|
Debtors
A debtor or debitor is a legal entity (legal person) that owes a debt to another entity. The entity may be an individual, a firm, a government, a company or other legal person. The counterparty is called a creditor. When the counterpart of this debt arrangement is a bank, the debtor is more often referred to as a borrower. If X borrowed money from their bank, X is the debtor and the bank is the creditor. If X puts money in the bank, X is the creditor and the bank is the debtor. It is not a crime to fail to pay a debt. Except in certain bankruptcy situations, debtors can choose to pay debts in any priority they choose. But if one fails to pay a debt, they have broken a contract or agreement between them and a creditor. Generally, most oral and written agreements for the repayment of consumer debt – debts for personal, family or household purposes secured primarily by a person's residence – are enforceable. For the most part, debts that are business-related must be made in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debtor's Prison
A debtors' prison is a prison for Natural person, people who are unable to pay debt. Until the mid-19th century, debtors' prisons (usually similar in form to locked workhouses) were a common way to deal with unpaid debt in Western Europe.Cory, Lucinda"A Historical Perspective on Bankruptcy" , ''On the Docket'', Volume 2, Issue 2, U.S. Bankruptcy Court, District of Rhode Island, April/May/June 2000, retrieved December 20, 2007. Destitute people who were unable to pay a court-ordered judgment would be incarcerated in these prisons until they had worked off their debt via labour or secured outside funds to pay the balance. The product of their labour went towards both the costs of their incarceration and their accrued debt. Increasing access and lenience throughout the history of bankruptcy law have made prison terms for unaggravated indigence obsolete over most of the world. Since the late 20th century, the term ''debtors' prison'' has also sometimes been applied by critics to crim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bankruptcy
Bankruptcy is a legal process through which people or other entities who cannot repay debts to creditors may seek relief from some or all of their debts. In most jurisdictions, bankruptcy is imposed by a court order, often initiated by the debtor. Bankrupt is not the only legal status that an insolvent person may have, meaning the term ''bankruptcy'' is not a synonym for insolvency. Etymology The word ''bankruptcy'' is derived from Italian language, Italian , literally meaning . The term is often described as having originated in Renaissance Italy, where there allegedly existed the tradition of smashing a banker's bench if he defaulted on payment. However, the existence of such a ritual is doubted. History In Ancient Greece, bankruptcy did not exist. If a man owed and he could not pay, he and his wife, children or servants were forced into "debt slavery" until the creditor recouped losses through their Manual labour, physical labour. Many city-states in ancient Greece lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord's Prayer
The Lord's Prayer, also known by its incipit Our Father (, ), is a central Christian prayer attributed to Jesus. It contains petitions to God focused on God’s holiness, will, and kingdom, as well as human needs, with variations across manuscripts and Christian traditions. Two versions of this prayer are recorded in the gospels: a longer form within the Sermon on the Mount in the Gospel of Matthew, and a shorter form in the Gospel of Luke when "one of his disciples said to him, 'Lord, teach us to pray, as John taught his disciples. Scholars generally agree that the differences between the Matthaean and Lucan versions of the Lord’s Prayer reflect independent developments from a common source. The first-century text '' Didache'' (at chapter VIII) reports a version closely resembling that of Matthew and the modern prayer. It ends with the Minor Doxology. Theologians broadly view the Lord’s Prayer as a model that aligns the soul with God’s will, emphasizing praise, tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loan Shark
A loan shark is a person who offers loans at Usury, extremely high or illegal interest rates, has strict terms of debt collection, collection, and generally operates criminal, outside the law, often using the threat of violence or other illegal, aggressive, and Extortion, extortionate actions when seeking to enforce the satisfaction of the debt. As a consistent or repeated illegal business operation or "racketeering, racket", loansharking is generally associated with organized crime and certain criminal organizations. Description Because loan sharks operate mostly illegally, they cannot use the legal system to collect such debts, thus they often resort to enforcing repayment by terms of blackmail and threats of violence. Historically, many moneylenders skirted between legal and Crime, criminal activity. In the recent western world, loan sharks have been a prominent feature of the organized crime, criminal underworld. Loan sharking is not to be confused with predatory lending wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Student Loan Debt
Student debt refers to the debt incurred by an individual to pay for education-related expenses. This debt is most commonly assumed to pay for tertiary education, such as university. The amount loaned or the loan agreement is often referred to as a student loan''.'' In many countries, student loans work differently compared to mortgages with differing laws governing renegotiation and bankruptcy. As with most other types of debt, student debt may be considered defaulted after a given period of no response to requests by the school or the lender for information, payment, or negotiation. Afterward, the debt is turned over to a student loan guarantor or a collection agency. Canada , Canada is ranked third in the world (behind Russia and South Korea) for the percentage of people ages 25–34 who have completed tertiary education. As of September 2012, the average debt for a Canadian post-university student was 28,000 Canadian dollars, with this accumulated debt taking an average of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Administration Of Justice Act 1970
The Administration of Justice Act 1970 (c. 31) is a UK act of Parliament. Section 11 reforms the Debtors Act 1869 by further restricting the circumstances in which debtors may be sent to prison. Section 40 includes a number of provisions forbidding creditors such as debt collection agencies from harassing debtors, including: * Excessive demands for payment * Falsely claiming that criminal proceedings will follow after failing to pay a debt * Falsely pretending to be officially authorised to collect payment * Producing false documents claiming to have some official status that they do not have Section 36 was enacted to return the law to the position which it was generally thought to be, and applied by the courts since the mid-1930s,Loveland, I. (2014). Peaceable entry to mortgaged premises: considering the doctrine’s compatibility with Art 8 HRA. Conveyancer and Property Lawyer, 2014(5), pp. 381-397. before the landmark bar to adjournments applied by the courts since 1962 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Promissory Note
A promissory note, sometimes referred to as a note payable, is a legal instrument (more particularly, a financing instrument and a debt instrument), in which one party (the ''maker'' or ''issuer'') promises in writing to pay a determinate sum of money to the other (the ''payee''), subject to any terms and conditions specified within the document. Overview The terms of a note typically include the :wikt:principal, principal amount, the interest rate if any, the parties, the date, the terms of repayment (which could include interest) and the maturity date. Sometimes, provisions are included concerning the payee's rights in the event of a default (finance), default, which may include foreclosure of the maker's assets. In foreclosures and contract breaches, promissory notes under CPLR 5001 allow creditors to recover prejudgement interest from the date interest is due until liability is established. For loans between individuals, writing and signing a promissory note are often instrum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Individual Voluntary Arrangement
An individual voluntary arrangement (IVA) is a formal alternative in England and Wales for individuals wishing to avoid bankruptcy in England and Wales, bankruptcy. In Scotland, the equivalent statutory debt solution is known as a protected trust deed. The IVA was established by and is governed by Part VIII of the Insolvency Act 1986. It constitutes a formal repayment proposal presented to a debtor's creditors via an insolvency practitioner. Usually but not necessarily, the IVA comprises only the claims of unsecured creditors and leaves the rights of secured creditors largely unchanged. Insolvency practitioners charge initial and ongoing fees that are in addition to the debt. An IVA is a composition with creditors, contractual arrangement with creditors and can be as flexible as an individual's own circumstances. It can therefore be based on capital, income, third-party payments or a combination of those. In this process, a debtor who has enough money left over after priori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
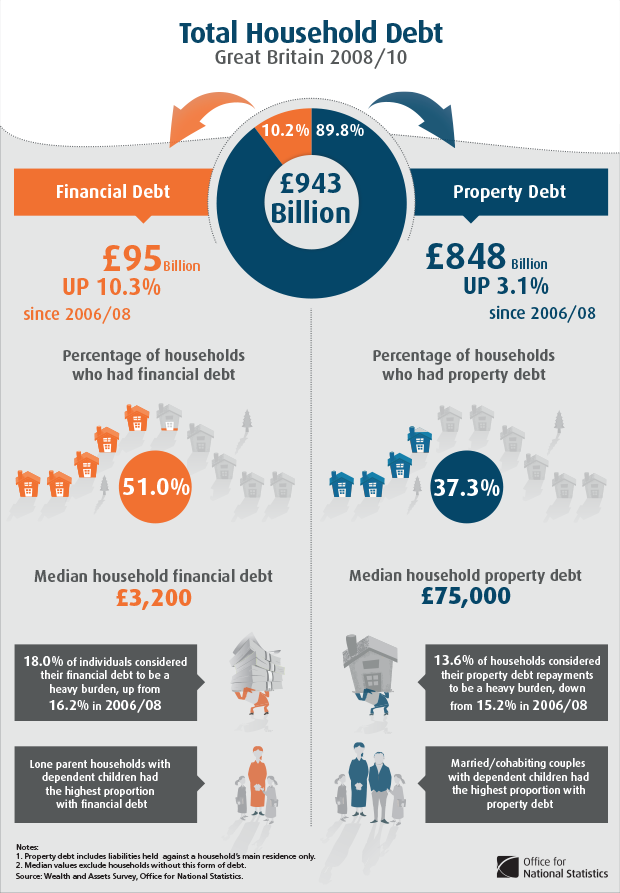
Household Debt
Household debt is the combined debt of all people in a household, including consumer debt and mortgage loans. A significant rise in the level of this debt coincides historically with many severe economic crises and was a cause of the U.S. and subsequent euro area crisis. Several economists have argued that lowering this debt is essential to economic recovery in the U.S. and selected Eurozone countries. Overview Household debt can be defined in several ways, based on what types of debt are included. Common debt types include home mortgages, home equity loans, auto loans, student loans, and credit cards. Household debt can also be measured across an economy, to measure how indebted households are relative to various measures of income (e.g., pre-tax and disposable income) or relative to the size of the economy (GDP). The burden of debt can also be measured in terms of the amount of interest it generates relative to the income of the borrower. For example, the U.S. Federal Reser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortgage Loan
A mortgage loan or simply mortgage (), in civil law (legal system), civil law jurisdictions known also as a hypothec loan, is a loan used either by purchasers of real property to raise funds to buy real estate, or by existing property owners to raise funds for any purpose while putting a lien on the property being mortgaged. The loan is "collateral (finance), secured" on the borrower's property through a process known as mortgage origination. This means that a Mortgage law, legal mechanism is put into place which allows the lender to take possession and sell the secured property ("foreclosure" or "repossession") to pay off the loan in the event the borrower defaults on the loan or otherwise fails to abide by its terms. The word ''mortgage'' is derived from a Law French term used in Legal professions in England and Wales, Britain in the Middle Ages meaning "death pledge" and refers to the pledge ending (dying) when either the obligation is fulfilled or the property is taken throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insolvency
In accounting, insolvency is the state of being unable to pay the debts, by a person or company ( debtor), at maturity; those in a state of insolvency are said to be ''insolvent''. There are two forms: cash-flow insolvency and balance-sheet insolvency. Cash-flow insolvency is when a person or company has enough assets to pay what is owed, but does not have the appropriate form of payment. For example, a person may own a large house and a valuable car, but not have enough liquid assets to pay a debt when it falls due. Cash-flow insolvency can usually be resolved by negotiation. For example, the bill collector may wait until the car is sold and the debtor agrees to pay a penalty. Balance-sheet insolvency is when a person or company does not have enough assets to pay all of their debts. The person or company might enter bankruptcy, but not necessarily. Once a loss is accepted by all parties, negotiation is often able to resolve the situation without bankruptcy. A company ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |