|
Cytochrome P450 Reductase
Cytochrome P450 reductase (also known as NADPH:ferrihemoprotein oxidoreductase, NADPH:hemoprotein oxidoreductase, NADPH:P450 oxidoreductase, P450 reductase, POR, CPR, CYPOR) is a membrane-bound enzyme required for electron transfer from NADPH to cytochrome P450 and other heme proteins including heme oxygenase in the endoplasmic reticulum of the eukaryotic cell. Gene Human POR gene has 16 exons and the exons 2-16 code for a 677-amino acid POR protein (NCBI NP_000932.2). There is a single copy of 50 kb POR gene (NCBI NM_000941.2) in humans on chromosome 7 (7q11.23). Paralogs of POR include nitric oxide synthase (), NADPH:sulfite reductase (), and methionine synthase reductase (). Protein structure The 3D crystal structure of human POR has been determined.); The molecule is composed of four structural domains: the FMN-binding domain, the connecting domain, the FAD-binding domain, and NADPH-binding domain. The FMN-binding domain is similar to the structure of FMN-containing prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
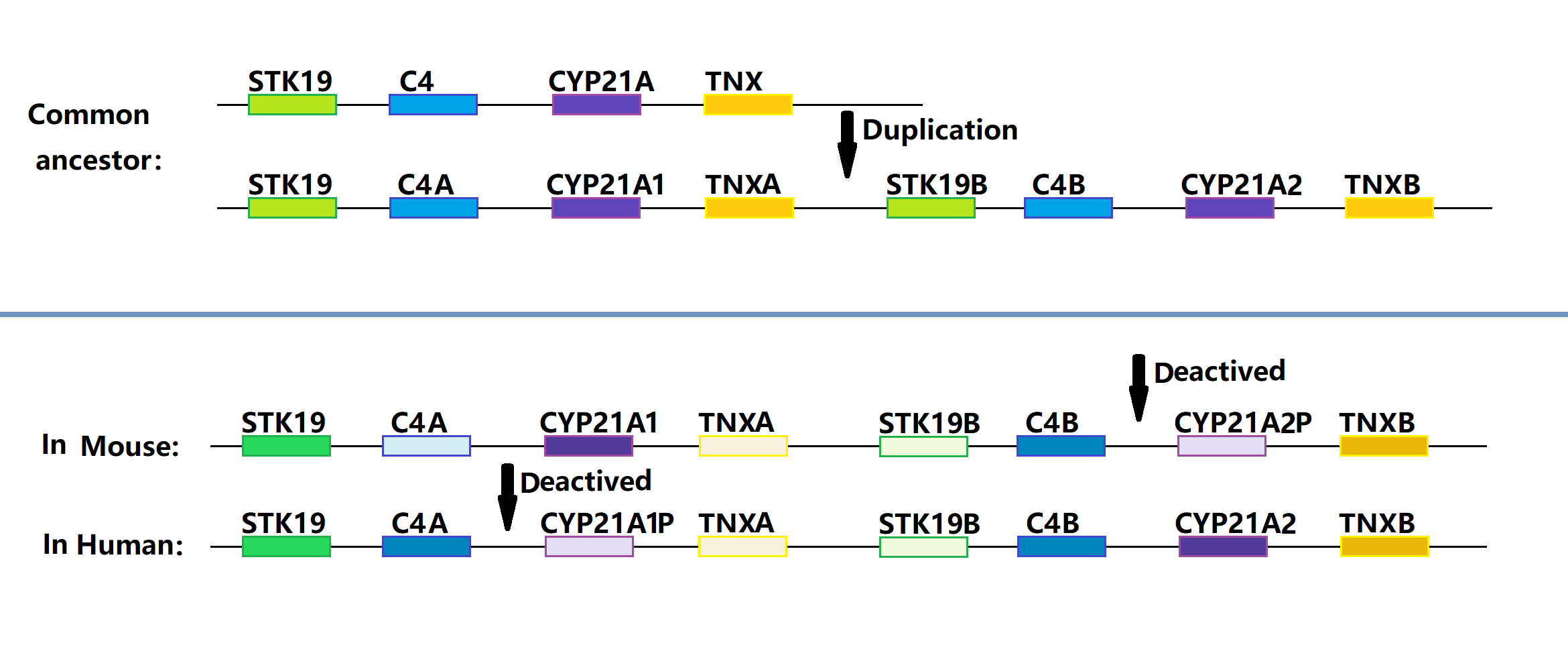
21-hydroxylase
Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CYP21A2'' gene. The protein is an enzyme that hydroxylates steroids at the C21 position on the molecule. Naming conventions for enzymes are based on the substrate acted upon and the chemical process performed. Biochemically, this enzyme is involved in the biosynthesis of the adrenal gland hormones aldosterone and cortisol, which are important in blood pressure regulation, sodium homeostasis and blood sugar control. The enzyme converts progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone into 11-deoxycorticosterone and 11-deoxycortisol, respectively, within metabolic pathways which in humans ultimately lead to aldosterone and cortisol creation—deficiency in the enzyme may cause congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a member of the cytochrome P450 family of monooxygenase enzymes that use an iron-containing heme cofactor to oxidize substrates. In humans, the enzyme is localized in endoplasmic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P450-containing Systems
Any enzyme system that includes cytochrome P450 protein or domain can be called a P450-containing system. P450 enzymes usually function as a terminal oxidase in multicomponent electron-transfer chains, called P450-containing monooxygenase systems, although self-sufficient, non-monooxygenase P450s have been also described. All known P450-containing monooxygenase systems share common structural and functional domain architecture. Apart from the cytochrome itself, these systems contain one or more fundamental redox domains: FAD-containing flavoprotein or domain, FMN domain, ferredoxin and cytochrome ''b''5. These ubiquitous redox domains, in various combinations, are widely distributed in biological systems. FMN domain, ferredoxin or cytochrome ''b''5 transfer electrons between the flavin reductase (protein or domain) and P450. While P450-containing systems are found throughout all kingdoms of life, some organisms lack one or more of these redox domains. FR/Fd/P450 systems Mitoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen Backdoor Pathway
The androgen backdoor pathway (the backdoor pathway of androgen biosynthesis) is a metabolic route in which androgens are produced from 21-carbon () steroids bypassing testosterone and androstenedione as intermediates. This process starts with 21-carbon () steroids, also known as pregnanes, and involves a step called "5α-Reduction (chemistry), reduction". Notably, this pathway does not require the intermediate formation of testosterone, hence the term "bypassing testosterone" is sometimes used in medical literature as the hallmark feature of this way of androgen biosynthesis. This feature is a key distinction from the conventional, canonical androgenic pathway, which necessitates the involvement of testosterone as an intermediate in the synthesis of androgens. These alternate androgen pathways play a crucial role in early male sexual development. In individuals with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to enzyme deficiencies like 21-Hydroxylase, 21-hydroxylase or cytochrome P4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone. Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in an adrenal gland. In other tissues, it is produced in lower quantities. By a Circadian rhythm, diurnal cycle, cortisol is released and increases in response to Stress (biology), stress and a low Blood sugar, blood-glucose concentration. It functions to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis, suppress the immune system, and aid in the metabolism of calories. It also decreases bone formation. These stated functions are carried out by cortisol binding to glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid receptors inside a cell, which then bind to DNA to affect gene expression. Health effects Metabolic response Metabolism of glucose Cortisol plays a crucial role in regulating glucose metabolism and promotes gluconeogenesis (glucose synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioulnar Synostosis
Radioulnar synostosis is a rare condition where there is an abnormal connection ( synostosis) between the radius and ulna bones of the forearm. This can be present at birth (congenital), when it is a result of a failure of the bones to form separately, or following an injury (post-traumatic). It typically causes restricted movement of the forearm, in particular rotation (pronation and supination), though is usually not painful unless it causes subluxation of the radial head. It can be associated with dislocation of the radial head which leads to limited elbow extension. Types Congenital Congenital radioulnar synostosis is rare, with approximately 350 cases reported in journals. It typically affects both sides (bilateral) and can be associated with other skeletal problems such as hip and knee abnormalities, finger abnormalities ( syndactyly or clinodactyly), or Madelung's deformity. It is sometimes part of known genetic syndromes such as Klinefelter syndrome (48,XXXY varian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cis-regulatory Element
''Cis''-regulatory elements (CREs) or ''cis''-regulatory modules (CRMs) are regions of non-coding DNA which regulate the transcription of neighboring genes. CREs are vital components of genetic regulatory networks, which in turn control morphogenesis, the development of anatomy, and other aspects of embryonic development, studied in evolutionary developmental biology. CREs are found in the vicinity of the genes that they regulate. CREs typically regulate gene transcription by binding to transcription factors. A single transcription factor may bind to many CREs, and hence control the expression of many genes ( pleiotropy). The Latin prefix ''cis'' means "on this side", i.e. on the same molecule of DNA as the gene(s) to be transcribed. CRMs are stretches of DNA, usually 100–1000 DNA base pairs in length, where a number of transcription factors can bind and regulate expression of nearby genes and regulate their transcription rates. They are labeled as ''cis'' because they are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megabase
A base pair (bp) is a fundamental unit of double-stranded nucleic acids consisting of two nucleobases bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. They form the building blocks of the DNA double helix and contribute to the folded structure of both DNA and RNA. Dictated by specific hydrogen bonding patterns, "Watson–Crick" (or "Watson–Crick–Franklin") base pairs (guanine–cytosine and adenine–thymine) allow the DNA helix to maintain a regular helical structure that is subtly dependent on its nucleotide sequence. The complementary nature of this based-paired structure provides a redundant copy of the genetic information encoded within each strand of DNA. The regular structure and data redundancy provided by the DNA double helix make DNA well suited to the storage of genetic information, while base-pairing between DNA and incoming nucleotides provides the mechanism through which DNA polymerase replicates DNA and RNA polymerase transcribes DNA into RNA. Many DNA-binding proteins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Williams Syndrome
Williams syndrome (WS), also Williams–Beuren syndrome (WBS), is a genetic disorder that affects many parts of the body. Facial features frequently include a broad forehead, underdeveloped chin, short nose, and full cheeks. Mild to moderate intellectual disability is observed, particularly challenges with visual spatial tasks such as drawing. Verbal skills are relatively unaffected. Many people have an outgoing personality, a happy disposition, an openness to engaging with other people, increased empathy and decreased aggression. Medical issues with teeth, heart problems (especially supravalvular aortic stenosis), and periods of hypercalcemia, high blood calcium are common. Williams syndrome is caused by a genetic abnormality, specifically a Deletion (genetics), deletion of about 27 genes from the long arm of one of the two chromosome 7s. Typically, this occurs as a random event during the formation of the egg or sperm from which a person develops. In a small number of cases, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Androgen Backdoor Pathway
The androgen backdoor pathway (the backdoor pathway of androgen biosynthesis) is a metabolic route in which androgens are produced from 21-carbon () steroids bypassing testosterone and androstenedione as intermediates. This process starts with 21-carbon () steroids, also known as pregnanes, and involves a step called "5α-Reduction (chemistry), reduction". Notably, this pathway does not require the intermediate formation of testosterone, hence the term "bypassing testosterone" is sometimes used in medical literature as the hallmark feature of this way of androgen biosynthesis. This feature is a key distinction from the conventional, canonical androgenic pathway, which necessitates the involvement of testosterone as an intermediate in the synthesis of androgens. These alternate androgen pathways play a crucial role in early male sexual development. In individuals with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to enzyme deficiencies like 21-Hydroxylase, 21-hydroxylase or cytochrome P4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromatase
Aromatase (), also called estrogen synthetase or estrogen synthase, is an enzyme responsible for a key step in the biosynthesis of estrogens. It is CYP19A1, a member of the cytochrome P450 superfamily, which are monooxygenases that catalyze many reactions involved in steroidogenesis. In particular, aromatase is responsible for the aromatization of androgens into estrogens. The enzyme aromatase can be found in many tissues including gonads ( granulosa cells), brain, adipose tissue, placenta, blood vessels, skin, and bone, as well as in tissue of endometriosis, uterine fibroids, breast cancer, and endometrial cancer. It is an important factor in sexual development. Function Aromatase is localized in the endoplasmic reticulum where it is regulated by tissue-specific promoters that are in turn controlled by hormones, cytokines, and other factors. It catalyzes the last steps of estrogen biosynthesis from androgens (specifically, it transforms androstenedione to estrone and te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
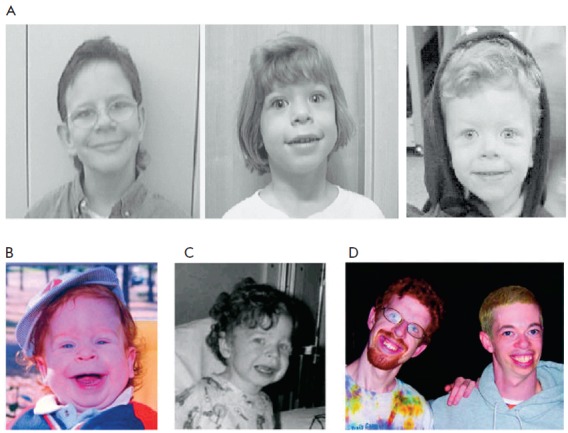
Cytochrome P450 Oxidoreductase Deficiency
Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency (PORD) is a rare disease and inborn error of metabolism caused by deficiency of cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase (POR). POR is a 2- flavin protein that is responsible for the transfer of electrons from NADPH to all 50 microsomal cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes. This includes the steroidogenic enzymes CYP17A1 (17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase), CYP19A1 (aromatase), and CYP21A2 (21-hydroxylase); CYP26B1 (metabolizes retinoic acid); and the hepatic drug- metabolizing CYP450 enzymes (e.g., CYP3A4), among many other CYP450 enzymes. Virilization of female infants in PORD may also be caused by alternative biosynthesis of 5α-dihydrotestosterone via the so-called "androgen backdoor pathway". The ABS component of severe forms of PORD is probably caused by CYP26B1 deficiency, which results in retinoic acid excess and defects during skeletal embryogenesis. All forms of PORD in humans are likely partial, as POR knockout in mice results in death during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |