, 2, 3, 4A, and 4B, with more expected to be released in the future. The Volumes 1–5 are intended to represent the central core of computer programming for sequential machines; the subjects of Volumes 6 and 7 are important but more specialized. When Knuth began the project in 1962, he originally conceived of it as a single book with twelve chapters. The first three volumes of what was then expected to be a seven-volume set were published in 1968, 1969, and 1973. Work began in earnest on Volume 4 in 1973, but was suspended in 1977 for work on typesetting prompted by the second edition of Volume 2. Writing of the final copy of Volume 4A began in longhand in 2001, and the first online pre-fascicle, 2A, appeared later in 2001. The first published installment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data Structure
In computer science, a data structure is a data organization and storage format that is usually chosen for Efficiency, efficient Data access, access to data. More precisely, a data structure is a collection of data values, the relationships among them, and the Function (computer programming), functions or Operator (computer programming), operations that can be applied to the data, i.e., it is an algebraic structure about data. Usage Data structures serve as the basis for abstract data types (ADT). The ADT defines the logical form of the data type. The data structure implements the physical form of the data type. Different types of data structures are suited to different kinds of applications, and some are highly specialized to specific tasks. For example, Relational database, relational databases commonly use B-tree indexes for data retrieval, while compiler Implementation, implementations usually use hash tables to look up Identifier (computer languages), identifiers. Data s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purely Functional Data Structure
In computer science, a purely functional data structure is a data structure that can be directly implemented in a purely functional language. The main difference between an arbitrary data structure and a purely functional one is that the latter is (strongly) immutable. This restriction ensures the data structure possesses the advantages of immutable objects: (full) persistency, quick copy of objects, and thread safety. Efficient purely functional data structures may require the use of lazy evaluation and memoization. Definition Persistent data structures have the property of keeping previous versions of themselves unmodified. On the other hand, non-persistent structures such as arrays admit a destructive update, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Data Type
In computer science, an abstract data type (ADT) is a mathematical model for data types, defined by its behavior (semantics) from the point of view of a '' user'' of the data, specifically in terms of possible values, possible operations on data of this type, and the behavior of these operations. This mathematical model contrasts with ''data structures'', which are concrete representations of data, and are the point of view of an implementer, not a user. For example, a stack has push/pop operations that follow a Last-In-First-Out rule, and can be concretely implemented using either a list or an array. Another example is a set which stores values, without any particular order, and no repeated values. Values themselves are not retrieved from sets; rather, one tests a value for membership to obtain a Boolean "in" or "not in". ADTs are a theoretical concept, used in formal semantics and program verification and, less strictly, in the design and analysis of algorithms, data structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
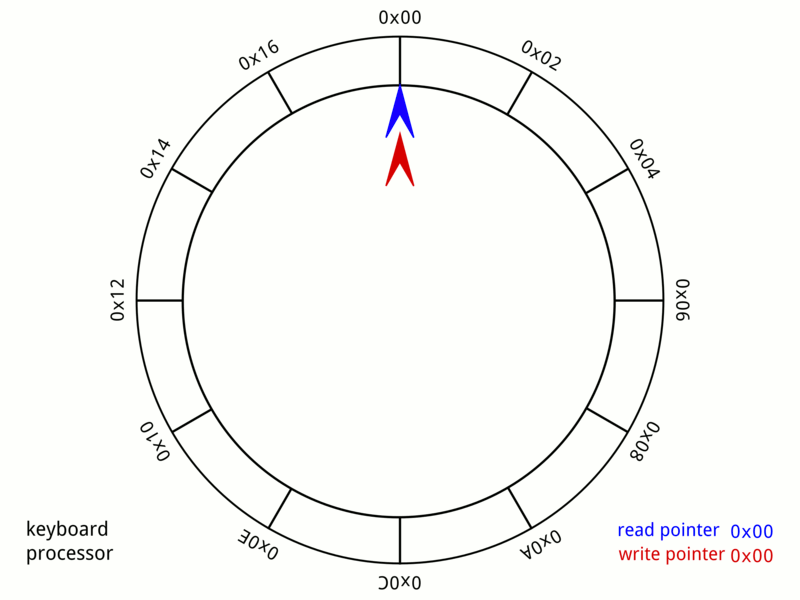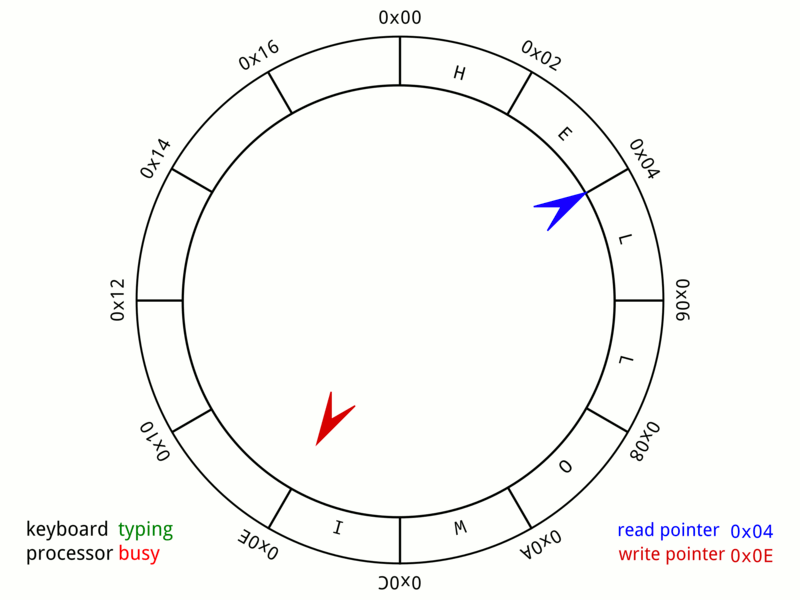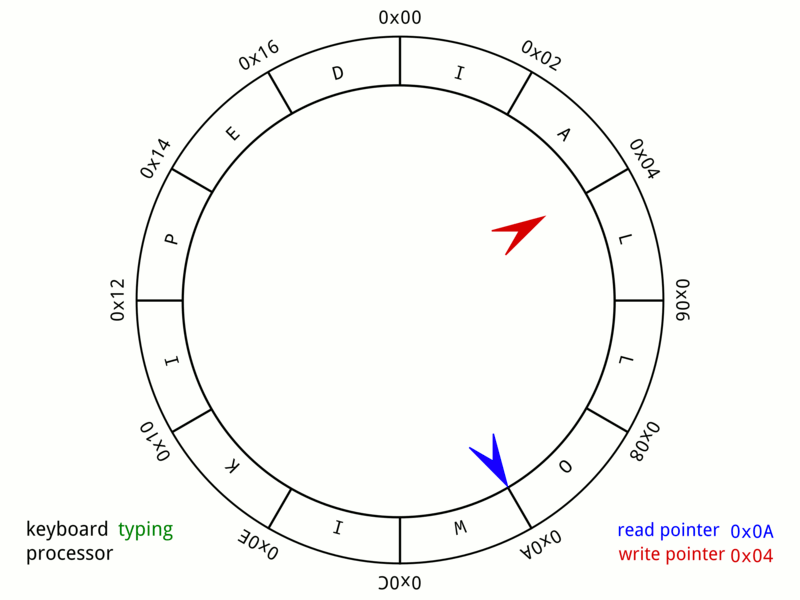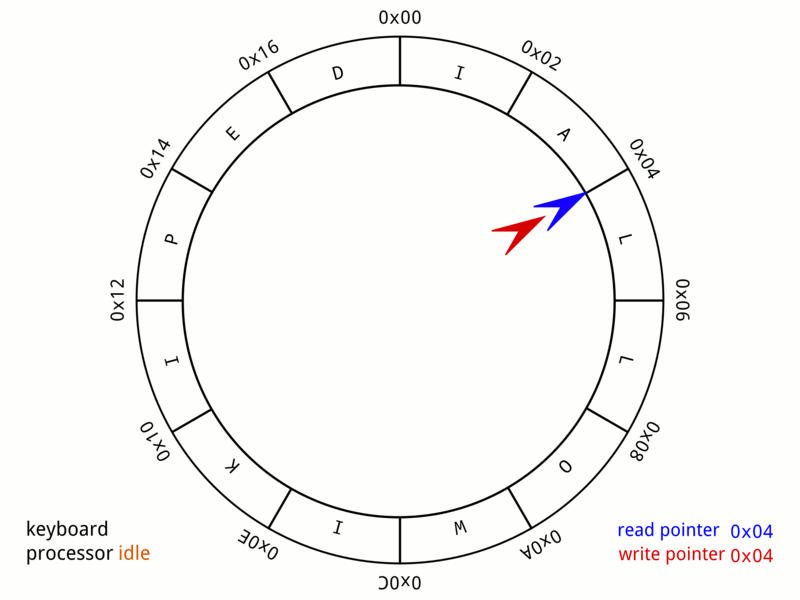
Circular Buffer
In computer science, a circular buffer, circular queue, cyclic buffer or ring buffer is a data structure that uses a single, fixed-size buffer as if it were connected end-to-end. This structure lends itself easily to buffering data streams. There were early circular buffer implementations in hardware. Overview A circular buffer first starts out empty and has a set length. In the diagram below is a 7-element buffer: : Assume that 1 is written in the center of a circular buffer (the exact starting location is not important in a circular buffer): : Then assume that two more elements are added to the circular buffer — 2 & 3 — which get put after 1: : If two elements are removed, the two oldest values inside of the circular buffer would be removed. Circular buffers use FIFO ('' first in, first out'') logic. In the example, 1 & 2 were the first to enter the circular buffer, they are the first to be removed, leaving 3 inside of the buffer. : If the buffer has 7 e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |