|
Degenerative Chain Transfer
In polymer chemistry, degenerative chain transfer (also called degenerate chain transfer) is a process that can occur in a radical polymerization whereby reactivity of active centres are changed, hence significantly influencing the molecular weight distribution of the resulting product. In chain polymerization processes it is observed that during the chemical reactions an active center (polymer science), active centre on a growing chain is transferred from a growing macromolecule - P• - or oligomer to another molecule (transfer agent XR) or to another site on the same molecule. :P• + XR → PX + R• This transfer involves termination of the initially growing chain to the completed macromolecule PX, where X denotes one end-group of the macromolecule. The example shows that the growing macromolecule as well as the transfer agent are consumed during this process. However, there are also chain transfer reactions that generate new chain carriers and new chain transfer agents at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union Of Pure And Applied Chemistry
The International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC ) is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations working for the advancement of the chemical sciences, especially by developing nomenclature and terminology. It is a member of the International Science Council (ISC). IUPAC is registered in Zürich, Switzerland, and the administrative office, known as the "IUPAC Secretariat", is in Research Triangle Park, North Carolina, United States. This administrative office is headed by IUPAC's executive director, currently Lynn Soby. IUPAC was established in 1919 as the successor of the International Congress of Applied Chemistry for the advancement of chemistry. Its members, the National Adhering Organizations, can be national chemistry societies, national academies of sciences, or other bodies representing chemists. There are fifty-four National Adhering Organizations and three Associate National Adhering Organizations. IUPAC's Inter-divisional Committee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer Chemistry
Polymer chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that focuses on the structures of chemicals, chemical synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules. The principles and methods used within polymer chemistry are also applicable through a wide range of other chemistry sub-disciplines like organic chemistry, analytical chemistry, and physical chemistry. Many materials have polymeric structures, from fully inorganic metals and ceramics to DNA and other biological molecules. However, polymer chemistry is typically related to synthetic and organic compositions. Synthetic polymers are ubiquitous in commercial materials and products in everyday use, such as plastics, and rubbers, and are major components of composite materials. Polymer chemistry can also be included in the broader fields of polymer science or even nanotechnology, both of which can be described as encompassing polymer physics and polymer engineering.Hans-Heinrich Moretto, Manfred Sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
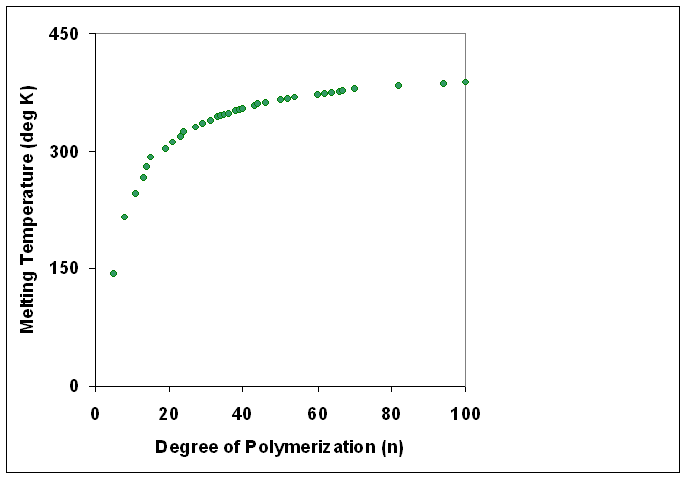
Molecular Weight Distribution
The molar mass distribution (or molecular weight distribution) describes the relationship between the number of moles of each polymer species (Ni) and the molar mass (Mi) of that species. In linear polymers, the individual polymer chains rarely have exactly the same degree of polymerization and molar mass, and there is always a distribution around an average value. The molar mass distribution of a polymer may be modified by polymer fractionation. Definitions of molar mass average Different average values can be defined, depending on the statistical method applied. In practice, four averages are used, representing the weighted mean taken with the mole fraction, the weight fraction, and two other functions which can be related to measured quantities: *''Number average molar mass'' (Mn), also loosely referred to as ''number average molecular weight'' (NAMW). *''Mass average molar mass'' (Mw), where ''w'' stands for weight; also commonly referred to as ''weight average'' or ''weigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Center (polymer Science)
An active center (sometimes called active site or kinetic-chain carrier) in polymer science Polymer science or macromolecular science is a subfield of materials science concerned with polymers, primarily synthetic polymers such as plastics and elastomers. The field of polymer science includes researchers in multiple disciplines includ ... refers to the site on a chain carrier at which reaction occurs. References Polymerization reactions {{polymer-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macromolecule
A macromolecule is a very large molecule important to biophysical processes, such as a protein or nucleic acid. It is composed of thousands of covalently bonded atoms. Many macromolecules are polymers of smaller molecules called monomers. The most common macromolecules in biochemistry are biopolymers (nucleic acids, proteins, and carbohydrates) and large non-polymeric molecules such as lipids, nanogels and macrocycles. Synthetic fibers and experimental materials such as carbon nanotubes are also examples of macromolecules. Definition The term ''macromolecule'' (''macro-'' + ''molecule'') was coined by Nobel laureate Hermann Staudinger in the 1920s, although his first relevant publication on this field only mentions ''high molecular compounds'' (in excess of 1,000 atoms). At that time the term ''polymer'', as introduced by Berzelius in 1832, had a different meaning from that of today: it simply was another form of isomerism for example with benzene and acetylene and ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligomer
In chemistry and biochemistry, an oligomer () is a molecule that consists of a few repeating units which could be derived, actually or conceptually, from smaller molecules, monomers.Quote: ''Oligomer molecule: A molecule of intermediate relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises a small plurality of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of lower relative molecular mass.'' The name is composed of Greek elements '' oligo-'', "a few" and '' -mer'', "parts". An adjective form is ''oligomeric''. The oligomer concept is contrasted to that of a polymer, which is usually understood to have a large number of units, possibly thousands or millions. However, there is no sharp distinction between these two concepts. One proposed criterion is whether the molecule's properties vary significantly with the removal of one or a few of the units. An oligomer with a specific number of units is referred to by the Greek prefix denoting that number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dispersity
In chemistry, the dispersity is a measure of the heterogeneity of sizes of molecules or particles in a mixture. A collection of objects is called uniform if the objects have the same size, shape, or mass. A sample of objects that have an inconsistent size, shape and mass distribution is called non-uniform. The objects can be in any form of chemical dispersion, such as particles in a colloid, droplets in a cloud, crystals in a rock, or polymer macromolecules in a solution or a solid polymer mass. Polymers can be described by molecular mass distribution; a population of particles can be described by size, surface area, and/or mass distribution; and thin films can be described by film thickness distribution. IUPAC has deprecated the use of the term ''polydispersity index'', having replaced it with the term ''dispersity'', represented by the symbol Đ (pronounced D-strokeStepto, R. F. T.; Gilbert, R. G.; Hess, M.; Jenkins, A. D.; Jones, R. G.; Kratochvíl P. (2009).Dispersity in P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degree Of Polymerization
The degree of polymerization, or DP, is the number of monomeric units in a macromolecule or polymer or oligomer molecule. For a homopolymer, there is only one type of monomeric unit and the ''number-average'' degree of polymerization is given by DP_n\equiv X_n=\frac, where Mn is the number-average molecular weight and M0 is the molecular weight of the monomer unit. For most industrial purposes, degrees of polymerization in the thousands or tens of thousands are desired. This number does not reflect the variation in molecule size of the polymer that typically occurs, it only represents the mean number of monomeric units. Some authors, however, define DP as the number of repeat units, where for copolymers the repeat unit may not be identical to the monomeric unit.Fried J.R. "Polymer Science and Technology" (Pearson Prentice-Hall, 2nd edn 2003), p.27 For example, in nylon-6,6, the repeat unit contains the two monomeric units —NH(CH2)6NH— and —OC(CH2)4CO—, so that a chain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
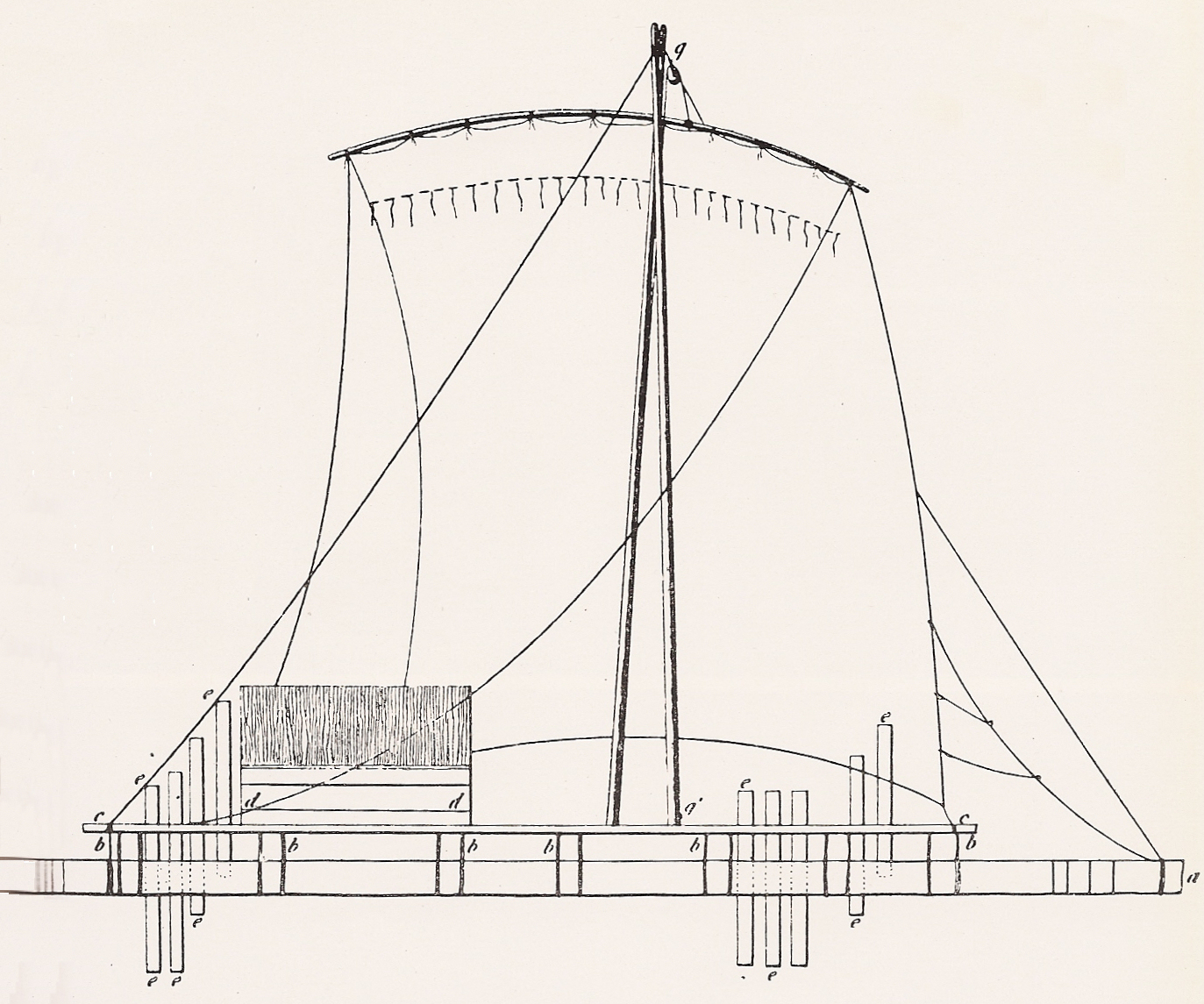
RAFT
A raft is any flat structure for support or transportation over water. It is usually of basic design, characterized by the absence of a hull. Rafts are usually kept afloat by using any combination of buoyant materials such as wood, sealed barrels, or inflated air chambers (such as pontoons), and are typically not propelled by an engine. Rafts are an ancient mode of transport; naturally-occurring rafts such as entwined vegetation and pieces of wood have been used to traverse water since the dawn of humanity. Human-made rafts Traditional or primitive rafts were constructed of wood or reeds. Modern rafts may also use pontoons, drums, or extruded polystyrene blocks. Inflatable rafts up to the 20th century used flotation chambers made of goat- or buffalo-skins, but most now use durable, multi-layered rubberized fabrics. Depending on its use and size, it may have a superstructure, masts, or rudders. Timber rafting is used by the logging industry for the transportation of logs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
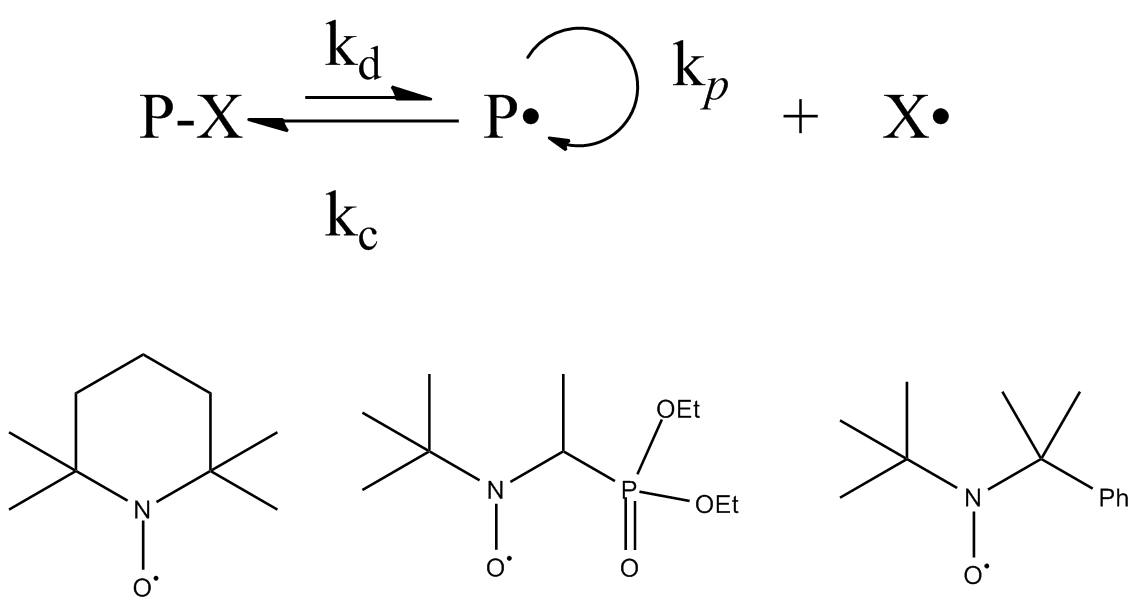
Living Free Radical Polymerization
Living free radical polymerization is a type of living polymerization where the active polymer chain end is a free radical. Several methods exist. IUPAC recommends to use the term "reversible-deactivation radical polymerization" instead of "living free radical polymerization", though the two terms are not synonymous. Reversible-deactivation polymerization There is a mode of polymerization referred to as reversible-deactivation polymerization which is distinct from living polymerization, despite some common features. Living polymerization requires a complete absence of termination reactions, whereas reversible-deactivation polymerization may contain a similar fraction of termination as conventional polymerization with the same concentration of active species. Some important aspects of these are compared in the table: Catalytic chain transfer and cobalt mediated radical polymerization Catalytic chain transfer polymerization is not a strictly living form of polymerization. Yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversible Deactivation Radical Polymerization
Reversible deactivation radical polymerizations (RDRPs) are members of the class of reversible deactivation polymerizations which exhibit much of the character of living polymerizations, but cannot be categorized as such as they are not without chain transfer or chain termination reactions. Several different names have been used in literature, which are: *Living radical polymerization *Living free radical polymerization *Controlled/"living" radical polymerization *Controlled radical polymerization *Reversible deactivation radical polymerization Though the term "living" radical polymerization was used in early days, it has been discouraged by IUPAC, because radical polymerization cannot be a truly living process due to unavoidable termination reactions between two radicals. The commonly used term controlled radical polymerization is permitted, but reversible-deactivation radical polymerization or controlled reversible-deactivation radical polymerization (RDRP) is recommended. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Living Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, living polymerization is a form of chain growth polymerization where the ability of a growing polymer chain to terminate has been removed. This can be accomplished in a variety of ways. Chain termination and chain transfer reactions are absent and the rate of chain initiation is also much larger than the rate of chain propagation. The result is that the polymer chains grow at a more constant rate than seen in traditional chain polymerization and their lengths remain very similar (i.e. they have a very low polydispersity index). Living polymerization is a popular method for synthesizing block copolymers since the polymer can be synthesized in stages, each stage containing a different monomer. Additional advantages are predetermined molar mass and control over end-groups. Living polymerization is desirable because it offers precision and control in macromolecular synthesis. This is important since many of the novel/useful properties of polymers result ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |