|
Cytochromes
Cytochromes are redox-active proteins containing a heme, with a central iron (Fe) atom at its core, as a cofactor. They are involved in the electron transport chain and redox catalysis. They are classified according to the type of heme and its mode of binding. Four varieties are recognized by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB), cytochromes a, cytochromes b, cytochromes c and cytochrome d. Cytochrome function is linked to the reversible redox change from ferrous (Fe(II)) to the ferric (Fe(III)) oxidation state of the iron found in the heme core. In addition to the classification by the IUBMB into four cytochrome classes, several additional classifications such as cytochrome o and cytochrome P450 can be found in biochemical literature. History Cytochromes were initially described in 1884 by Charles Alexander MacMunn as respiratory pigments (myohematin or histohematin). In the 1920s, Keilin rediscovered these respiratory pigments and nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome C Family
Cytochromes ''c'' (cyt ''c'', c-type cytochromes) cytochromes, or heme-containing proteins, that have heme C covalently attached to the peptide backbone via one or two thioether bonds. These bonds are in most cases part of a specific Cys-X-X-Cys- His (CXXCH) binding motif, where X denotes a miscellaneous amino acid. Two thioether bonds of cysteine residues bind to the vinyl sidechains of heme, and the histidine residue coordinates one axial binding site of the heme iron. Less common binding motifs can include a single thioether linkage, a lysine or a methionine instead of the axial histidine or a CXnCH binding motif with n>2. The second axial site of the iron can be coordinated by amino acids of the protein, substrate molecules or water. Cytochromes ''c'' possess a wide range of properties and function as electron transfer proteins or catalyse chemical reactions involving redox processes. A prominent member of this family is mitochondrial cytochrome c. Classification ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Phosphorylation
Oxidative phosphorylation(UK , US : or electron transport-linked phosphorylation or terminal oxidation, is the metabolic pathway in which Cell (biology), cells use enzymes to Redox, oxidize nutrients, thereby releasing chemical energy in order to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In eukaryotes, this takes place inside mitochondria. Almost all aerobic organisms carry out oxidative phosphorylation. This pathway is so pervasive because it releases more energy than alternative fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation processes such as anaerobic glycolysis. The energy stored in the chemical bonds of glucose is released by the cell in the citric acid cycle, producing carbon dioxide and the energetic reducing agent, electron donors NADH and FADH. Oxidative phosphorylation uses these molecules and O2 to ATP synthase, produce ATP, which is used throughout the cell whenever energy is needed. During oxidative phosphorylation, electrons are transferred from the electron donors to a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome D
Cytochrome ''d'', previously known as cytochrome ''a''2, is a name for all cytochromes (electron-transporting heme proteins) that contain heme D as a cofactor. Two unrelated classes of cytochrome ''d'' are known: Cytochrome ''bd'', an enzyme that generates a charge across the membrane so that protons will move, and cytochrome ''cd1'' (NirS; SCOP ), a nitrite reductase. Cytochrome ''bd'' is found in plenty of aerobic bacteria, especially when it has grown with a limited oxygen supply. Compared to other terminal oxidases, it is notable for its high oxygen affinity and resistance to cyanide poisoning. It has a group of very similar relatives that do not use heme D, known as cyanide insensitive oxidases (CIOs). Function Cytochrome d is, as other proteins of its family, a membrane-bound hemoprotein, but unlike cytochromes a and b, cytochrome D has a heme D instead of a heme A or heme B group. Cytochrome d is part of the cytochrome bd terminal oxidase which catalyse the two el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron Transport Chain
An electron transport chain (ETC) is a series of protein complexes and other molecules which transfer electrons from electron donors to electron acceptors via redox reactions (both reduction and oxidation occurring simultaneously) and couples this electron transfer with the transfer of protons (H+ ions) across a membrane. Many of the enzymes in the electron transport chain are embedded within the membrane. The flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is an exergonic process. The energy from the redox reactions creates an electrochemical proton gradient that drives the synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). In aerobic respiration, the flow of electrons terminates with molecular oxygen as the final electron acceptor. In anaerobic respiration, other electron acceptors are used, such as sulfate. In an electron transport chain, the redox reactions are driven by the difference in the Gibbs free energy of reactants and products. The free energy released when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytochrome P450
Cytochromes P450 (P450s or CYPs) are a Protein superfamily, superfamily of enzymes containing heme as a cofactor (biochemistry), cofactor that mostly, but not exclusively, function as monooxygenases. However, they are not omnipresent; for example, they have not been found in ''Escherichia coli''. In mammals, these enzymes oxidize steroids, fatty acids, xenobiotics, and participate in many biosyntheses. By hydroxylation, CYP450 enzymes convert xenobiotics into hydrophilic derivatives, which are more readily excreted. P450s are, in general, the terminal oxidase enzymes in electron transfer chains, broadly categorized as P450-containing systems. The term "P450" is derived from the spectrophotometry, spectrophotometric peak at the wavelength of the absorption spectroscopy, absorption maximum of the enzyme (450 nanometre, nm) when it is in the redox, reduced state and complexed with carbon monoxide. Most P450s require a protein partner to deliver one or more electrons to reduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heme
Heme (American English), or haem (Commonwealth English, both pronounced /Help:IPA/English, hi:m/ ), is a ring-shaped iron-containing molecule that commonly serves as a Ligand (biochemistry), ligand of various proteins, more notably as a Prosthetic group, component of hemoglobin, which is necessary to bind oxygen in the bloodstream. It is composed of four pyrrole rings with 2 Vinyl group, vinyl and 2 propionic acid side chains. Heme is biosynthesized in both the bone marrow and the liver. Heme plays a critical role in multiple different redox reactions in mammals, due to its ability to carry the oxygen molecule. Reactions include oxidative metabolism (cytochrome c oxidase, succinate dehydrogenase), xenobiotic detoxification via cytochrome P450 pathways (including Drug metabolism, metabolism of some drugs), gas sensing (Guanylate cyclase, guanyl cyclases, nitric oxide synthase), and microRNA processing (DGCR8). Heme is a coordination complex "consisting of an iron ion coordinated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globular Protein
In biochemistry, globular proteins or spheroproteins are spherical ("globe-like") proteins and are one of the common protein types (the others being fibrous, disordered and membrane proteins). Globular proteins are somewhat water-soluble (forming colloids in water), unlike the fibrous or membrane proteins. There are multiple fold classes of globular proteins, since there are many different architectures that can fold into a roughly spherical shape. The term globin can refer more specifically to proteins including the globin fold. Globular structure and solubility The term globular protein is quite old (dating probably from the 19th century) and is now somewhat archaic given the hundreds of thousands of proteins and more elegant and descriptive structural motif vocabulary. The globular nature of these proteins can be determined without the means of modern techniques, but only by using ultracentrifuges or dynamic light scattering techniques. The spherical structure is induce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
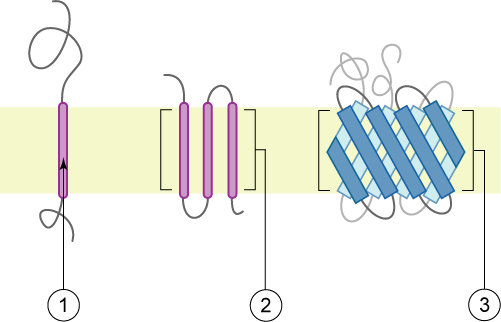
Membrane Protein
Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (Transmembrane protein, transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane (Integral monotopic protein, integral monotopic). Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane. Membrane proteins are common, and medically important—about a third of all human proteins are membrane proteins, and these are targets for more than half of all drugs. Nonetheless, compared to other classes of proteins, determining membrane protein structures remains a challenge in large part due to the difficulty in establishing experimental conditions that can preserve the correct (Native state, native) Protein structure, conformation of the protein in isolation from its native ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group (periodic table), group in the periodic table, a highly reactivity (chemistry), reactive nonmetal (chemistry), nonmetal, and a potent oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other chemical compound, compounds. Oxygen is abundance of elements in Earth's crust, the most abundant element in Earth's crust, making up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of various oxides such as water, carbon dioxide, iron oxides and silicates.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. It is abundance of chemical elements, the third-most abundant element in the universe after hydrogen and helium. At standard temperature and pressure, two oxygen atoms will chemical bond, bind covalent bond, covalently to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the chemical formula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coenzyme Q – Cytochrome C Reductase
The coenzyme Q : cytochrome ''c'' – oxidoreductase, sometimes called the cytochrome ''bc''1 complex, and at other times complex III, is the third complex in the electron transport chain (), playing a critical role in biochemical generation of ATP (oxidative phosphorylation). Complex III is a multisubunit transmembrane protein encoded by both the mitochondrial (cytochrome b) and the nuclear genomes (all other subunits). Complex III is present in the mitochondria of all animals and all aerobic eukaryotes and the inner membranes of most bacteria. Mutations in Complex III cause exercise intolerance as well as multisystem disorders. The bc1 complex contains 11 subunits, 3 respiratory subunits (cytochrome B, cytochrome C1, Rieske protein), 2 core proteins and 6 low-molecular weight proteins. Ubiquinol—cytochrome-c reductase catalyzes the chemical reaction :QH2 + 2 ferricytochrome c \rightleftharpoons Q + 2 ferrocytochrome c + 2 H+ Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are qui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |