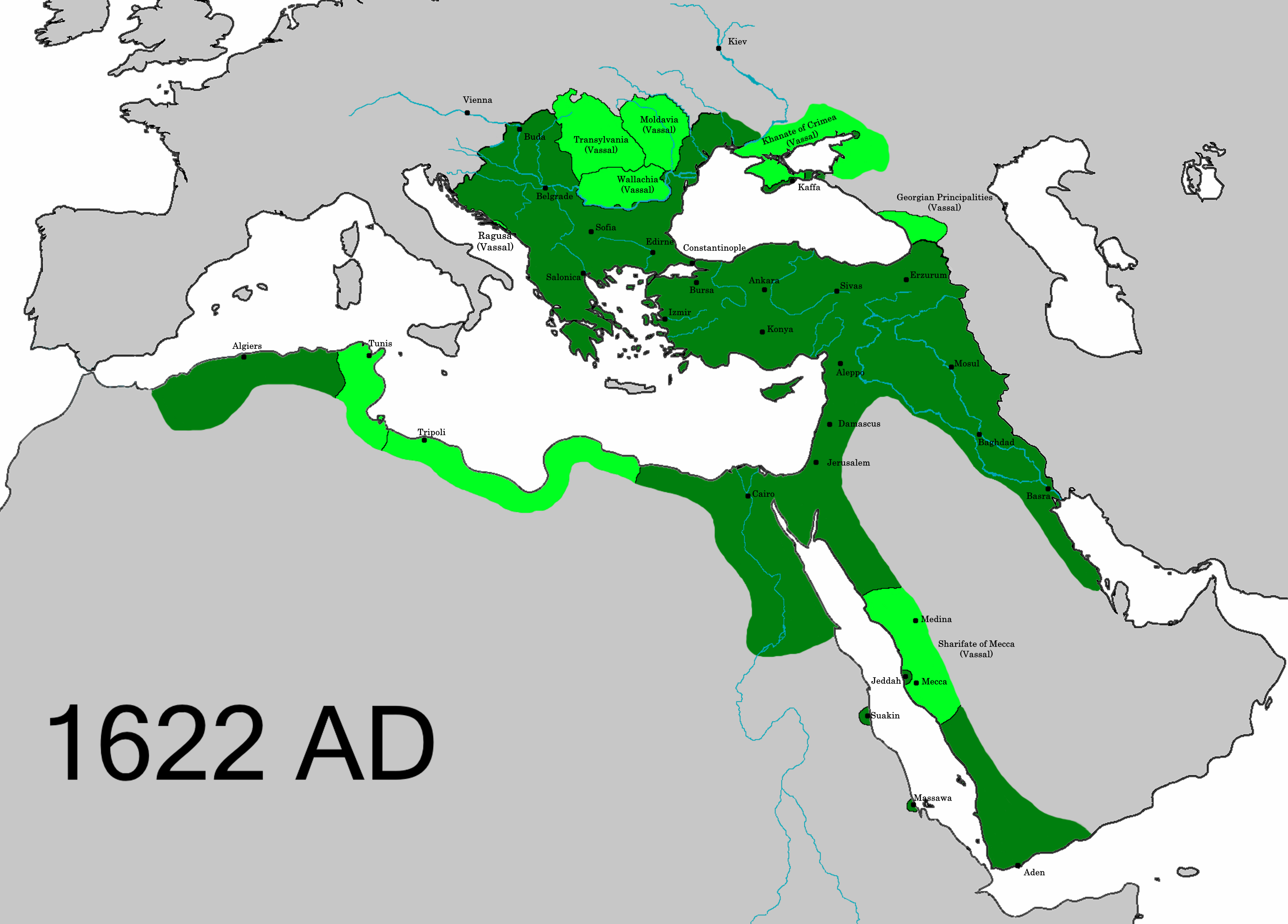
|
Defterdar
This is a list of the top officials in charge of the finances of the Ottoman Empire, called (Turkish for bookkeepers; from the Persian , + ) between the 14th and 19th centuries and ''Maliye Naziri'' ( Minister of Finance) between 19th and 20th centuries. They were originally in charge of the defters (tax registers) in the Ottoman Empire, hence the name . History of the office The exact date of the formal establishment of the office is unknown. According to some sources, the first ''defterdar'' was the ''Kadı'' (judge) of Mihaliç, Çelebi bin Mehmed, appointed in 1359 or 1360, during the reign of Murad I. During the reign of Bayezid I (1389–1402), the poet Zahiri is mentioned as the ''defterdar''. In the classical period, the finances of the Empire were organized under a single ''Defterdar'', literally the main bookkeeper, in charge of a single imperial treasury (''Hazine-i Amire''). Starting in 1793, smaller treasuries independent of the imperial treasury were organize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divan-ı Hümayun
The Imperial Council or Imperial Divan ( ota, ديوان همايون, Dîvân-ı Hümâyûn), was the ''de facto'' cabinet of the Ottoman Empire for most of its history. Initially an informal gathering of the senior ministers presided over by the Sultan in person, in the mid-15th century the Council's composition and function became firmly regulated. The Grand vizier, who became the Sultan's deputy as the head of government, assumed the role of chairing the Council, which comprised also the other viziers, charged with military and political affairs, the two ''kadi'askers'' or military judges, the ''defterdars'' in charge of finances, the ''nişancı'' in charge of the palace scribal service, and later the Kapudan Pasha, the head of the Ottoman Navy, and occasionally the ''beylerbey'' of Rumelia and the Agha of the Janissaries. The Council met in a dedicated building in the Second Courtyard of the Topkapi Palace, initially daily, then for four days a week by the 16th century. Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sofu Mehmet Pasha
Sofu Mehmed Pasha (died August 1649), also known as Mevlevi Mehmed Pasha, was an Ottoman statesman who served as grand vizier and defterdar (finance minister). Early years He was a chamberlain/deputy (''kethüda'') of a ''defterdar'' (the head of the treasury). During the reign of Murad IV in 1636, he was appointed as the defterdar and served until 1639. During his retirement, he became a member of Mevlevi Order gaining the title Mevlevi or Sofu. During the turbulent events taking place just before the dethronement of Ibrahim in 1648, the previous grand vizier Hezarpare Ahmet Pasha had been lynched by an angry mob, and the Janissary leaders forced the sultan to appoint Sofu Mehmed Pasha as the grand vizier. The sultan reluctantly agreed on 8 August 1648. Nevertheless, the sultan was dethroned five days after his appointment. Despite this dethronement, Sofu Mehmed Pasha was still afraid of the former sultan, as there was a possibility of the Janissaries re-enthroning him. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maktul Hacı Ibrahim Pasha
Ibrahim Pasha (also known as Hacı Ibrahim Pasha or Maktul Ibrahim Pasha or among his Arab subjects as Ibrahim Pasha al-Maqtul, ''Maktul'' meaning the Slain; died 24 September 1604) was an Ottoman statesman who served shortly as the governor of Egypt in 1604 before he was murdered by mutinying sepahi soldiers of the Ottoman Army. He also served as defterdar (finance minister) of the Ottoman Empire four times (1582–83, 1587–88, 1593–94, 1596). Background Ibrahim Pasha appears to have lived in Konya in his early life and been a dervish and a follower of the ascetic Muslim mystic Rumi. As such, he was sometimes known by the epithet "Sufi" by historians. He was also a kadı (judge) at some point in his life prior to becoming the four-time defterdar of the empire and governor of Egypt. Tenure as the governor of Egypt In 1604, sultan Ahmed I appointed Ibrahim Pasha as the governor of Egypt, Egypt then being the seat of the Egypt Eyalet of the Ottoman Empire. His offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman The Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳānūnī Sulṭān Süleymān) in his realm, was the tenth and longest-reigning Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1520 until his death in 1566. Under his administration, the Ottoman Empire ruled over at least 25 million people. Suleiman succeeded his father, Selim I, as sultan on 30 September 1520 and began his reign with campaigns against the Christian powers in central Europe and the Mediterranean. Belgrade fell to him in 1521 and the island of Rhodes in 1522–23. At Mohács, in August 1526, Suleiman broke the military strength of Hungary. Suleiman became a prominent monarch of 16th-century Europe, presiding over the apex of the Ottoman Empire's economic, military and political power. Suleiman personally led Ottoman armies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defter
A ''defter'' (plural: ''defterler'') was a type of tax register and land cadastre in the Ottoman Empire. Description The information collected could vary, but ''tahrir defterleri'' typically included details of villages, dwellings, household heads (adult males and widows), ethnicity/religion (because these could affect tax liabilities/exemptions), and land use. The defter-i hakâni was a land registry, also used for tax purposes. Each town had a defter and typically an officiator or someone in an administrative role to determine whether the information should be recorded. The officiator was usually some kind of learned man who had knowledge of state regulations. The defter was used to record family interactions such as marriage and inheritance. These records are useful for historians because such information allows for a more in-depth understanding of land ownership among Ottomans. This is particularly helpful when attempting to study the daily affairs of Ottoman citizens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mustafa I
Mustafa I (; ; 1600, Constantinople – 20 January 1639, Constantinople), called Mustafa the Saint (Veli Mustafa) during his second reign, and often called Mustafa the Mad (Deli Mustafa) by historians, was the son of Sultan Mehmed III and Halime Sultan. He was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 22 November 1617 to 26 February 1618, and from 20 May 1622 to 10 September 1623. Early life Mustafa was born in the Manisa Palace, as the younger half-brother of Sultan Ahmed I (1603–1617). His mother was Halime Sultan, an Abkhazian lady. Before 1603 it was customary for an Ottoman Sultan to have his brothers executed shortly after ascending the throne, (Mustafa's father Mehmed III had executed 19 of his own brothers). But when the thirteen-year-old Ahmed I was enthroned in 1603, he spared the life of Mustafa. A factor in Mustafa's survival is the influence of Kösem Sultan (Ahmed's favorite consort), who may have wished to preempt the succession of Sultan Osman II, Ah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emir Mehmed Pasha
Seyyid Emir Mehmed Pasha ( tr, Şerif/Seyyid/Emir Mehmed Paşa), known by the epithet "al-Sharif" among his Arab subjects, was an Ottoman statesman who served as defterdar (finance minister) (1589–1593, 1595), Ottoman governor of Egypt (1596–1598), and Ottoman governor of Damascus (1599–1600). He was a descendant of Hussein ibn Ali, earning him the epithet " sayyid." While he was the governor of Egypt (with the title beylerbey, often known as viceroy), he was reportedly a frequent visitor of the Al-Hussein Mosque in Cairo. In 1599, he became a vizier. See also * List of Ottoman Ministers of Finance * List of Ottoman governors of Egypt * List of Ottoman governors of Damascus This is a list of rulers of Damascus from ancient times to the present. :''General context: History of Damascus''. Aram Damascus * Rezon I (c. 950 BC) * Tabrimmon *Ben-Hadad I (c. 885 BCE–c. 865 BC) *Hadadezer (c. 865 BC–c. 842 BC) *Hazael ( ... References * Süreyya, Bey M, Nuri Akba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piri Mehmed Pasha
Piri Mehmed Pasha (1465 – 1532 Silivri) was an Ottoman Turk statesman, and grand vizier of the Ottoman Empire from 1518 to 1523.İsmail Hâmi Danişmend, Osmanlı Devlet Erkânı, Türkiye Yayınevi, İstanbul, 1971, p. 15. (Turkish) Biography Life before becoming the Grand Vizier Piri Mehmed Pasha was a grandchild of Cemaleddin Aksarayî, one of the professors of Zinciriye Madrasah in Aksaray. He was born to Sheikh Cemâl-i Halvetî, also known as the Çelebi Khalifa. His father was the sheikh of Halvetiyye in Amasya and the founder of the Cemâliyya branch of the sect.Yılmaz, Mehmed, "Mehmed Paşa (Piri)", (1999) ''Yaşamları ve Yapıtlarıyla Osmanlılar Ansiklopedisi'', İstanbul:Yapı Kredi Kültür Sanat Yayıncılık A.Ş. C.2 s.164 ISBN 975-08-0072-9 Matrilineally, he descended from Mevlana Hamazatuddin, buried in Larende (Karaman). Piri was educated in the madrasa of Amasya. He completed his studies in Istanbul. In 1491 he was employed as a clerk at the Amasya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murad IV
Murad IV ( ota, مراد رابع, ''Murād-ı Rābiʿ''; tr, IV. Murad, was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1623 to 1640, known both for restoring the authority of the state and for the brutality of his methods. Murad IV was born in Constantinople, the son of Sultan Ahmed I (r. 1603–17) and Kösem Sultan. He was brought to power by a palace conspiracy when he was just 11 years old, and he succeeded his uncle Mustafa I (r. 1617–18, 1622–23). Until he assumed absolute power on 18 May 1632, the empire was ruled by his mother, Kösem Sultan, as ''nāʾib-i salṭanat'' (regent). His reign is most notable for the Ottoman–Safavid War, of which the outcome would partition the Caucasus between the two Imperial powers for around two centuries, while it also roughly laid the foundation for the current Turkey–Iran–Iraq borders. Early life Murad IV was born on 27 July 1612 to Ahmed I (reign 16031617) and his consort and later wife Kösem Sultan, an ethnic Greek. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman II
Osman II ( ota, عثمان ثانى ''‘Osmān-i sānī''; tr, II. Osman; 3 November 1604 – 20 May 1622), also known as Osman the Young ( tr, Genç Osman), was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 26 February 1618 until his regicide on 20 May 1622. Early life Osman II was born at Topkapı Palace, Constantinople, the son of Sultan Ahmed I (1603–17) and one of his consorts Mahfiruz Hatun. According to later traditions, at a young age, his mother had paid a great deal of attention to Osman's education, as a result of which Osman II became a known poet and was believed to have mastered many languages, including Arabic, Persian, Greek, Latin, and Italian; although this has since been refuted. Osman was born eleven months after his father Ahmed's transition to the throne. He was trained in the palace. According to foreign observers, he was one of the most cultured of Ottoman princes. Osman's failure to capture the throne at the death of his father Ahmed might have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahmed I
Ahmed I ( ota, احمد اول '; tr, I. Ahmed; 18 April 1590 – 22 November 1617) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1603 until his death in 1617. Ahmed's reign is noteworthy for marking the first breach in the Ottoman tradition of royal fratricide; henceforth Ottoman rulers would no longer systematically execute their brothers upon accession to the throne. He is also well known for his construction of the Blue Mosque, one of the most famous mosques in Turkey. Early life Ahmed was probably born in 18 April 1590 at the Manisa Palace, Manisa, when his father Şehzade Mehmed was still a prince and the governor of the Sanjak of Manisa. His mother was Handan Sultan. After his grandfather Murad III's death in 1595, his father came to Constantinople and ascended the throne as Sultan Mehmed III. Mehmed ordered the execution of his nineteen half brothers. Ahmed's elder brother Şehzade Mahmud was also executed by his father Mehmed on 7 June 1603, just before Mehmed's own death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed III
Mehmed III (, ''Meḥmed-i sālis''; tr, III. Mehmed; 26 May 1566 – 22 December 1603) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1595 until his death in 1603. Mehmed was known for ordering the execution of his brothers and leading the army in the Long Turkish war, during which the Ottoman army was victorious at the decisive Battle of Keresztes. This victory was however undermined by some military losses such as in Gyor and Nikopol. He also ordered the successful quelling of the Jeleli rebellions. The sultan also communicated with the court of Elizabeth I on the grounds of stronger commercial relations and in the hopes of England to ally with the Ottomans against the Spanish. Early life Mehmed was born at the Manisa Palace in 1566, during the reign of his great-grandfather, Suleiman the Magnificent. He was the son of Murad III, himself the son of Selim II, who was the son of Sultan Suleiman and Hurrem Sultan. His mother was Safiye Sultan, an Albanian from the Dukagjin hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |