|
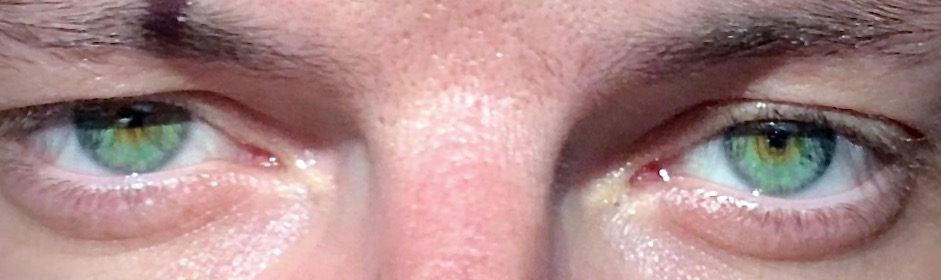
Cycloplegia
Cycloplegia is paralysis of the ciliary muscle of the eye, resulting in a loss of accommodation. Because of the paralysis of the ciliary muscle, the curvature of the lens can no longer be adjusted to focus on nearby objects. This results in similar problems as those caused by presbyopia, in which the lens has lost elasticity and can also no longer focus on close-by objects. Cycloplegia with accompanying mydriasis (dilation of pupil) is usually due to topical application of muscarinic antagonists such as atropine and cyclopentolate. Belladonna alkaloids are used for testing the error of refraction and examination of eye. Management Cycloplegic drugs are generally muscarinic receptor antagonists such as atropine, cyclopentolate, homatropine, scopolamine and tropicamide. They are indicated for use in cycloplegic refraction (to paralyze the ciliary muscle in order to determine the true refractive error of the eye) and the treatment of uveitis. All cycloplegics are also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopentolate
Cyclopentolate is a muscarinic antagonist. It is commonly used as an eye drop during pediatric eye examinations to dilate the eye (mydriatic) and prevent the eye from focusing/Accommodation (eye), accommodating (cycloplegia, cycloplegic). Cyclopentolate or atropine can also be administered to reverse muscarinic and central nervous system effects of indirect cholinomimetic (anti-AChase) administration. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. After instillation of cyclopentolate, pupil dilation (mydriasis) typically lasts up to 24 hours, while paralysis of the ciliary muscle (cycloplegia) typically lasts 6-24 hours. During this time, patients may be more light sensitive than normal and may notice close objects blurred (and possibly distant objects blurred, depending on the patient's visual system). Cyclopentolate is often chosen as a milder, shorter-lasting, cycloplegic alternative to atropine, another cyclopleg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cycloplegic Refraction
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess vision and ability to focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the eyes. Eye examinations are primarily performed by an optometrist, ophthalmologist, or an orthoptist. Health care professionals often recommend that all people should have periodic and thorough eye examinations as part of routine primary care, especially since many eye diseases are asymptomatic. Typically, a healthy individual who otherwise has no concerns with their eyes receives an eye exam once in their 20s and twice in their 30s. Eye examinations may detect potentially treatable blinding eye diseases, ocular manifestations of systemic disease, or signs of tumors or other anomalies of the brain. A full eye examination consists of a comprehensive evaluation of medical history, followed by 8 steps of visual acuity, pupil function, extraocular muscle motility and alignment, int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ciliary Muscle
The ciliary muscle is an intrinsic muscle of the eye formed as a ring of smooth muscleSchachar, Ronald A. (2012). "Anatomy and Physiology." (Chapter 4) . in the eye's middle layer, the uvea ( vascular layer). It controls accommodation for viewing objects at varying distances and regulates the flow of aqueous humor into Schlemm's canal. It also changes the shape of the lens within the eye but not the size of the pupil which is carried out by the sphincter pupillae muscle and dilator pupillae. The ciliary muscle, pupillary sphincter muscle and pupillary dilator muscle sometimes are called intrinsic ocular muscles or intraocular muscles. Structure Development The ciliary muscle develops from mesenchyme within the choroid and is considered a cranial neural crest derivative. Nerve supply The ciliary muscle receives parasympathetic fibers from the short ciliary nerves that arise from the ciliary ganglion. The parasympathetic postganglionic fibers are part of cranial n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accommodation (eye)
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus (optics), focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point—the maximum distance from the eye for which a clear image of an object can be seen, to the near point—the minimum distance for a clear image. Accommodation usually acts like a reflex, including part of the accommodation-convergence reflex, but it can also be consciously controlled. The main ways animals may change focus are: * Changing the shape of the lens. * Changing the position of the lens relative to the retina. * Changing the axial length of the eyeball. * Changing the shape of the cornea. Focusing mechanisms Focusing the light scattered by objects in a three dimensional environment into a two dimensional collection of individual bright points of light requires the light to be bent. To get a good image of these points of light on a defined area re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mydriasis
Mydriasis is the Pupillary dilation, dilation of the pupil, usually having a non-physiological cause, or sometimes a physiological pupillary response. Non-physiological causes of mydriasis include disease, Physical trauma, trauma, or the use of certain types of drug, drugs. It may also be of unknown cause. Normally, as part of the pupillary light reflex, the pupil dilates in the dark and miosis, constricts in the light to respectively improve vividity at night and to protect the retina from sunlight damage during the day. A ''mydriatic'' pupil will remain excessively large even in a bright environment. The excitation of the radial fibres of the iris which increases the pupillary aperture is referred to as a mydriasis. More generally, mydriasis also refers to the natural dilation of pupils, for instance in low light conditions or under sympathetic stimulation. Mydriasis is frequently induced by drugs for certain Ophthalmology, ophthalmic examinations and procedures, particularly th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miosis
Miosis, or myosis (), is excessive constriction of the pupil. citing: Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th ed. The opposite condition, mydriasis, is the dilation of the pupil. Anisocoria is the condition of one pupil being more dilated than the other. Causes Age * Senile miosis (a reduction in the size of a person's pupil in old age)Diseases *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Gunn Pupil
A relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD), also known as a Marcus Gunn pupil (after Robert Marcus Gunn), is a medical sign observed during the swinging-flashlight test whereupon the patient's pupils excessively dilate when a bright light is swung from the unaffected eye to the affected eye. The affected eye still senses the light and produces pupillary sphincter constriction to some degree, albeit reduced. Depending on severity, different symptoms may appear during the swinging flash light test: Mild RAPD initially presents as a weak pupil constriction, after which dilation occurs. When RAPD is moderate, pupil size initially remains same, after which it dilates. When RAPD is severe, the pupil dilates quickly. Cause The most common cause of Marcus Gunn pupil is a lesion of the optic nerve (between the retina and the optic chiasm) due to glaucoma, a severe retinal disease, or due to multiple sclerosis. It is named after Scottish ophthalmologist Robert Marcus Gunn. A s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anisocoria
Anisocoria is a condition characterized by an unequal size of the eyes' pupils. Affecting up to 20% of the population, anisocoria is often entirely harmless, but can be a sign of more serious medical problems. Causes Anisocoria is a common condition, defined by a diameter difference of 0.4 mm or more between the sizes of the pupils of the eyes. Anisocoria has various causes: * Physiological anisocoria: About 20% of the population has a slight difference in pupil size, which is known as physiological anisocoria. In this condition, the difference between pupils is usually less than 1 mm. * Horner's syndrome * Mechanical anisocoria: Occasionally, previous trauma, eye surgery, or inflammation ( uveitis, angle closure glaucoma) can lead to adhesions between the iris and the lens. * Adie tonic pupil: Tonic pupil is usually an isolated benign entity, presenting in young women. It may be associated with loss of deep tendon reflex (Adie's syndrome). Tonic pupil is charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Examination
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. Eye examinations are primarily performed by an optometrist, ophthalmologist, or an orthoptist. Health care professionals often recommend that all people should have periodic and thorough eye examinations as part of routine primary care, especially since many eye diseases are asymptomatic. Typically, a healthy individual who otherwise has no concerns with their eyes receives an eye exam once in their 20s and twice in their 30s. Eye examinations may detect potentially treatable blindness, blinding eye diseases, ocular manifestation of systemic disease, ocular manifestations of systemic disease, or signs of tumour, tumors or other anomalies of the Human brain, brain. A full eye examination consists of a comprehensive evaluation of medical h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium ''Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms depend on the stage it presents: primary, secondary, latent syphilis, latent or tertiary. The primary stage classically presents with a single chancre (a firm, painless, non-itchy Ulcer_(dermatology), skin ulceration usually between 1 cm and 2 cm in diameter), though there may be multiple sores. In secondary syphilis, a diffuse rash occurs, which frequently involves the palms of the hands and soles of the feet. There may also be sores in the mouth or vagina. Latent syphilis has no symptoms and can last years. In tertiary syphilis, there are Gumma (pathology), gummas (soft, non-cancerous growths), neurological problems, or heart symptoms. Syphilis has been known as "The Great Imitator, the great imitator", because it may cause symptoms similar to many other diseases. Syphilis is most commonly spread through human sexual activi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parinaud's Syndrome
Parinaud's syndrome is a constellation of neurological signs indicating injury to the dorsal midbrain. More specifically, compression of the vertical gaze center at the rostral interstitial nucleus of medial longitudinal fasciculus (riMLF). It is a group of abnormalities of eye movement and pupil dysfunction and is named for Henri Parinaud (1844–1905), considered to be the father of French ophthalmology. Signs and symptoms Parinaud's syndrome is a cluster of abnormalities of eye movement and pupil dysfunction, characterized by: * Paralysis of upwards gaze: Downward gaze is usually preserved. This vertical palsy is supranuclear, so doll's head maneuver should elevate the eyes, but eventually all upward gaze mechanisms fail. In the extreme form, conjugate down gaze in the primary position, or the "setting-sun sign" is observed. Neurosurgeons see this sign most commonly in patients with hydrocephalus. * Pseudo- Argyll Robertson pupils: Accommodative paresis ensues, and pup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adie Syndrome
Adie syndrome, also known as Holmes–Adie syndrome, is a neurological disorder characterized by a tonically dilated pupil that reacts slowly to light but shows a more definite response to accommodation (i.e., light-near dissociation). It is frequently seen in females with absent knee or ankle jerks and impaired sweating. The syndrome is caused by damage to the postganglionic fibers of the parasympathetic innervation of the eye, usually by a viral or bacterial infection that causes inflammation, and affects the pupil of the eye and the autonomic nervous system. It is named after the British neurologists William John Adie and Gordon Morgan Holmes, who independently described the same disease in 1931. Signs and symptoms Adie syndrome presents with three hallmark symptoms, namely at least one abnormally dilated pupil (mydriasis) which does not constrict in response to light, loss of deep tendon reflexes, and abnormalities of sweating. Other signs may include hyperopia du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |