|
Dental Notation
Dental professionals, in writing or speech, use several different dental notation systems for associating information with a specific tooth. The three most common systems are the FDI World Dental Federation notation (ISO 3950), the Universal Numbering System, and the Palmer notation. The FDI notation is used worldwide, and the Universal is used widely in the United States. The FDI notation can be easily adapted to computerized charting. Another system is used by paleoanthropologists. History A committee of the American Dental Association (ADA) recommended the use of the Palmer notation method in 1947. Since Palmer notation method required the use of symbols, its use was difficult on keyboards. As a result, the association officially supported the Universal system in 1968. The World Health Organization and the Fédération Dentaire Internationale officially uses the two-digit numbering system of the FDI system. However, in 1996, the ADA adopted the ISO System as an alterna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') or modern humans are the most common and widespread species of primate, and the last surviving species of the genus ''Homo''. They are Hominidae, great apes characterized by their Prehistory of nakedness and clothing#Evolution of hairlessness, hairlessness, bipedality, bipedalism, and high Human intelligence, intelligence. Humans have large Human brain, brains, enabling more advanced cognitive skills that facilitate successful adaptation to varied environments, development of sophisticated tools, and formation of complex social structures and civilizations. Humans are Sociality, highly social, with individual humans tending to belong to a Level of analysis, multi-layered network of distinct social groups — from families and peer groups to corporations and State (polity), political states. As such, social interactions between humans have established a wide variety of Value theory, values, norm (sociology), social norms, languages, and traditions (co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
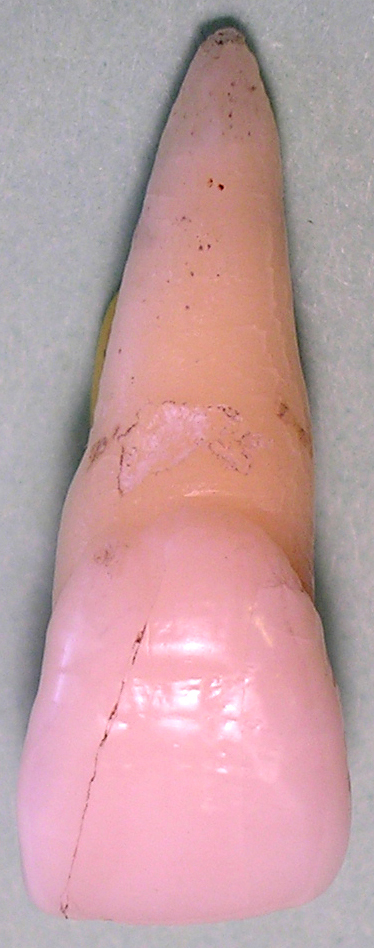
Maxillary Second Premolar
The maxillary second premolar is one of two teeth located in the upper maxilar, laterally (away from the midline of the face) from both the maxillary first premolars of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both maxillary first molars. The function of this premolar is similar to that of first molars in regard to grinding being the principal action during mastication, commonly known as chewing. There are two cusps on maxillary second premolars, but both of them are less sharp than those of the maxillary first premolars. There are no deciduous (baby) maxillary premolars. Instead, the teeth that precede the permanent maxillary premolars are the deciduous maxillary molars. In the universal system of notation, the permanent maxillary premolars are designated by a number. The right permanent maxillary second premolar is known as "4", and the left one is known as "13". In the Palmer notation Palmer notation (sometimes called the "Military System" and named f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Premolar
The premolars, also called premolar Tooth (human), teeth, or bicuspids, are transitional teeth located between the Canine tooth, canine and Molar (tooth), molar teeth. In humans, there are two premolars per dental terminology#Quadrant, quadrant in the permanent teeth, permanent set of teeth, making eight premolars total in the mouth. They have at least two Cusp (dentistry), cusps. Premolars can be considered transitional teeth during chewing, or mastication. They have properties of both the canines, that lie anterior and molars that lie Posterior (anatomy), posterior, and so food can be transferred from the canines to the premolars and finally to the molars for grinding, instead of directly from the canines to the molars. Human anatomy The premolars in humans are the maxillary first premolar, maxillary second premolar, mandibular first premolar, and the mandibular second premolar. Premolar teeth by definition are permanent teeth Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular Central Incisor
The mandibular central incisor is the tooth located on the jaw, adjacent to the midline of the face. It is mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular lateral incisors. As with all incisors, its function includes shearing or cutting food during mastication, commonly known as chewing. There are no cusps on the tooth. Instead, the surface area of the tooth used in eating is called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Though the two are similar, there are some minor differences between the deciduous (baby) mandibular central incisor and that of the permanent mandibular central incisor. The mandibular central incisors are usually the first teeth to appear in the mouth, typically around the age of 6–8 months. Notation In the universal system of notation, the deciduous mandibular central incisors are designated by a letter written in uppercase. The right deciduous mandibular central incisor is known as "P", and the left one is known as "O". The international nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular Lateral Incisor
The mandibular lateral incisor is the tooth located distally (away from the midline of the face) from both mandibular central incisors of the mouth and mesially (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular canines. As with all incisors, their function is for shearing or cutting food during mastication, commonly known as chewing. There are no cusps on the teeth. Instead, the surface area of the tooth used in eating is called an incisal ridge or incisal edge. Though relatively the same, there are some minor differences between the deciduous (baby) mandibular lateral incisor and that of the permanent mandibular lateral incisor. In the universal system of notation, the deciduous mandibular lateral incisors are designated by a letter written in uppercase. The right deciduous mandibular lateral incisor is known as "Q", and the left one is known as "N". The international notation has a different system of notation. Thus, the right deciduous mandibular lateral incisor k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular Canine
The mandibular canine is the tooth located distally (away from the midline of the face) from both mandibular lateral incisors of the mouth but mesially (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular first premolars. Both the maxillary and mandibular canines are called the "cornerstone" of the mouth because they are all located three teeth away from the midline, and separate the premolars from the incisors. The location of the canines reflect their dual function as they complement both the premolars and incisors during mastication, commonly known as chewing. Nonetheless, the most common action of the canines is tearing of food. The canine teeth are able to withstand the tremendous lateral pressures from chewing. There is a single cusp on canines, and they resemble the prehensile teeth found in carnivorous animals. Though relatively the same, there are some minor differences between the deciduous (baby) mandibular canine and that of the permanent mandibular canine. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular First Premolar
The mandibular first premolar is the tooth located laterally (away from the midline of the face) from both the mandibular canines of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular second premolars. The function of this premolar is similar to that of canines in regard to tearing being the principal action during mastication, commonly known as chewing. Mandibular first premolars have two cusp (dentistry), cusps. The one large and sharp is located on the buccal side (closest to the cheek) of the tooth. Since the lingual cusp (located nearer the tongue) is small and nonfunctional (which refers to a cusp not active in chewing), the mandibular first premolar resembles a small canine. There are no deciduous teeth, deciduous (baby) mandibular premolars. Instead, the teeth that precede the permanent teeth, permanent mandibular premolars are the deciduous mandibular molars. Sometimes, premolars are referred to as bicuspids. Even though the terms are synonymo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular Second Premolar
The mandibular second premolar is the tooth located distally (away from the midline of the face) from both the mandibular first premolars of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular first molars. The function of this premolar is assist the mandibular first molar during mastication, commonly known as chewing. Mandibular second premolars have three cusps. There is one large cusp on the buccal side (closest to the cheek) of the tooth. The lingual cusps (located nearer the tongue) are well developed and functional (which refers to cusps assisting during chewing). Therefore, whereas the mandibular first premolar resembles a small canine, the mandibular second premolar is more alike to the first molar. There are no deciduous (baby) mandibular premolars. Instead, the teeth that precede the permanent mandibular premolars are the deciduous mandibular molars. Anatomy: The mandibular second premolar most commonly has three cusps but can have two as w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular First Molar
The mandibular first molar or six-year molar is the tooth located distally (away from the midline of the face) from both the mandibular second premolars of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular second molars. It is located on the mandibular (lower) arch of the mouth, and generally opposes the maxillary (upper) first molars and the maxillary 2nd premolar in normal class I occlusion. The function of this molar is similar to that of all molars in regard to grinding being the principal action during mastication, commonly known as chewing. There are usually five well-developed cusps on mandibular first molars: two on the buccal (side nearest the cheek), two lingual (side nearest the tongue), and one distal. The shape of the developmental and supplementary grooves, on the occlusal surface, are described as being M-shaped. There are great differences between the deciduous (baby) mandibular molars and those of the permanent mandibular molars, even th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular Second Molar
The mandibular second molar is the tooth located distally (away from the midline of the face) from both the mandibular first molars of the mouth but mesial (toward the midline of the face) from both mandibular third molars. This is true only in permanent teeth. The function of this molar is similar to that of all molars in regard to grinding being the principal action during mastication, commonly known as chewing. Though there is more variation between individuals than that of the first mandibular molar, there are usually four cusps on mandibular second molars: two on the buccal (side nearest the cheek) and two lingual (side nearest the tongue). There are great differences between the deciduous (baby) mandibular molars and those of the permanent mandibular molars, even though their function is similar. The permanent mandibular molars are not considered to have any teeth that precede them. Despite being named molars, the deciduous molars are followed by permanent premolars. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mandibular Third Molar
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla). The jawbone is the skull's only movable, posable bone, sharing joints with the cranium's temporal bones. The mandible hosts the lower teeth (their depth delineated by the alveolar process). Many muscles attach to the bone, which also hosts nerves (some connecting to the teeth) and blood vessels. Amongst other functions, the jawbone is essential for chewing food. Owing to the Neolithic advent of agriculture (), human jaws evolved to be smaller. Although it is the strongest bone of the facial skeleton, the mandible tends to deform in old age; it is also subject to fracturing. Surgery allows for the removal of jawbone fragments (or its entirety) as well as regenerative methods. Additionally, the bone is of great forensic significance. Stru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Maxillary Central Incisor
The maxillary central incisor is a human tooth in the front upper jaw, or maxilla, and is usually the most visible of all teeth in the mouth. It is located Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, mesial (closer to the midline of the face) to the maxillary lateral incisor. As with all incisors, their function is for Shearing (physics), shearing or cutting food during mastication (chewing). There is typically a single cusp (dentistry), cusp on each tooth, called an Commonly used terms of relationship and comparison in dentistry, incisal ridge or incisal edge. Formation of these teeth begins at 14 weeks in utero for the deciduous teeth, deciduous (baby) set and 3–4 months of age for the permanent teeth, permanent set. There are some minor differences between the deciduous maxillary central incisor and that of the permanent maxillary central incisor. The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 8–12 months of age and shed at 6–7 years, and is replaced b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |