|
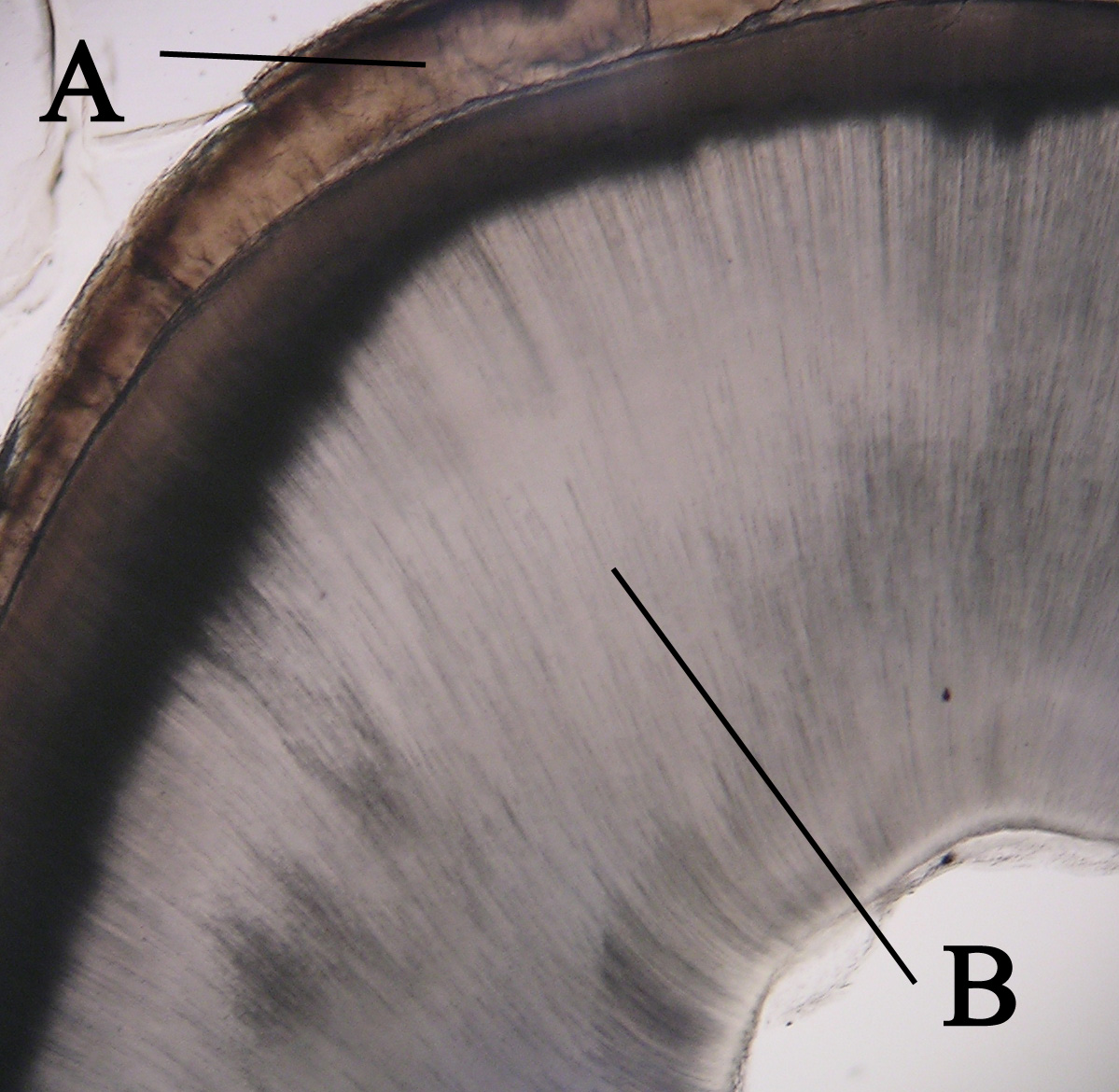
Dentin Sensitivity
Dentin ( ) (American English) or dentine ( or ) (British English) () is a calcified tissue of the body and, along with enamel, cementum, and pulp, is one of the four major components of teeth. It is usually covered by enamel on the crown and cementum on the root and surrounds the entire pulp. By volume, 45% of dentin consists of the mineral hydroxyapatite, 33% is organic material, and 22% is water. Yellow in appearance, it greatly affects the color of a tooth due to the translucency of enamel. Dentin, which is less mineralized and less brittle than enamel, is necessary for the support of enamel. Dentin rates approximately 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness. There are two main characteristics which distinguish dentin from enamel: firstly, dentin forms throughout life; secondly, dentin is sensitive and can become hypersensitive to changes in temperature due to the sensory function of odontoblasts, especially when enamel recedes and dentin channels become exposed. Developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dentinoenamel Junction
The dentinoenamel junction or dentin-enamel junction (DEJ) is the boundary between the enamel and the underlying dentin that form the solid architecture of a tooth A tooth (: teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tea .... It is also known as the amelo- dentinal junction, or ADJ. The dentinoenamel junction is thought to be of a scalloped structure which has occurred as an exaptation of the epithelial folding that is undergone during ontogeny. This scalloped exaptation has then provided stress relief during mastication and a reduction in dentin-enamel sliding and has thus, not been selected against, making it an accidental adaptation. Composition of Dentinoenamel Junction (DEJ) The crown of a human tooth, or more precisely, the tooth's dentin, is coated in enamel. Derived from the me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Permeability
Vascular permeability, often in the form of capillary permeability or microvascular permeability, characterizes the permeability of a blood vessel wall–in other words, the blood vessel wall's capacity to allow for the flow of small molecules (such as drugs, nutrients, water, or ions) or even whole cells (such as lymphocytes on their way to a site of inflammation) in and out of the vessel. Blood vessel walls are lined by a single layer of endothelial cells. The gaps between endothelial cells (cell junctions) are strictly regulated depending on the type and physiological state of the tissue. There are several techniques to measure vascular permeability to certain molecules. For instance, the cannulation of a single microvessel with a micropipette: the microvessel is perfused with a certain pressure, occluded downstream, and then the velocity of some cells will be related to the permeability.Michel, C. C., Mason, J. C., Curry, F. E. & Tooke, J. E. Development of Landis Techn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tenascin
Tenascins are extracellular matrix glycoproteins. They are abundant in the extracellular matrix of developing vertebrate embryos and they reappear around healing wounds and in the stroma of some tumors. Types There are four members of the tenascin gene family: tenascin-C, tenascin-R, tenascin-X and tenascin-W. * Tenascin-C is the founding member of the gene family. In the embryo it is made by migrating cells like the neural crest; it is also abundant in developing tendons, bone and cartilage. * Tenascin-R is found in the developing and adult nervous system. * Tenascin-X is found primarily in loose connective tissue; mutations in the human tenascin-X gene can lead to a form of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome. * Tenascin-W is found in the kidney and in developing bone. The basic structure is 14 EGF-like repeats towards the N-terminal end, and 8 or more fibronectin-III domains which vary upon species and variant. Tenascin-C is the most intensely studied member of the family. It h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transferrin
Transferrins are glycoproteins found in vertebrates which bind and consequently mediate the transport of iron (Fe) through blood plasma. They are produced in the liver and contain binding sites for two Iron(III), Fe3+ ions. Human transferrin is encoded by the ''TF'' gene and produced as a 76 Dalton (unit), kDa glycoprotein. Transferrin glycoproteins bind iron tightly, but reversibly. Although iron bound to transferrin is less than 0.1% (4 mg) of total body iron, it forms the most vital iron pool with the highest rate of turnover (25 mg/24 h). Transferrin has a molecular weight of around 80 atomic mass unit, kDa and contains two specific high-affinity Fe(III) binding sites. The affinity of transferrin for Fe(III) is extremely high (association constant is 1020 M−1 at pH 7.4) but decreases progressively with decreasing pH below neutrality. Transferrins are not limited to only binding to iron but also to different metal ions. These glycoproteins are located in various b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albumin
Albumin is a family of globular proteins, the most common of which are the serum albumins. All of the proteins of the albumin family are water- soluble, moderately soluble in concentrated salt solutions, and experience heat denaturation. Albumins are commonly found in blood plasma and differ from other blood proteins in that they are not glycosylated. Substances containing albumins are called ''albuminoids''. A number of blood transport proteins are evolutionarily related in the albumin family, including serum albumin, alpha-fetoprotein, vitamin D-binding protein and afamin. This family is only found in vertebrates. ''Albumins'' in a less strict sense can mean other proteins that coagulate under certain conditions. See ' for lactalbumin, ovalbumin and plant "2S albumin". Function Albumins in general are transport proteins that bind to various ligands and carry them around. Human types include: * Human serum albumin is the main protein of human blood plasma. It m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odontoblast Process
An odontoblast process (also called Tomes's fibers or Tomes fibers, or by a dated term Tomes's fibrils) is an extension of a cell called an odontoblast, which forms dentin in a tooth. The odontoblast process is located in dentinal tubules. It forms during dentinogenesis and results from a part of the odontoblast staying in its location as the main body of the odontoblast moves toward the center of the tooth's pulp. The odontoblast process causes the secretion of hydroxyapatite crystals and mineralization of the matrix secreted by the odontoblasts. References * See also *Tomes's process *John Tomes Sir John Tomes (21 March 1815 – 29 July 1895) was an English dental surgeon. Life The eldest son of John Tomes and Sarah, his wife, daughter of William Baylies of Welford-on-Avon, then in Gloucestershire, he was born at Weston-on-Avon in Glo ... Tooth development {{dentistry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cell (biology), cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Metalloproteinase
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), also known as matrix metallopeptidases or matrixins, are metalloproteinases that are calcium-dependent zinc-containing endopeptidases; other family members are adamalysins, serralysins, and astacins. The MMPs belong to a larger family of proteases known as the metzincin superfamily. Collectively, these enzymes are capable of degrading all kinds of extracellular matrix proteins, but also can process a number of Biological activity, bioactive molecules. They are known to be involved in the cleavage of cell surface Receptor (biochemistry), receptors, the release of apoptosis, apoptotic ligands (such as the FAS ligand), and chemokine/cytokine inactivation. MMPs are also thought to play a major role in cell behaviors such as cell proliferation, cell migration, migration (cell adhesion, adhesion/dispersion), Cellular differentiation, differentiation, angiogenesis, apoptosis, and Immune system, host defense. They were first described in vertebrates in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Phosphatase
The enzyme alkaline phosphatase (ALP, alkaline phenyl phosphatase, also abbreviated PhoA) is a phosphatase with the physiological role of dephosphorylating compounds. The enzyme is found across a multitude of organisms, prokaryotes and eukaryotes alike, with the same general function, but in different structural forms suitable to the environment they function in. Alkaline phosphatase is found in the periplasmic space of '' E. coli'' bacteria. This enzyme is heat stable and has its maximum activity at high pH. In humans, it is found in many forms depending on its origin within the body – it plays an integral role in metabolism within the liver and development within the skeleton. Due to its widespread prevalence in these areas, its concentration in the bloodstream is used by diagnosticians as a biomarker in helping determine diagnoses such as hepatitis or osteomalacia. The level of alkaline phosphatase in the blood is checked through the ALP test, which is often par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proteoglycan
Proteoglycans are proteins that are heavily glycosylated. The basic proteoglycan unit consists of a "core protein" with one or more covalently attached glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chain(s). The point of attachment is a serine (Ser) residue to which the glycosaminoglycan is joined through a tetrasaccharide bridge (e.g. chondroitin sulfate- GlcA- Gal-Gal- Xyl-PROTEIN). The Ser residue is generally in the sequence -Ser- Gly-X-Gly- (where X can be any amino acid residue but proline), although not every protein with this sequence has an attached glycosaminoglycan. The chains are long, linear carbohydrate polymers that are negatively charged under physiological conditions due to the occurrence of sulfate and uronic acid groups. Proteoglycans occur in connective tissue. Types Proteoglycans are categorized by their relative size (large and small) and the nature of their glycosaminoglycan chains. Types include: Certain members are considered members of the "small leucine-rich pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphoprotein
A phosphoprotein is a protein that is posttranslationally modified by the attachment of either a single phosphate group, or a complex molecule such as 5'-phospho-DNA, through a phosphate group. The target amino acid is most often serine, threonine, or tyrosine residues (mostly in eukaryotes), or aspartic acid or histidine residues (mostly in prokaryotes). Biological function The phosphorylation of proteins is a major regulatory mechanism in cells. Clinical significance Phosphoproteins have been proposed as biomarkers for breast cancer Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from breast tissue. Signs of breast cancer may include a Breast lump, lump in the breast, a change in breast shape, dimpling of the skin, Milk-rejection sign, milk rejection, fluid coming from the nipp .... See also * Protein phosphorylation * Phosphoserine References Phosphoproteins {{protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |