|
Dead Code Elimination
In compiler theory, dead-code elimination (DCE, dead-code removal, dead-code stripping, or dead-code strip) is a compiler optimization to remove dead code (code that does not affect the program results). Removing such code has several benefits: it shrinks executable, program size, an important consideration in some contexts, it reduces resource usage such as the number of bytes to be transferredMalavolta, Ivano et al. “JavaScript Dead Code Identification, Elimination, and Empirical Assessment.” IEEE transactions on software engineering 49.7 (2023): 3692–3714. Web. and it allows the running program to avoid executing irrelevant CPU instruction, operations, which reduces its execution (computing), running time. It can also enable further optimizations by simplifying program structure. Dead code includes code that can never be executed (unreachable code), and code that only affects dead variables (written to, but never read again), that is, irrelevant to the program. Examples C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Compiler Theory
In computing, a compiler is a computer program that Translator (computing), translates computer code written in one programming language (the ''source'' language) into another language (the ''target'' language). The name "compiler" is primarily used for programs that translate source code from a high-level programming language to a lower level language, low-level programming language (e.g. assembly language, object code, or machine code) to create an executable program.Compilers: Principles, Techniques, and Tools by Alfred V. Aho, Ravi Sethi, Jeffrey D. Ullman - Second Edition, 2007 There are many different types of compilers which produce output in different useful forms. A ''cross-compiler'' produces code for a different Central processing unit, CPU or operating system than the one on which the cross-compiler itself runs. A ''bootstrap compiler'' is often a temporary compiler, used for compiling a more permanent or better optimised compiler for a language. Related software ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Static Single-assignment Form
In compiler design, static single assignment form (often abbreviated as SSA form or simply SSA) is a type of intermediate representation (IR) where each variable is assigned exactly once. SSA is used in most high-quality optimizing compilers for imperative languages, including LLVM, the GNU Compiler Collection, and many commercial compilers. There are efficient algorithms for converting programs into SSA form. To convert to SSA, existing variables in the original IR are split into versions, new variables typically indicated by the original name with a subscript, so that every definition gets its own version. Additional statements that assign to new versions of variables may also need to be introduced at the join point of two control flow paths. Converting from SSA form to machine code is also efficient. SSA makes numerous analyses needed for optimizations easier to perform, such as determining use-define chains, because when looking at a use of a variable there is only one place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Simplification (symbolic Computation)
In mathematics and computer science, computer algebra, also called symbolic computation or algebraic computation, is a scientific area that refers to the study and development of algorithms and software for manipulating mathematical expressions and other mathematical objects. Although computer algebra could be considered a subfield of scientific computing, they are generally considered as distinct fields because scientific computing is usually based on numerical computation with approximate floating point numbers, while symbolic computation emphasizes ''exact'' computation with expressions containing variables that have no given value and are manipulated as symbols. Software applications that perform symbolic calculations are called ''computer algebra systems'', with the term ''system'' alluding to the complexity of the main applications that include, at least, a method to represent mathematical data in a computer, a user programming language (usually different from the languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Redundant Code
In computer programming, redundant code is source code or compiled code in a computer program that is unnecessary, such as: * recomputing a value that has previously been calculated and is still available, * code that is never executed (known as unreachable code), * code which is executed but has no external effect (e.g., does not change the output produced by a program; known as dead code). A NOP instruction might be considered to be redundant code that has been explicitly inserted to pad out the instruction stream or introduce a time delay, for example to create a timing loop by "wasting time". Identifiers that are declared, but never referenced, are termed redundant declarations. Examples The following examples are in C. int foo(int iX) The second iX*2 expression is redundant code and can be replaced by a reference to the variable iY. Alternatively, the definition int iY = iX*2 can instead be removed. Consider: #define min(A,B) ((A)(B)?(A):(B)) int random(int cutoff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Hot Patching
A patch is data that is intended to be used to modify an existing software resource such as a program or a file, often to fix bugs and security vulnerabilities. A patch may be created to improve functionality, usability, or performance. A patch is typically provided by a vendor for updating the software that they provide. A patch may be created manually, but commonly it is created via a tool that compares two versions of the resource and generates data that can be used to transform one to the other. Typically, a patch needs to be applied to the specific version of the resource it is intended to modify, although there are exceptions. Some patching tools can detect the version of the existing resource and apply the appropriate patch, even if it supports multiple versions. As more patches are released, their cumulative size can grow significantly, sometimes exceeding the size of the resource itself. To manage this, the number of supported versions may be limited, or a complete cop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Dynamic Software Updating
In computer science, dynamic software updating (DSU) is a field of research pertaining to upgrade, upgrading programs while they are running. DSU is not currently widely used in industry. However, researchers have developed a wide variety of systems and techniques for implementing DSU. These systems are commonly tested on real-world programs. Current operating systems and programming languages are typically not designed with DSU in mind. As such, DSU implementations commonly either utilize existing tools, or implement specialty compilers. These compilers preserve the semantics of the original program, but instrument either the source code or object code to produce a dynamically updateable program. Researchers compare DSU-capable variants of programs to the original program to assess safety and performance overhead. Introduction Any running program can be thought of a tuple (\delta, P), where \delta is the current program state and P is the current program code. Dynamic software u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Just-in-time Compilation
In computing, just-in-time (JIT) compilation (also dynamic translation or run-time compilations) is compilation (of computer code) during execution of a program (at run time) rather than before execution. This may consist of source code translation but is more commonly bytecode translation to machine code, which is then executed directly. A system implementing a JIT compiler typically continuously analyses the code being executed and identifies parts of the code where the speedup gained from compilation or recompilation would outweigh the overhead of compiling that code. JIT compilation is a combination of the two traditional approaches to translation to machine code— ahead-of-time compilation (AOT), and interpretation—and combines some advantages and drawbacks of both. Roughly, JIT compilation combines the speed of compiled code with the flexibility of interpretation, with the overhead of an interpreter and the additional overhead of compiling and linking (not j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Assembly Language
In computing, assembly language (alternatively assembler language or symbolic machine code), often referred to simply as assembly and commonly abbreviated as ASM or asm, is any low-level programming language with a very strong correspondence between the instructions in the language and the architecture's machine code instructions. Assembly language usually has one statement per machine instruction (1:1), but constants, comments, assembler directives, symbolic labels of, e.g., memory locations, registers, and macros are generally also supported. The first assembly code in which a language is used to represent machine code instructions is found in Kathleen and Andrew Donald Booth's 1947 work, ''Coding for A.R.C.''. Assembly code is converted into executable machine code by a utility program referred to as an '' assembler''. The term "assembler" is generally attributed to Wilkes, Wheeler and Gill in their 1951 book '' The Preparation of Programs for an Electronic Dig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Ahead-of-time Compilation
In computer science, ahead-of-time compilation (AOT compilation) is the act of compiling an (often) higher-level programming language into an (often) lower-level language before execution of a program, usually at build-time, to reduce the amount of work needed to be performed at run time. It is most commonly associated with the act of compiling a higher-level programming language such as C or C++, or an intermediate representation such as Java bytecode or Common Intermediate Language (CIL) code, into native machine code so that the resulting binary file can execute natively, just like a standard native compiler. When being used in this context, it is often seen as an opposite of just-in-time (JIT) compiling. Speaking more generally, the target languages of an AOT compilation are not necessarily specific to native machine code but are defined rather arbitrarily. Some academic papers use this word to mean the act of compiling the Java bytecode to C or the timing when op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Late Linking
In computing, a dynamic linker is the part of an operating system that loads and links the shared libraries needed by an executable when it is executed (at " run time"), by copying the content of libraries from persistent storage to RAM, filling jump tables and relocating pointers. The specific operating system and executable format determine how the dynamic linker functions and how it is implemented. Linking is often referred to as a process that is performed when the executable is compiled, while a dynamic linker is a special part of an operating system that loads external shared libraries into a running process and then binds those shared libraries dynamically to the running process. This approach is also called dynamic linking or late linking. Implementations Microsoft Windows Dynamic-link library, or DLL, is Microsoft's implementation of the shared library concept in the Microsoft Windows and OS/2 operating systems. These libraries usually have the file extension DL ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Dynamic Loading
Dynamic loading is a mechanism by which a computer program can, at run time, load a library (or other binary) into memory, retrieve the addresses of functions and variables contained in the library, execute those functions or access those variables, and unload the library from memory. It is one of the three mechanisms by which a computer program can use some other software within the program; the others are static linking and dynamic linking. Unlike static linking and dynamic linking, dynamic loading allows a computer program to start up in the absence of these libraries, to discover available libraries, and to potentially gain additional functionality. History Dynamic loading was a common technique for IBM's operating systems for System/360 such as OS/360, particularly for I/O subroutines, and for COBOL and PL/I runtime libraries, and continues to be used in IBM's operating systems for z/Architecture, such as z/OS. As far as the application programmer is concerned, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
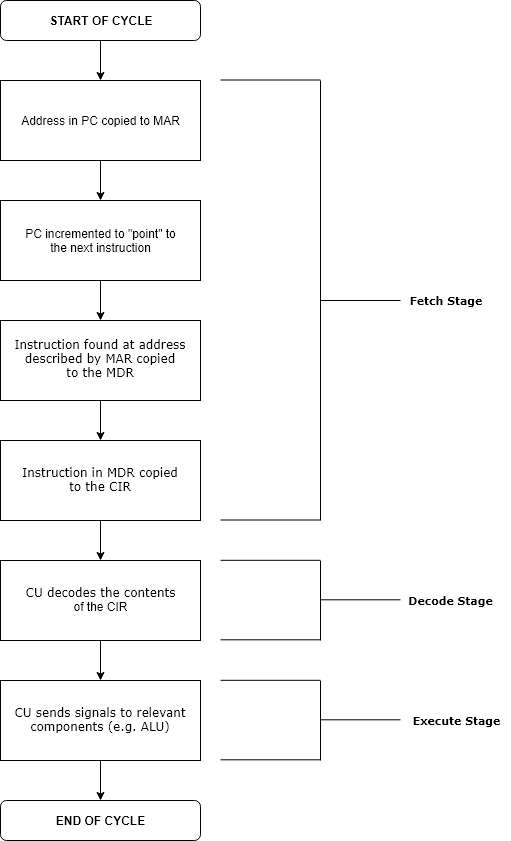 |
Runtime (computing)
Execution in computer and software engineering is the process by which a computer or virtual machine interprets and acts on the instructions of a computer program. Each instruction of a program is a description of a particular action which must be carried out, in order for a specific problem to be solved. Execution involves repeatedly following a " fetch–decode–execute" cycle for each instruction done by the control unit. As the executing machine follows the instructions, specific effects are produced in accordance with the semantics of those instructions. Programs for a computer may be executed in a batch process without human interaction or a user may type commands in an interactive session of an interpreter. In this case, the "commands" are simply program instructions, whose execution is chained together. The term run is used almost synonymously. A related meaning of both "to run" and "to execute" refers to the specific action of a user starting (or ''launching'' or ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |