|
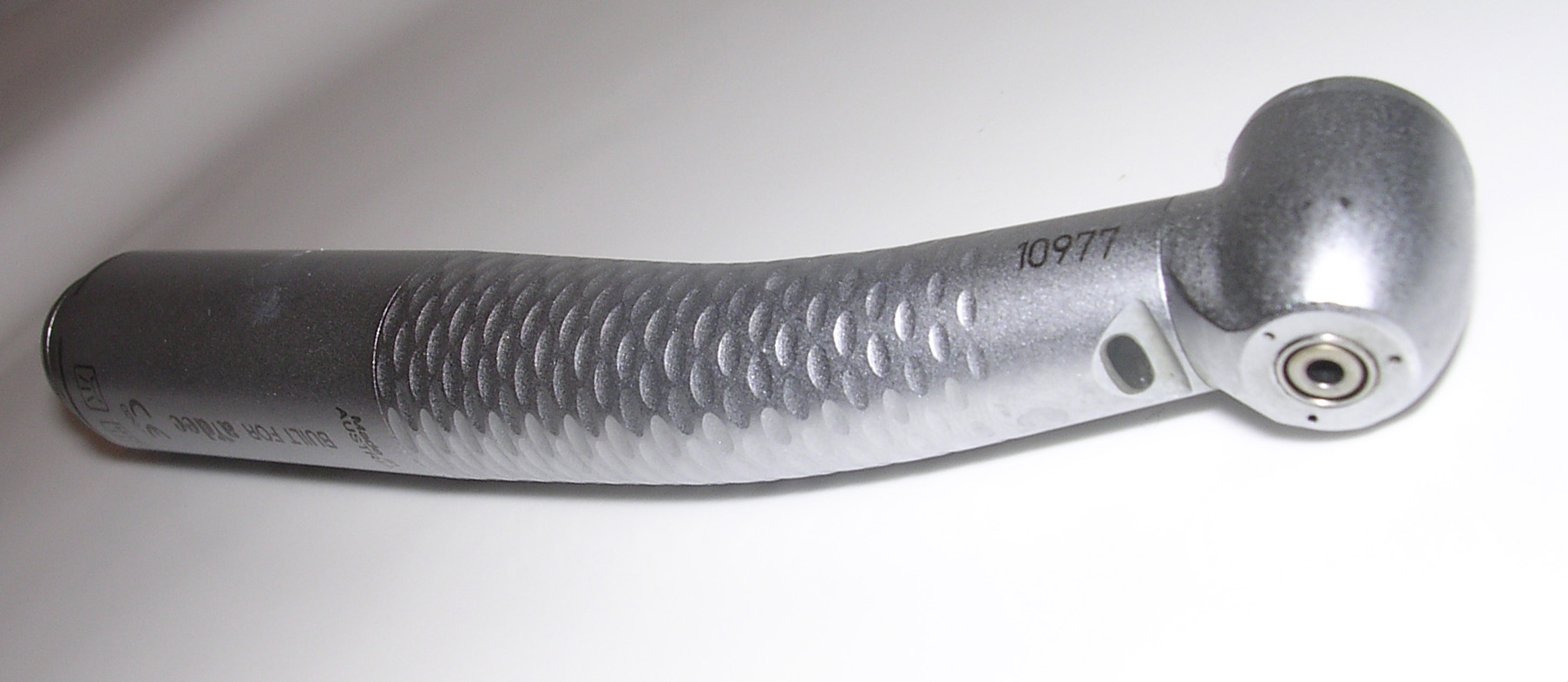
Dental Drill
A dental drill or dental handpiece is a hand-held, mechanical instrument used to perform a variety of common dentistry, dental procedures, including removing tooth decay, decay, polishing dental filling, fillings, performing cosmetic dentistry, and altering Dental prosthesis, prostheses. The handpiece itself consists of internal mechanical components that initiate a rotational force and provide power to the cutting instrument, usually a dental burr. The type of apparatus used clinically will vary depending on the required function dictated by the dental procedure. It is common for a light source and water cooling, cooling water-spray system to also be incorporated into certain handpieces; this improves visibility, accuracy, and the overall success of the procedure. The burrs are usually made of tungsten carbide or diamond. High-speed handpiece Depending on their mechanisms, handpieces are classified as air turbine or electric (including speed-increasing). However, in a clinical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pounds Per Square Inch
The pound per square inch (abbreviation: psi) or, more accurately, pound-force per square inch (symbol: lbf/in2), is a unit of measurement of pressure or of stress based on avoirdupois units and used primarily in the United States. It is the pressure resulting from a force with magnitude of one pound-force applied to an area of one square inch. In SI units, 1 psi is approximately . The pound per square inch absolute (psia) is used to make it clear that the pressure is relative to a vacuum rather than the ambient atmospheric pressure. Since atmospheric pressure at sea level is around , this will be added to any pressure reading made in air at sea level. The converse is pound per square inch gauge (psig), indicating that the pressure is relative to atmospheric pressure. For example, a bicycle tire pumped up to 65 psig in a local atmospheric pressure at sea level (14.7 psi) will have a pressure of 79.7 psia (14.7 psi + 65 psi). When gauge pressure is referenced to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Strength
Physical strength is the measure of an individual's exertion of force on physical objects. Increasing physical strength is the goal of strength training. Overview An individual's physical strength is determined by two factors: the cross-sectional area of muscle fibers recruited to generate force and the intensity of the recruitment. Individuals with a high proportion of Muscle fibre#Type I, type I slow twitch muscle fibers will be relatively weaker than a similar individual with a high proportion of Muscle fibre#Type II, type II fast twitch fibers, but would have greater endurance. The genetic inheritance of muscle fiber type sets the outermost boundaries of physical strength possible (barring the use of enhancing agents such as testosterone), although the unique position within this envelope is determined by training. Individual muscle fiber ratios can be determined through a muscle biopsy. Other considerations are the ability to recruit muscle fibers for a particular activity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rake Angle
In machining, the rake angle is a parameter used in various cutting processes, describing the angle of the cutting face relative to the workpiece. There are three types of rake angles: ''positive'', ''zero'' or ''neutral'', and ''negative''. * Positive rake: A tool has a positive rake when the face of the cutting tool slopes away from the cutting edge at inner side. * Zero rake: A tool has a zero (or neutral) rake when the face of the cutting tool is perpendicular to the cutting edge at inner side. * Negative rake: A tool has a negative rake angle when the face of the cutting tool slopes away from the cutting edge at outer side. Positive rake angles generally: * Make the tool more sharp and pointed. This reduces the strength of the tool, as the small included angle in the tip may cause it to chip away. * Reduce cutting forces and power requirements. * Helps in the formation of continuous chips in ductile materials. * Can help avoid the formation of a built-up edge. Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obtuse Angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight lines at a point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a plane formed by two rays, called the '' sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the '' vertex'' of the angle. More generally angles are also formed wherever two lines, rays or line segments come together, such as at the corners of triangles and other polygons. An angle can be considered as the region of the plane bounded by the sides. Angles can also be formed by the intersection of two planes or by two intersecting curves, in which case the rays lying tangent to each curve at the point of intersection define the angle. The term ''angle'' is also used for the size, magnitude or quantity of these types of geometric figures and in this context an angle consists of a number and unit of measurement. Angular measure or measure of angle are sometimes used to distinguish between the measurement an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle
In Euclidean geometry, an angle can refer to a number of concepts relating to the intersection of two straight Line (geometry), lines at a Point (geometry), point. Formally, an angle is a figure lying in a Euclidean plane, plane formed by two Ray (geometry), rays, called the ''Side (plane geometry), sides'' of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the ''vertex (geometry), vertex'' of the angle. More generally angles are also formed wherever two lines, rays or line segments come together, such as at the corners of triangles and other polygons. An angle can be considered as the region of the plane bounded by the sides. Angles can also be formed by the intersection of two planes or by two intersecting curves, in which case the rays lying tangent to each curve at the point of intersection define the angle. The term ''angle'' is also used for the size, magnitude (mathematics), magnitude or Physical quantity, quantity of these types of geometric figures and in this context an a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blade
A blade is the Sharpness (cutting), sharp, cutting portion of a tool, weapon, or machine, specifically designed to puncture, chop, slice, or scrape surfaces or materials. Blades are typically made from materials that are harder than those they are intended to cut. This includes early examples made from flaked stones like flint or obsidian, evolving through the ages into metal forms like copper, bronze, and iron, and culminating in modern versions made from steel or ceramics. Serving as one of humanity's oldest tools, blades continue to have wide-ranging applications, including in combat, cooking, and various other everyday and specialized tasks. Blades function by concentrating force at the cutting edge. Design variations, such as serrated edges found on bread knives and saws, serve to enhance this force concentration, adapting blades for specific functions and materials. Blades thus hold a significant place both historically and in contemporary society, reflecting an evolution i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burr (cutter)
Burrs or burs (sometimes called rotary files) are small cutting tools; not to be confused with small pieces of metal formed from cutting metal, used in die grinders, rotary tools, or dental drills. The name may be considered appropriate when their small-sized head (3 mm diameter shaft) is compared to a bur (fruit seed with hooks) or their teeth are compared to a metal burr. Description Burrs are a rotary analog to files that cut linearly (hence their alternate name, rotary files). They share many similarities with endmills and router bits, with the notable distinction that the latter typically have their toolpaths dictated by the machine, while burrs are frequently operated in a freehand manner. However, there is substantial overlap in the use and toolpath control of these various classes of cutters, and the outcomes accomplished with them. For example, endmills can be used in routers, and burrs can be used like endmills in milling by CNC or manual machine tools. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dental Rotary Instruments - Boreri
{{Disambig ...
Dental may refer to: * Dental consonant, in phonetics * Dental Records, an independent UK record label * Dentistry, oral medicine * Teeth See also * * Dental care (other) * Dentist (other) * Tooth (other) A tooth (: teeth) is a small, calcified, whitish structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates. Tooth or Teeth may also refer to: Music *Teeth (Filipino band), a Filipino rock band *Teeth (electronic band), UK electronic pop punk b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill Long
A drill is a tool used for making round holes or driving fasteners. It is fitted with a drill bit for making holes, or a screwdriver bit for securing fasteners. Historically, they were powered by hand, and later mains power, but cordless battery-powered drills are proliferating due to increased efficiency and ease of use. Drills are commonly used in woodworking, metalworking, construction, machine tool fabrication, and utility projects. Specially designed versions are made for surgery, dentistry, miniatures, and other applications. History Around 35,000 BC, ''Homo sapiens'' discovered the benefits of the application of rotary tools. This would have rudimentarily consisted of a pointed rock being spun between the hands to bore a hole through another material. This led to the hand drill, a smooth stick, that was sometimes attached to flint point, and was rubbed between the palms. This was used by many ancient civilizations around the world including the Mayans. The earlies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumatic Motor
A pneumatic motor (air motor), or compressed-air engine, is a type of motor which does mechanical work by expanding compressed air. Pneumatic motors generally convert the compressed-air energy to mechanical work through either linear or rotary motion. Linear motion can come from either a diaphragm or piston actuator, while rotary motion is supplied by either a vane type air motor, piston air motor, air turbine or gear type motor. Pneumatic motors have existed in many forms over the past two centuries, ranging in size from hand-held motors to engines of up to several hundred horsepower. Some types rely on pistons and cylinders; others on slotted rotors with vanes (vane motors) and others use turbines. Many compressed-air engines improve their performance by heating the incoming air or the engine itself. Pneumatic motors have found widespread success in the hand-held tool industry, but are also used stationary in a wide range of industrial applications. Continual attempts are b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Train
A gear train or gear set is a machine element of a mechanical system formed by mounting two or more gears on a frame such that the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next. Features of gears and gear trains include: * The gear ratio of the pitch circles of mating gears defines the speed ratio and the mechanical advantage of the gear set. * A planetary gear train provides high gear reduction in a compact package. * It is possible to design gear teeth for gears that are non-circular, yet still transmit torque smoothly. * The speed ratios of chain and belt drives are computed in the same way as gear ratios. See bicycle gearing. The transmission of rotation between contacting toothed wheels can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of Greece and the south-pointing chariot of China. Illustrations by the Renaissan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |