 |
Deep Scattering Layer
The deep scattering layer, sometimes referred to as the sound scattering layer, is a layer in the ocean consisting of a variety of marine animals. It was discovered through the use of sonar, as ships found a layer that scattered the sound and was thus sometimes mistaken for the seabed. For this reason it is sometimes called the false bottom or phantom bottom. It can be seen to rise and fall each day in keeping with diel vertical migration. Sonar operators, using the newly developed sonar technology during World War II, were puzzled by what appeared to be a false sea floor 300–500 metres (980–1,640 ft) deep at day, and less deep at night. Initially, this mysterious phenomenon was called the ECR layer using the initials of its three discoverers. It turned out to be due to millions of marine organisms, most particularly small mesopelagic fish, with swim bladders that reflected the sonar. These organisms migrate up into shallower water at dusk to feed on plankton. The laye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Static Image Of Sonar Data Scan
Static may refer to: Places *Static Nunatak, in Antarctica *Static, Kentucky and Tennessee, U.S. *Static Peak, a mountain in Wyoming, U.S. **Static Peak Divide, a mountain pass near the peak Science and technology Physics *Static electricity, a net charge of an object **Triboelectric effect, due to frictional contact between different materials *Static spacetime, a spacetime having a global, non-vanishing, timelike Killing vector field which is irrotational *Statics, a branch of physics concerned with physical systems in equilibrium **Hydrostatics, the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at rest Engineering *Static pressure, in aircraft instrumentation and fluid dynamics **Static port, a proprietary sensor used on aircraft to measure static pressure *White noise or static noise, a random signal with a flat power spectral density **Radio noise, in radio reception **Noise (video), the random black-and-white image produced by televisions attempting to display a weak or inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Squid
A squid (: squid) is a mollusc with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight cephalopod limb, arms, and two tentacles in the orders Myopsida, Oegopsida, and Bathyteuthida (though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called ''squid'' despite not strictly fitting these criteria). Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, Symmetry (biology)#Bilateral symmetry, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle (mollusc), mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar Ecological niche, role to teleost fish as open-water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open-water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Sonar Data Scan Of The Water Column
Sonar (sound navigation and ranging or sonic navigation and ranging) is a technique that uses sound propagation (usually underwater, as in submarine navigation) to navigate, measure distances (ranging), communicate with or detect objects on or under the surface of the water, such as other vessels. "Sonar" can refer to one of two types of technology: ''passive'' sonar means listening for the sound made by vessels; ''active'' sonar means emitting pulses of sounds and listening for echoes. Sonar may be used as a means of acoustic location and of measurement of the echo characteristics of "targets" in the water. Acoustic location in air was used before the introduction of radar. Sonar may also be used for robot navigation, and sodar (an upward-looking in-air sonar) is used for atmospheric investigations. The term ''sonar'' is also used for the equipment used to generate and receive the sound. The acoustic frequencies used in sonar systems vary from very low (infrasonic) to extreme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
YouTube
YouTube is an American social media and online video sharing platform owned by Google. YouTube was founded on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim who were three former employees of PayPal. Headquartered in San Bruno, California, it is the second-most-visited website in the world, after Google Search. In January 2024, YouTube had more than 2.7billion monthly active users, who collectively watched more than one billion hours of videos every day. , videos were being uploaded to the platform at a rate of more than 500 hours of content per minute, and , there were approximately 14.8billion videos in total. On November 13, 2006, YouTube was purchased by Google for $1.65 billion (equivalent to $ billion in ). Google expanded YouTube's business model of generating revenue from advertisements alone, to offering paid content such as movies and exclusive content produced by and for YouTube. It also offers YouTube Premium, a paid subs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1,000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton in the United States to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United States customary units) and the long ton ( British imperial units). It is equivalent to approximately 2,204.6 pounds, 1.102 short tons, and 0.984 long tons. The official SI unit is the megagram (Mg), a less common way to express the same amount. Symbol and abbreviations The BIPM symbol for the tonne is t, adopted at the same time as the unit in 1879.Table 6 . BIPM. Retrieved on 2011-07-10. Its use is also official for the metric ton in the United States, having been adopted by the United States |
|
 |
Ecology
Ecology () is the natural science of the relationships among living organisms and their Natural environment, environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community (ecology), community, ecosystem, and biosphere levels. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and is the study of abundance (ecology), abundance, biomass (ecology), biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment. It encompasses life processes, interactions, and adaptations; movement of materials and energy through living communities; ecological succession, successional development of ecosystems; cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species; and patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes. Ecology has practical applications in fields such as conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Biomass (ecology)
Biomass is the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. Biomass can refer to ''species biomass'', which is the mass of one or more species, or to ''community biomass'', which is the mass of all species in the community. It can include microorganisms, plants or animals. The mass can be expressed as the average mass per unit area, or as the total mass in the community. How biomass is measured depends on why it is being measured. Sometimes, the biomass is regarded as the natural mass of organisms ''in situ'', just as they are. For example, in a salmon fishery, the salmon biomass might be regarded as the total wet weight the salmon would have if they were taken out of the water. In other contexts, biomass can be measured in terms of the dried organic mass, so perhaps only 30% of the actual weight might count, the rest being water. For other purposes, only biological tissues count, and teeth, bones and shells are excluded. In some application ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Lanternfish
Lanternfish (or myctophids, from the Greek language, Greek μυκτήρ ''myktḗr'', "nose" and ''ophis'', "serpent") are small mesopelagic fish of the large family (biology), family Myctophidae. One of two families in the order Myctophiformes, the Myctophidae are represented by 246 species in 33 genus, genera, and are found in oceans worldwide. Lanternfishes are aptly named after their conspicuous use of bioluminescence. Their sister family, the Neoscopelidae, are much fewer in number but superficially very similar; at least one neoscopelid shares the common name "lanternfish": the large-scaled lantern fish, ''Neoscopelus macrolepidotus''. Lanternfish are among the most widely distributed, diverse and populous vertebrates, with some estimates suggesting that they may have a total global Biomass (ecology), biomass of 1.8 to 16 gigatonnes, accounting for up to 65% of all deep-sea fish biomass. Commercial fisheries for them exist off South Africa, in the Antarctica, sub-Antarctic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
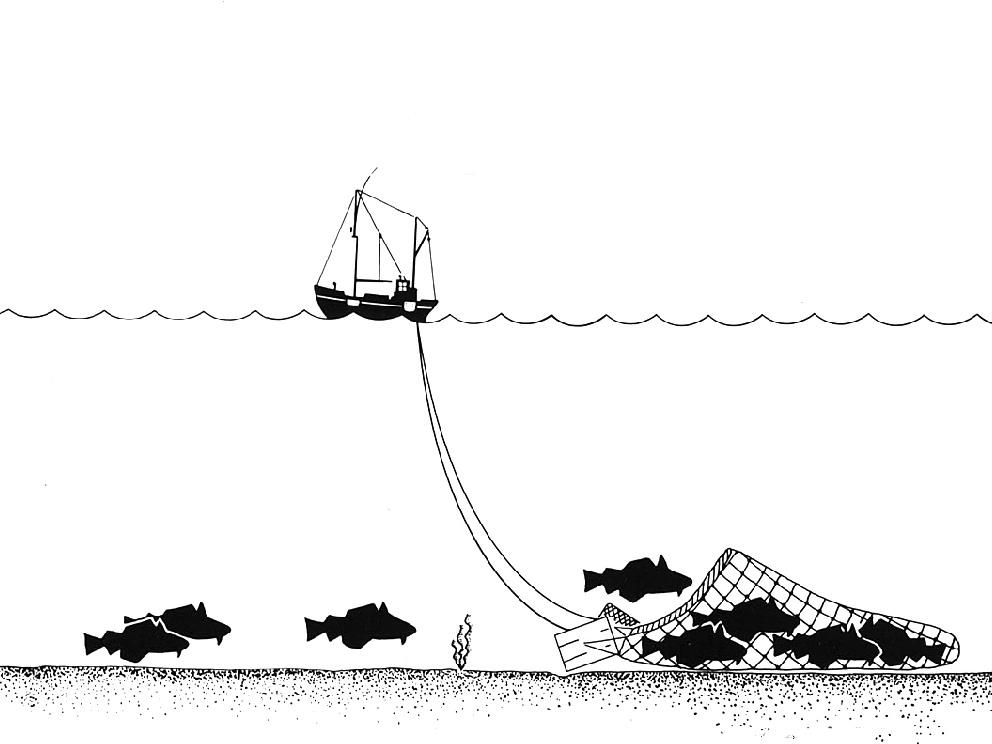 |
Trawling
Trawling is an industrial method of fishing that involves pulling a fishing net through the water behind one or more boats. The net used for trawling is called a trawl. This principle requires netting bags which are towed through water to catch different species of fishes or sometimes targeted species. Trawls are often called towed gear or dragged gear. The boats that are used for trawling are called trawlers or draggers. Trawlers vary in size from small open boats with as little as 30 hp (22 kW) engines to large factory trawlers with over 10,000 hp (7.5 MW). Trawling can be carried out by one trawler or by two trawlers fishing cooperatively (pair trawling). Trawling can be contrasted with trolling. While trawling involves a net and is typically done for commercial usage, trolling instead involves a reel, rod and a bait or a lure and is typically done for recreational purposes. Trawling is also commonly used as a scientific sampling, or survey, method. Bottom vs. mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Thermocline
A thermocline (also known as the thermal layer or the metalimnion in lakes) is a distinct layer based on temperature within a large body of fluid (e.g. water, as in an ocean or lake; or air, e.g. an atmosphere) with a high gradient of distinct temperature differences associated with depth. In the ocean, the thermocline divides the upper mixed layer from the calm deep water below. Depending largely on season, latitude, and turbulent mixing by wind, thermoclines may be a semi-permanent feature of the body of water in which they occur, or they may form temporarily in response to phenomena such as the radiative heating/cooling of surface water during the day/night. Factors that affect the depth and thickness of a thermocline include seasonal weather variations, latitude, and local environmental conditions, such as tides and currents. Oceans Most of the heat energy of the sunlight that strikes the Earth is absorbed in the first few centimeters at the ocean's surface, which hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Swimbladder
The swim bladder, gas bladder, fish maw, or air bladder is an internal gas-filled organ in bony fish that functions to modulate buoyancy, and thus allowing the fish to stay at desired water depth without having to maintain lift via swimming, which expends more energy. Also, the dorsal position of the swim bladder means that the expansion of the bladder moves the center of mass downwards, allowing it to act as a stabilizing apparatus. Additionally, the swim bladder functions as a resonating chamber to produce or receive sound. The swim bladder is evolutionarily homologous to the lungs of tetrapods and lungfish, and some ray-finned fish such as bowfins have also evolved similar respiratory functions in their swim bladders. Charles Darwin remarked upon this in ''On the Origin of Species'', and reasoned that the lung in air-breathing vertebrates had derived from a more primitive swim bladder as a specialized form of enteral respiration. Some species, such as mostly bottom dwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |