|
De Havilland Propellers
de Havilland Propellers was established in 1935, as a division of the de Havilland Aircraft company when that company acquired a licence from the Hamilton Standard company of America for the manufacture of variable-pitch propellers at a cost of about £20,000. Licence negotiations were completed in June 1934. At the same time an extensive new factory, claimed to be one of the largest in the world, was laid down at Lostock, Bolton, some distance away from de Havilland's main aircraft plant at Hatfield. This factory was built in only nine months as part of the government's emergency pre-war shadow-factory programme. de Havilland Propellers, Ltd., was incorporated on 27 April 1946, with the main headquarters at Hatfield as the centre of design, development, and flight-testing, but with the main production plant still at Lostock in Lancashire. Work on missiles began in the late 1940s, early 1950s at the Hatfield plant in facilities which had been used during the war for the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aircraft
An aircraft ( aircraft) is a vehicle that is able to flight, fly by gaining support from the Atmosphere of Earth, air. It counters the force of gravity by using either Buoyancy, static lift or the Lift (force), dynamic lift of an airfoil, or, in a few cases, direct Powered lift, downward thrust from its engines. Common examples of aircraft include airplanes, rotorcraft (including helicopters), airships (including blimps), Glider (aircraft), gliders, Powered paragliding, paramotors, and hot air balloons. Part 1 (Definitions and Abbreviations) of Subchapter A of Chapter I of Title 14 of the U. S. Code of Federal Regulations states that aircraft "means a device that is used or intended to be used for flight in the air." The human activity that surrounds aircraft is called ''aviation''. The science of aviation, including designing and building aircraft, is called ''aeronautics.'' Aircrew, Crewed aircraft are flown by an onboard Aircraft pilot, pilot, whereas unmanned aerial vehicles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BAE Systems
BAE Systems plc is a British Multinational corporation, multinational Aerospace industry, aerospace, military technology, military and information security company, based in London. It is the largest manufacturer in Britain as of 2017. It is the largest defence contractor in Europe and the seventh largest in the world based on applicable 2021 revenues. Its largest operations are in the United Kingdom and in the United States, where its BAE Systems Inc. subsidiary is one of the six largest suppliers to the United States Department of Defense, US Department of Defense. Its next biggest markets are Saudi Arabia, then Australia; other major markets include Canada, Japan, India, Turkey, Qatar, Oman and Sweden. The company was formed on 30 November 1999 by the British pound sterling, £7.7 billion purchase of and merger of Marconi Electronic Systems (MES), the defence electronics and naval shipbuilding subsidiary of the General Electric Company plc (GEC), with British Aerospace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibre-reinforced Plastic
Fibre-reinforced plastic (FRP; also called fibre-reinforced polymer, or in American English ''fiber'') is a composite material made of a polymer matrix reinforced with fibres. The fibres are usually glass (in fibreglass), carbon (in carbon-fibre-reinforced polymer), aramid, or basalt. Rarely, other fibres such as paper, wood, boron, or asbestos have been used. The polymer is usually an epoxy, vinyl ester, or polyester thermosetting plastic, though phenol formaldehyde resins are still in use. FRPs are commonly used in the aerospace, automotive, marine, and construction industries. They are commonly found in ballistic armour and cylinders for self-contained breathing apparatuses. History Bakelite was the first fibre-reinforced plastic. Leo Baekeland had originally set out to find a replacement for shellac (made from the excretion of lac bugs). Chemists had begun to recognize that many natural resins and fibres were polymers, and Baekeland investigated the reactions of phenol an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair
Convair, previously Consolidated Vultee Aircraft Corporation, was an American aircraft-manufacturing company that later expanded into rockets and spacecraft. The company was formed in 1943 by the merger of Consolidated Aircraft and Vultee Aircraft. In 1953, it was purchased by General Dynamics, and operated as their Convair Division for most of its corporate history. Convair is best known for its military aircraft; it produced aircraft such as the Convair B-36 Peacemaker and Convair B-58 Hustler strategic bombers, and the Convair F-102 Delta Dagger and Convair F-106 Delta Dart interceptors. It also manufactured the first Atlas rockets, including the rockets that were used for the crewed orbital flights of Project Mercury. The company's subsequent Atlas-Centaur design continued this success and derivatives of the design remain in use as of 2025. The company also entered the jet airliner business with its Convair 880 and Convair 990 designs. These were smaller than conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blue Streak (missile)
The de Havilland Propellers Blue Streak was a British Intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM), and later the first stage of the Europa satellite launch vehicle. Blue Streak was cancelled without entering full production. The project was intended to maintain an independent British nuclear deterrent, replacing the V bomber fleet which would become obsolete by 1965. The operational requirement for the missile was issued in 1955 and the design was complete by 1957. During development, it became clear that the missile system was too expensive and too vulnerable to a surprise attack. The missile project was cancelled in 1960, with US-led Skybolt the preferred replacement. Partly to avoid political embarrassment from the cancellation, the UK government proposed that the rocket be used as the first stage of a civilian satellite launcher called Black Prince. As the cost was thought to be too great for the UK alone, international collaboration was sought. This led to the formati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aberporth
Aberporth is a seaside village, community (Wales), community and electoral ward in Ceredigion, Wales. The population at the 2001 Census, was 2,485, of whom 49 per cent could speak the Welsh language. At the 2011 Census, the population of the community was 2,374 and of the village 1241. Aberporth's beaches have earned Blue Flag beach, Blue Flag status. Location Aberporth is on the Ceredigion Coast Path, part of the Wales Coast Path, at the southern end of Cardigan Bay, about northeast of Cardigan, Ceredigion, Cardigan and southwest of New Quay. The Fishguard to Bangor Trunk Road (A487 road, A487) is reached via the B4333 road in about . Etymology The name Aberporth is first recorded in 1284, and is derived from the Old Welsh “aber” (mouth) and “porth” (port). History In the 16th century, boats, nets and salt for Curing (food preservation), preserving were brought in from Ireland. Aberporth became a subsidiary port of Cardigan. The landing point developed rapidly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Woomera Prohibited Area
The RAAF Woomera Range Complex (WRC) is a major Australian military and civil aerospace facility and operation located in South Australia, approximately north-west of Adelaide. The WRC is operated by the Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), a Service of the Australian Defence Force (ADF). The complex has a land area of or roughly the size of North Korea or Pennsylvania. The airspace above the area is restricted and controlled by the RAAF for safety and security. The WRC is a highly specialised ADF test and evaluation capability operated by the RAAF for the purposes of testing defence materiel. The complex has been variously known as the Anglo-Australian Long Range Weapons Establishment and then the Woomera Rocket Range; the RAAF Woomera Test Range and in 2013, the facility was reorganised and renamed to the RAAF Woomera Range Complex (WRC). The ground area of the WRC is defined by the Woomera Prohibited Area (WPA) and includes the Nurrungar Test Area (NTA); with a land area of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walkden
Walkden is a town in the City of Salford in Greater Manchester, England, northwest of central Salford, and of Manchester. Walkden has been designated as one of seven main town centres in the City of Salford, and now largely functions as a retail centre and commuter suburb of Greater Manchester. Historically in the township of Worsley in Lancashire, Walkden was a centre for coal mining and textile manufacture. In 2021, the electoral wards of Walkden North, Walkden South and Little Hulton had a combined population of 39,761. History The name Walkden or ''Walkeden'' derives from the Old English ''denu'', a valley, belonging to a man possibly called Wealca ( fuller), an Old English personal name. It has been in existence since at least the 13th century. The name was recorded in documents dating to 1246. A Roman road crossed the area roughly on the line of the present A6 road through Walkden and Little Hulton. In 1313, in a dispute involving land, a jury decided that Walkde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farnworth
Farnworth is a town in the Metropolitan Borough of Bolton, Greater Manchester, England, southeast of Bolton, 4 miles south-west of Bury (7 km), and northwest of Manchester. Within the historic county of Lancashire, Farnworth lies on the River Irwell and River Croal. At the 2011 Census, it had a population of 26,939. History Toponymy Farnworth derives from the Old English ''fearn'', fern and ''worth'' an enclosure. Farnworth was recorded as Farneworth and Farnewrth in 1278 and 1279 and Ffornword in a land survey of 1282. Middle Ages Farnworth was originally a hamlet in Barton. In the 13th century it was held by the Lords of Barton and Manchester. By 1320 Adam Lever, Richard Hulton and Richard Redford held the manor as tenants. Later the manor was acquired by the Hultons of Over Hulton. In 1666 there were 91 hearths in Farnworth liable to pay tax. The commons were enclosed in 1798. There was a watermill on the River Croal. Industrial Revolution The town expand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
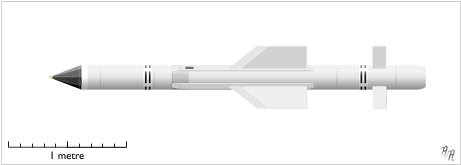
Firestreak
The de Havilland Firestreak is a British first-generation, passive infrared homing (heat seeking) air-to-air missile. It was developed by de Havilland Propellers (later Hawker Siddeley) in the early 1950s, entering service in 1957. It was the first such weapon to enter active service with the Royal Air Force (RAF) and Fleet Air Arm, equipping the English Electric Lightning, de Havilland Sea Vixen and Gloster Javelin. It was a rear-aspect, fire and forget pursuit weapon, with a field of attack of 20 degrees either side of the target.Gibson 2007, p. 33 Developed under the rainbow code "Blue Jay", Firestreak was the third heat-seeking missile to enter service, after the US AIM-4 Falcon and AIM-9 Sidewinder, both of which entered service the previous year. In comparison to those designs, the Firestreak was larger and almost twice as heavy, carrying a much larger warhead. It had otherwise similar performance in terms of speed and range. It was also a very complex system, with an unus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Supply
The Ministry of Supply (MoS) was a department of the UK government formed on 1 August 1939 by the Ministry of Supply Act 1939 ( 2 & 3 Geo. 6. c. 38) to co-ordinate the supply of equipment to all three British armed forces, headed by the Minister of Supply. A separate ministry, however, was responsible for aircraft production, and the Admiralty retained responsibilities for supplying the Royal Navy.Hornby (1958) During the war years the MoS was based at Shell Mex House in The Strand, London. The Ministry of Supply also took over all army research establishments in 1939. The Ministry of Aircraft Production was abolished in 1946, and the MoS took over its responsibilities for aircraft, including the associated research establishments. In the same year, it also took on increased responsibilities for atomic weapons, including the H-bomb development programme. The Ministry of Supply was abolished in late 1959 and its responsibilities passed to the Ministry of Aviation, the War Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |