|
Deaf-blind
Deafblindness is the condition of little or no useful hearing (sense), hearing and little or no useful visual perception, sight. Different degrees of Visual impairment, vision loss and Deaf, auditory loss occur within each individual. Because of this inherent diversity, each deafblind individual's needs regarding lifestyle, communication, education, and work need to be addressed based on their degree of dual-modality deprivation, to improve their ability to live independently. In 1994, an estimated 35,000–40,000 United States residents were medically deafblind. Laura Bridgman was the first American deafblind person known to become well educated. Helen Keller was a well-known example of an educated deafblind individual. To further her lifelong mission to help the deafblind community to expand its horizons and gain opportunities, the Helen Keller National Center for Deaf-Blind Youths and Adults (also called the Helen Keller National Center or HKNC), with a residential training progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Keller National Center For Deaf-Blind Youths And Adults
The Helen Keller National Center for Deaf-Blind Youths and Adults (also known as the Helen Keller National Center or HKNC) is a foundation in the United States that provides services for individuals who, like Helen Keller, are both blind and deaf. Authorized by an Act of Congress in 1967, the Center provides nationwide services for people who are Deafblindness, deaf-blind according to the definition of deaf-blindness in the Helen Keller Act. It operates a residential rehabilitation and training facility at its headquarters in Sands Point, New York, which opened in 1976, and a system of ten regional field offices, also supporting families and professional carers. In 2010 the Center served 72 adult training clients and specialized short term training for 26 clients; in addition the regional programs served 1,478 consumers, 441 families, and 881 organizations. The organization provides independent living skills training, referral, employment training, counseling, and transition assi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
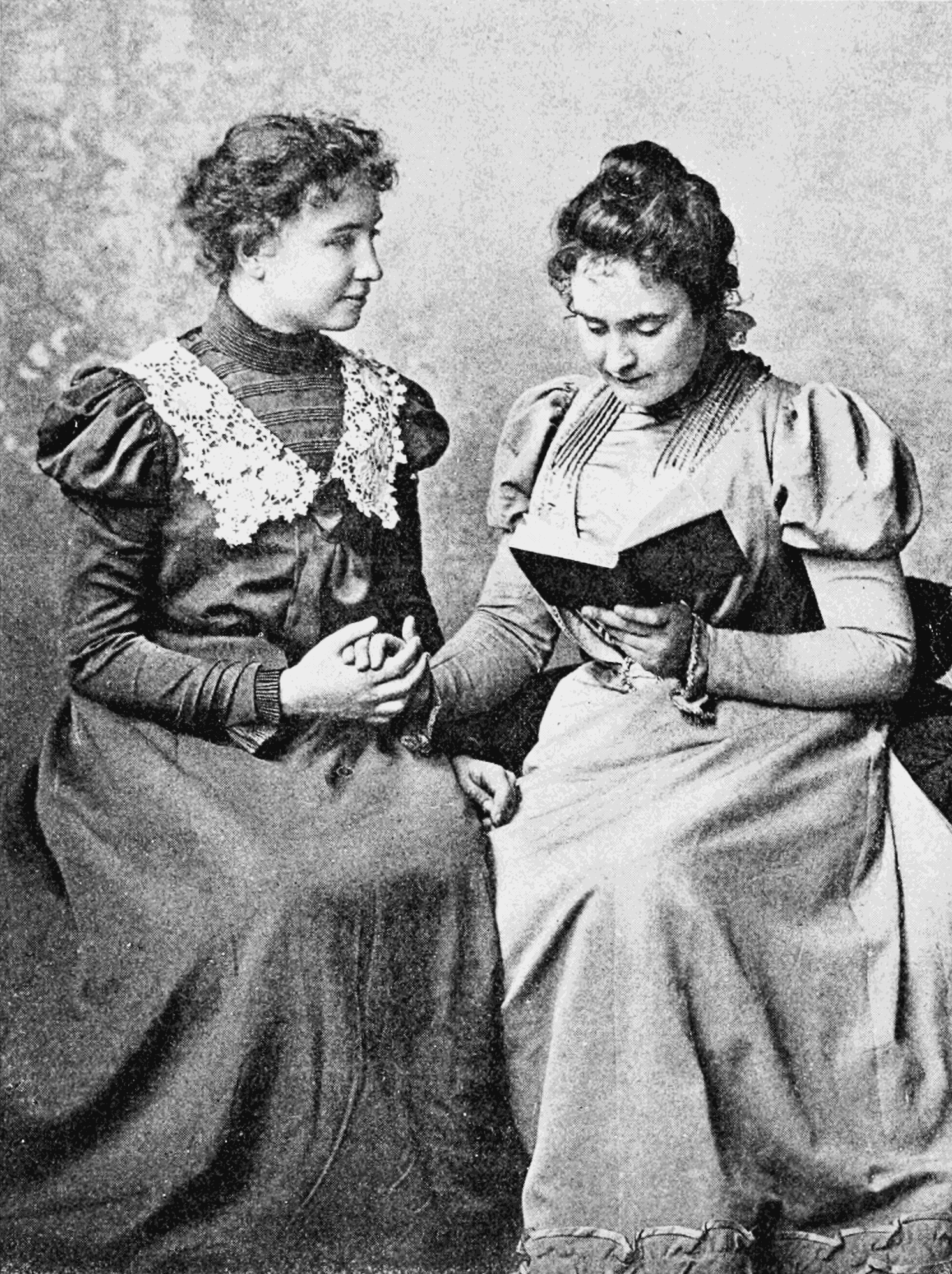
Laura Bridgman
Laura Dewey Lynn Bridgman (December 21, 1829 – May 24, 1889) was the first deaf-blind American child to gain a significant education in the English language, forty-five years before the more famous Helen Keller; Bridgman’s friend Anne Sullivan became Helen Keller's aide. Bridgman was left deaf-blind at the age of two after contracting scarlet fever. She was educated at the Perkins Institution for the Blind where, under the direction of Samuel Gridley Howe, she learned to read and communicate using Braille and the manual alphabet developed by Charles-Michel de l'Épée. For several years, Bridgman gained celebrity status when Charles Dickens met her during his 1842 American tour and wrote about her accomplishments in his ''American Notes''. Her fame was short-lived, however, and she spent the remainder of her life in relative obscurity, most of it at the Perkins Institute, where she passed her time sewing and reading books in Braille. Early years Bridgman was born in Hanover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Keller
Helen Adams Keller (June 27, 1880 – June 1, 1968) was an American author, disability rights advocate, political activist and lecturer. Born in West Tuscumbia, Alabama, she lost her sight and her hearing after a bout of illness when she was 19 months old. She then communicated primarily using home signs until the age of seven, when she met her first teacher and life-long companion Anne Sullivan. Sullivan taught Keller language, including reading and writing. After an education at both specialist and mainstream schools, Keller attended Radcliffe College of Harvard University and became the first deafblind person in the United States to earn a Bachelor of Arts degree. Keller was also a prolific author, writing 14 books and hundreds of speeches and essays on topics ranging from animals to Mahatma Gandhi. Keller campaigned for those with disabilities and for women's suffrage, labor rights, and world peace. In 1909, she joined the Socialist Party of America (SPA). She w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Usher Syndrome
Usher syndrome, also known as Hallgren syndrome, Usher–Hallgren syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa–dysacusis syndrome or dystrophia retinae dysacusis syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder caused by a mutation in any one of at least 11 genes resulting in a combination of hearing loss and visual impairment. It is the most common cause of deafblindness and is at present incurable. Usher syndrome is classed into three subtypes (I, II, and III) according to the genes responsible and the onset of deafness. All three subtypes are caused by mutations in genes involved in the function of the inner ear and retina. These mutations are inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The occurrence of Usher syndrome varies across the world and across the different syndrome types, with rates as high as 1 in 12,500 in Germany to as low as 1 in 28,000 in Norway. Type I is most common in Ashkenazi Jewish and Acadian populations, and type III is rarely found outside Ashkenazi Jewish and Finnish popu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
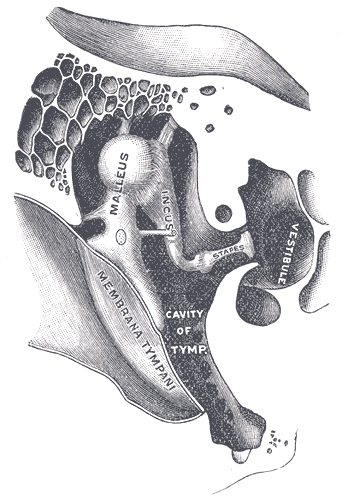
Hearing (sense)
Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science. Sound may be heard through solid Solid is a state of matter where molecules are closely packed and can not slide past each other. Solids resist compression, expansion, or external forces that would alter its shape, with the degree to which they are resisted dependent upon the ..., liquid, or gaseous matter. It is one of the traditional five senses. Partial or total inability to hear is called hearing loss. In humans and other vertebrates, hearing is performed primarily by the auditory system: mechanical waves, known as vibrations, are detected by the ear and transduction (physiology), transduced into nerve impulses that are perceived by the brain (primarily in the temporal lobe). Like touch, audition requires sensitivity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stickler Syndrome
Stickler syndrome (hereditary progressive arthro-ophthalmodystrophy) is a group of rare genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen. Stickler syndrome is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI. Stickler syndrome is characterized by distinctive facial abnormalities, ocular problems, hearing loss, and joint and skeletal problems. It was first studied and characterized by Gunnar B. Stickler in 1965. Signs and symptoms Individuals with Stickler syndrome experience a range of signs and symptoms. Some people have no signs and symptoms; others have some or all of the features described below. In addition, each feature of this syndrome may vary from subtle to severe. A characteristic feature of Stickler syndrome is a somewhat flattened facial appearance. This is caused by underdeveloped bones in the middle of the face, including the cheekbones and the bridge of the nose. A particular group of physical features, called the Pierre Robin sequence, is common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochleosaccular Degeneration With Progressive Cataracts
Cochleosaccular degeneration with progressive cataracts, also known as autosomal dominant progressive sensorineural hearing loss and cataracts is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the adult-onset combination of cochleosaccular degeneration and progressive cataract which is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait for generations in entire families, essentially resulting in familial deafblindness. Additional features include unstable gait. Only 15 cases from 2 multi-generational families in the United States and Italy (respectively) have been described in medical literature. Cases *1982: J B Nadol Jr. ''et al.'' describes 7 members from 5 sibships belonging to a four-generation American family. The proband was a 65-year-old man who had died as a result of a motorcycle accident. He had a cataract already present in his right eye since birth (a clinical finding known as congenital cataract Congenital cataracts are a lens opacity that is present at birth. Congenital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marshall Syndrome
Marshall syndrome is a genetic disorder of the connective tissue that can cause hearing loss. The three most common areas to be affected are the eyes, which are uncommonly large, joints and the mouth and facial structures. Marshall syndrome and Stickler syndrome closely resemble each other; in fact they are so similar, some say they are the same. The condition is named for D. Weber. Presentation Eyes Myopia is the most common eye problem in Marshall syndrome. Cataracts also occur more frequently and detached retina less frequently than in Stickler syndrome. Myopia also is the most common problem with the eyes in Stickler syndrome. In the latter syndrome, extreme myopia may lead to severe eye problems such as detached retina more frequently than in Marshall syndrome. Joints The joint changes include hyperextensibility (double-jointedness) and arthritis. Babies and young children with Stickler syndrome usually have very hyperextensible joints. As an affected child gets older, they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congenital Rubella Syndrome
Congenital rubella syndrome (CRS) occurs when a human fetus is infected with the rubella virus (German measles) via maternal-fetal transmission and develops birth defects. The most common congenital defects affect the ophthalmologic, cardiac, auditory, and neurologic systems. Rubella infection in pregnancy can result in various outcomes ranging from asymptomatic infection to congenital defects to miscarriage and fetal death. If infection occurs 0–11 weeks after conception, the infant has a 90% risk of being affected. If the infection occurs 12–20 weeks after conception, the risk is 20%. Infants are not generally affected if rubella is contracted during the third trimester. Diagnosis of congenital rubella syndrome is made through a series of clinical and laboratory findings and management is based on the infant's clinical presentation. Maintaining rubella outbreak control via vaccination is essential in preventing congenital rubella infection and congenital rubella syndrome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alport Syndrome
Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder affecting around 1 in 5,000–10,000 children, characterized by glomerulonephritis, end-stage kidney disease, and hearing loss. Alport syndrome can also affect the eyes, though the changes do not usually affect vision, except when changes to the lens occur in later life. Blood in urine is universal. Proteinuria is a feature as kidney disease progresses. The disorder was first identified in a British family by the physician Cecil A. Alport in 1927. Alport syndrome once also had the label hereditary nephritis, but this is misleading as there are many other causes of hereditary kidney disease and 'nephritis'. Alport syndrome is caused by an inherited defect in type IV collagen—a structural material needed for the normal function of different body parts. Since type IV collagen is found in the ears, eyes, and kidneys, this explains why Alport syndrome affects different seemingly unrelated parts of the body (ears, eyes, kidneys, etc.). Dependi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patau Syndrome
Patau syndrome is a syndrome caused by a chromosomal abnormality, in which some or all of the cells of the body contain extra genetic material from chromosome 13. The extra genetic material disrupts normal development, causing multiple and complex organ defects. This can occur either because each cell contains a full extra copy of chromosome 13 (a disorder known as trisomy 13 or trisomy D or T13), or because each cell contains an extra partial copy of the chromosome, or because there are two different lines of cells—one healthy with the correct number of chromosomes 13 and one that contains an extra copy of the chromosome—mosaic Patau syndrome. Full trisomy 13 is caused by nondisjunction of chromosomes during meiosis; the mosaic form is caused by nondisjunction during mitosis. Like all nondisjunction conditions (such as Down syndrome and Edwards syndrome), the risk of this syndrome in the offspring increases with maternal age at pregnancy, with about 31 years being th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |