|
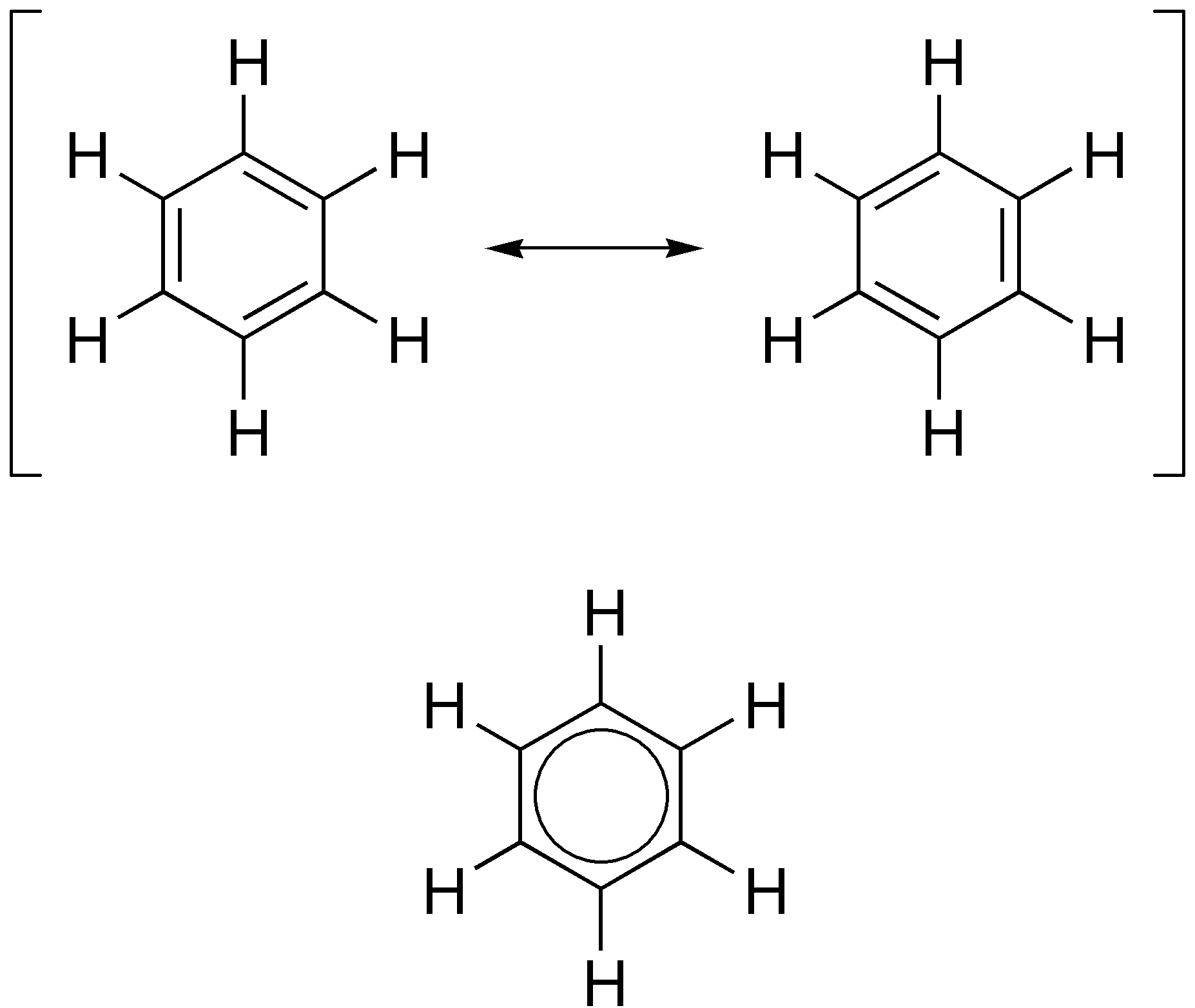
Cyclododecahexaene
Cyclododecahexaene or [12]annulene () is a member of the series of annulenes with some interest in organic chemistry with regard to the study of aromaticity. Cyclododecahexaene is non-aromatic due to the lack of planarity of the structure. On the other hand the dianion with 14 electrons is a Hückel's rule, aromatic by Hückel's rules and more stable. According to in silico experiments the tri-trans isomer is expected to be the most stable, followed by the 1,7-ditrans and the all cis-isomers (+1 kcal/mol) and by the 1,5-ditrans isomer (+5 kcal/mol). The first [12]annulene with sym-tri-trans configuration was synthesized in 1970 from a tricyclic precursor by photolysis at low temperatures. On heating the compound rearranges to a bicyclic [6.4.0] isomer. Organic reduction, Reducing the compound at low temperatures allowed analysis of the dianion by proton NMR with the inner protons resonating at −4.5 ppm relative to TMS, evidence of an aromatic diamagnetic ring current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulene
Annulenes are monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds (' mancude'). They have the general formula C''n''H''n'' (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd number). The IUPAC accepts the use of 'annulene nomenclature' in naming carbocyclic ring systems with 7 or more carbon atoms, using the name ' 'n''nnulene' for the mancude hydrocarbon with ''n'' carbon atoms in its ring, though in certain contexts (e.g., discussions of aromaticity for different ring sizes), smaller rings (''n'' = 3 to 6) can also be informally referred to as annulenes. Using this form of nomenclature 1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene is nnulene and benzene is nnulene (and occasionally referred to as just 'annulene'). The discovery that 8nnulene possesses a number of key properties associated with other aromatic molecules was an important development in the understanding of aromaticity as a chemical concept. In the related annul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulenes
Annulenes are cyclic compound, monocyclic hydrocarbons that contain the maximum number of non-cumulated or conjugated double bonds ('wikt:mancude, mancude'). They have the general formula C''n''H''n'' (when ''n'' is an even number) or C''n''H''n''+1 (when ''n'' is an odd number). The IUPAC nomenclature, IUPAC accepts the use of 'annulene nomenclature' in naming carbocyclic ring systems with 7 or more carbon atoms, using the name '[''n'']annulene' for the mancude hydrocarbon with ''n'' carbon atoms in its ring, though in certain contexts (e.g., discussions of aromaticity for different ring sizes), smaller rings (''n'' = 3 to 6) can also be informally referred to as annulenes. Using this form of nomenclature 1,3,5,7-cyclooctatetraene is [8]annulene and benzene is [6]annulene (and occasionally referred to as just 'annulene'). The discovery that [18]annulene possesses a number of key properties associated with other aromatic molecules was an important development in the understanding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiaromatic Compounds
Antiaromaticity is a chemical property of a cyclic molecule with a π electron system that has higher energy, i.e., it is less stable due to the presence of 4n delocalised (π or lone pair) electrons in it, as opposed to aromaticity. Unlike aromatic compounds, which follow Hückel's rule ( ''n''+2π electrons) and are highly stable, antiaromatic compounds are highly unstable and highly reactive. To avoid the instability of antiaromaticity, molecules may change shape, becoming non-planar and therefore breaking some of the π interactions. In contrast to the diamagnetic ring current present in aromatic compounds, antiaromatic compounds have a paramagnetic ring current, which can be observed by NMR spectroscopy. Examples of antiaromatic compounds are pentalene (A), biphenylene (B), cyclopentadienyl cation (C). The prototypical example of antiaromaticity, cyclobutadiene, is the subject of debate, with some scientists arguing that antiaromaticity is not a major factor contributing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hückel's Rule
In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule predicts that a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties if it has 4''n'' + 2 π-electrons, where ''n'' is a non-negative integer. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was first worked out by physical chemist Erich Hückel in 1931. The succinct expression as the 4''n'' + 2 rule has been attributed to W. v. E. Doering (1951), although several authors were using this form at around the same time. In agreement with the Möbius–Hückel concept, a cyclic ring molecule follows Hückel's rule when the number of its π-electrons equals 4''n'' + 2, although clearcut examples are really only established for values of ''n'' = 0 up to about ''n'' = 6. Hückel's rule was originally based on calculations using the Hückel method, although it can also be justified by considering a particle in a ring system, by the LCAO method and by the Pariser–Parr–Pople method. Aroma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehydrohalogenation
In chemistry, dehydrohalogenation is an elimination reaction which removes a hydrogen halide from a substrate (chemistry), substrate. The reaction is usually associated with the synthesis of alkenes, but it has wider applications. Dehydrohalogenation from alkyl halides Traditionally, alkyl halides are substrates for dehydrohalogenations. The alkyl halide must be able to form an alkene, thus halides having no C–H bond on an adjacent carbon are not suitable substrates. Aryl halides are also unsuitable. Upon treatment with strong base, chlorobenzene dehydrohalogenates to give phenol#Hydrolysis of chlorobenzene, phenol via a benzyne intermediate. Base-promoted reactions to alkenes When treated with a strong base many alkyl chlorides convert to corresponding alkene. It is also called a β-elimination reaction and is a type of elimination reaction. Some prototypes are shown below: :\begin \ce\ &\ce \\ \ce\ &\ce \\ \ce\ &\ce \end Here ethyl chloride reacts with potassium hydroxide, ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, aromaticity is a chemical property describing the way in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibits a stabilization stronger than would be expected from conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August Wilhelm Hofmann in 1855. There is no general relationship between aromaticity as a chemical property and the olfactory properties of such compounds. Aromaticity can also be considered a manifestation of cyclic delocalization and of resonance. This is usually considered to be because electrons are free to cycle around circular arrangements of atoms that are alternately single- and double- bonded to one another. This commonly seen model of aromatic rings, namely the idea that benzene was formed from a six-membered carbon ring with alternating single and double bonds (cyclohexatriene), was developed by Kekulé (see History section below). Each bond may be seen as a hybrid of a single bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptalene
Heptalene is a polycyclic hydrocarbon with chemical formula , composed of two fused cycloheptatriene rings. It is an unstable, non-planar compound which is non-aromatic. The dianion, however, satisfies Hückel's rule In organic chemistry, Hückel's rule predicts that a planar ring molecule will have aromatic properties if it has 4''n'' + 2 π-electrons, where ''n'' is a non-negative integer. The quantum mechanical basis for its formulation was f ..., is thermally stable, and is planar. See also * Benzocyclooctatetraene References {{Hydrocarbon-stub Polycyclic nonaromatic hydrocarbons Bicyclic compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Room Temperature
Room temperature, colloquially, denotes the range of air temperatures most people find comfortable indoors while dressed in typical clothing. Comfortable temperatures can be extended beyond this range depending on humidity, air circulation, and other factors. In certain fields, like science and engineering, and within a particular context, room temperature can mean different agreed-upon ranges. In contrast, ambient temperature is the actual temperature, as measured by a thermometer, of the air (or other medium and surroundings) in any particular place. The ambient temperature (e.g. an unheated room in winter) may be very different from an ideal ''room temperature''. Food and beverages may be served at "room temperature", meaning neither heated nor cooled. Comfort temperatures Comfort temperature is interchangeable with neutral temperature in the scientific literature, which can be calculated through regression analysis between thermal sensation votes and indoor temperature. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12annulene2006
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Shift
In nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, the chemical shift is the resonant frequency of an atomic nucleus relative to a standard in a magnetic field. Often the position and number of chemical shifts are diagnostic of the structure of a molecule. Chemical shifts are also used to describe signals in other forms of spectroscopy such as photoemission spectroscopy. Some atomic nuclei possess a magnetic moment (nuclear spin), which gives rise to different energy levels and resonance frequencies in a magnetic field. The total magnetic field experienced by a nucleus includes local magnetic fields induced by currents of electrons in the molecular orbitals (electrons have a magnetic moment themselves). The electron distribution of the same type of nucleus (e.g. ) usually varies according to the local geometry (binding partners, bond lengths, angles between bonds, and so on), and with it the local magnetic field at each nucleus. This is reflected in the spin energy levels (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical Anion
In organic chemistry, a radical anion is a free radical species that carries a negative charge. Radical anions are encountered in organic chemistry as reduced derivatives of polycyclic aromatic compounds, e.g. sodium naphthenide. An example of a non-carbon radical anion is the superoxide anion, formed by transfer of one electron to an oxygen molecule. Radical anions are typically indicated by M^. Polycyclic radical anions Many aromatic compounds can undergo one-electron reduction by alkali metals. The electron is transferred from the alkali metal ion to an unoccupied antibonding p-p п* orbital of the aromatic molecule. This transfer is usually only energetically favorable if the aprotic solvent efficiently solvates the alkali metal ion. Effective solvents are those that bind to the alkali metal cation: diethyl ether < THF < [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |