|
Cycle (music)
In music, a cycle can be several things. Acoustically, it is one complete vibration, the base unit of Hertz being one cycle per second. Theoretically, an interval cycle is a collection of pitch classes created by a sequence of identical intervals. Cycles are also individual pieces of larger works, like the movements in a suite, symphony sonata, or string quartet. This can range from settings of the Mass or a song cycle to an opera cycle. Another cycle is the complete performance of an individual composer's work in one genre. Harmonic cycles—repeated sequences of a harmonic progression—are at the root of many musical genres, such as the twelve-bar blues. In compositions of this genre, the chord progression may be repeated indefinitely, with melodic and lyrical variation forming the musical interest. The form theme and variations is essentially of this type, but generally on a larger scale. Composition using a tone row is another example of a cycle of pitch material, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Music
Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all human societies. Definitions of music vary widely in substance and approach. While scholars agree that music is defined by a small number of elements of music, specific elements, there is no consensus as to what these necessary elements are. Music is often characterized as a highly versatile medium for expressing human creativity. Diverse activities are involved in the creation of music, and are often divided into categories of musical composition, composition, musical improvisation, improvisation, and performance. Music may be performed using a wide variety of musical instruments, including the human voice. It can also be composed, sequenced, or otherwise produced to be indirectly played mechanically or electronically, such as via a music box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
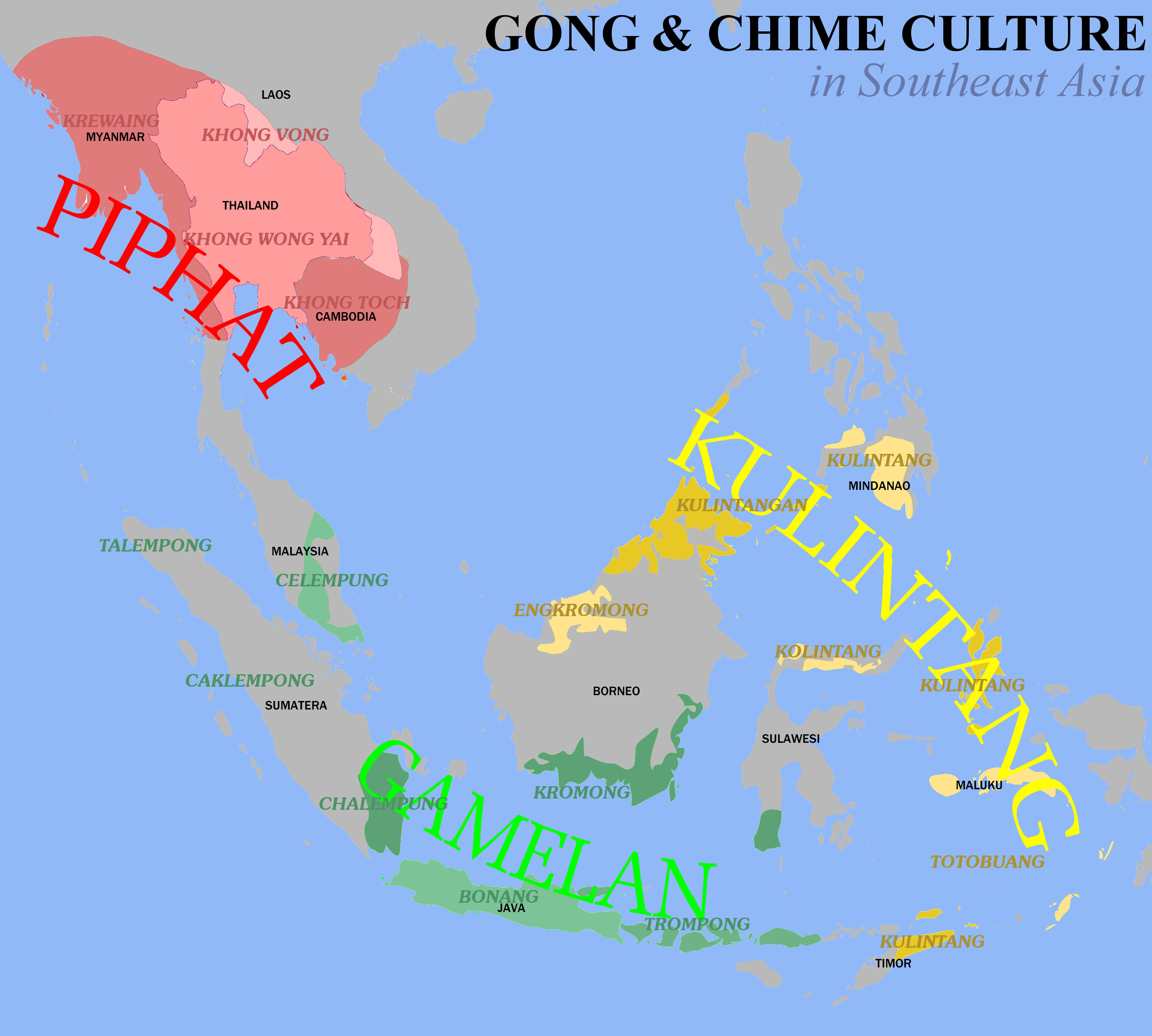
Pi Phat
A ''piphat'' () is a kind of ensemble in the classical music of Thailand, which features wind and percussion instruments. It is considered the primary form of ensemble for the interpretation of the most sacred and "high-class" compositions of the Thai classical repertoire, including the Buddhist invocation entitled ''sathukan'' () as well as the suites called ''phleng rueang''. It is also used to accompany traditional Thai theatrical and dance forms including ''khon'' () (masked dance-drama), '' lakhon'' (classical dance), and shadow puppet theater. Piphat in the earlier time was called ''phinphat''. It is analogous to its Cambodian musical ensemble of pinpeat and Laotian ensemble of pinphat. Types of ''piphat'' The smallest ''piphat'', called ''piphat khrueang ha'', is composed of six instruments: '' pi nai'' (oboe); ''ranat ek'' (xylophone); '' khong wong yai'' (gong circle); '' taphon'' or other Thai drums; '' glong thad'', a set of two large barrel drums beaten with st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Timbre
In music, timbre (), also known as tone color or tone quality (from psychoacoustics), is the perceived sound of a musical note, sound or tone. Timbre distinguishes sounds according to their source, such as choir voices and musical instruments. It also enables listeners to distinguish instruments in the same category (e.g., an oboe and a clarinet, both woodwinds). In simple terms, timbre is what makes a particular musical instrument or human voice have a different sound from another, even when they play or sing the same note. For instance, it is the difference in sound between a guitar and a piano playing the same note at the same volume. Both instruments can sound equally tuned in relation to each other as they play the same note, and while playing at the same amplitude level each instrument will still sound distinctive with its own unique tone color. Musicians distinguish instruments based on their varied timbres, even instruments playing notes at the same pitch and volume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Articulation (music)
Articulation is a Elements of music, musical parameter that determines how a single Note (music), note or other discrete event is sounded. Articulations primarily structure an event's start and end, determining the length of its sound and the shape of its Envelope (music), attack and decay. They can also modify an event's timbre, Dynamics (music), dynamics, and Pitch (music), pitch. Musical articulation is analogous to the Articulation (phonetics), articulation of speech, and during the Baroque music, Baroque and Classical period (music), Classical periods it was taught by comparison to Rhetoric, oratory. Western music has a set of traditional articulations that were standardized in the 19th century#Music, 19th century and remain widely used. Composers are not limited to these, however, and may invent new articulations as a piece requires. When writing Electronic music, electronic and computer music, composers can design articulations from the ground up. In addition to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dynamics (music)
In music, the dynamics of a piece are the variation in loudness between notes or phrases. Dynamics are indicated by specific musical notation, often in some detail. However, dynamics markings require interpretation by the performer depending on the musical context: a specific marking may correspond to a different volume between pieces or even sections of one piece. The execution of dynamics also extends beyond loudness to include changes in timbre and sometimes tempo rubato. Purpose and interpretation Dynamics are one of the expressive elements of music. Used effectively, dynamics help musicians sustain variety and interest in a musical performance, and communicate a particular emotional state or feeling. Dynamic markings are always relative. (''piano'' - "soft") never indicates a precise level of loudness; it merely indicates that music in a passage so marked should be considerably quieter than (''forte'' - "loud"). There are many factors affecting the interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Serial Music
In music, serialism is a method of composition using series of pitches, rhythms, dynamics, timbres or other musical elements. Serialism began primarily with Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique, though some of his contemporaries were also working to establish serialism as a form of post-tonal thinking. Twelve-tone technique orders the twelve notes of the chromatic scale, forming a row or series and providing a unifying basis for a composition's melody, harmony, structural progressions, and variations. Other types of serialism also work with sets, collections of objects, but not necessarily with fixed-order series, and extend the technique to other musical dimensions (often called " parameters"), such as duration, dynamics, and timbre. The idea of serialism is also applied in various ways in the visual arts, design, and architecture, and the musical concept has also been adapted in literature. Integral serialism or total serialism is the use of series for aspects suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Relatively Prime
In number theory, two integers and are coprime, relatively prime or mutually prime if the only positive integer that is a divisor of both of them is 1. Consequently, any prime number that divides does not divide , and vice versa. This is equivalent to their greatest common divisor (GCD) being 1. One says also ''is prime to'' or ''is coprime with'' . The numbers 8 and 9 are coprime, despite the fact that neither—considered individually—is a prime number, since 1 is their only common divisor. On the other hand, 6 and 9 are not coprime, because they are both divisible by 3. The numerator and denominator of a reduced fraction are coprime, by definition. Notation and testing When the integers and are coprime, the standard way of expressing this fact in mathematical notation is to indicate that their greatest common divisor is one, by the formula or . In their 1989 textbook '' Concrete Mathematics'', Ronald Graham, Donald Knuth, and Oren Patashnik proposed an alter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Isorhythm
Isorhythm (from the Greek for "the same rhythm") is a musical technique using a repeating rhythmic pattern, called a ''talea'', in at least one voice part throughout a composition. ''Taleae'' are typically applied to one or more melodic patterns of pitches or '' colores'', which may be of the same or a different length from the ''talea''. History and development Isorhythms first appear in French motets of the 13th century, such as in the '' Montpellier Codex''. Although 14th-century theorists used the words ''talea'' and ''color''—the latter in a variety of senses related to repetition and embellishment—the term ''isorhythm'' was coined in 1904 by musicologist Friedrich Ludwig, initially to describe the practice in 13th-century polyphony. Ludwig later extended its use to the 14th-century music of Guillaume de Machaut. Subsequently, Heinrich Besseler and other musicologists expanded its scope further as an organizing structural element in 14th- and early 15th-century composi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Period (music)
In music theory, the term period refers to forms of repetition and contrast between adjacent small-scale Musical form, formal structures such as phrases. In twentieth-century music scholarship, the term is usually used similarly to the definition in the ''Oxford Companion to Music'': "a period consists of two phrases, antecedent and consequent, each of which begins with the same basic motif (music), motif." Earlier and later usages vary somewhat, but usually refer to notions of symmetry, difference, and an open section followed by a closure. The concept of a musical period originates in comparisons between music structure and rhetoric at least as early as the 16th century. Western art music In Western art music or Classical music, a period is a group of phrase (music), phrases consisting usually of at least one antecedent phrase and one consequent phrase totaling about 8 bar (music), bars in length (though this varies depending on meter and tempo). Generally, the antecedent end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bell Pattern
A bell pattern is a rhythmic pattern of striking a hand-held bell or other instrument of the idiophone family, to make it emit a sound at desired intervals. It is often a ''key pattern'' (also known as a ''guide pattern'', ''phrasing referent'', ''timeline'', or ''asymmetrical timeline''Kubik, Gerhard (1999: 54) ''Africa and the Blues''. Jackson, MS: University Press of Mississippi. .), in most cases it is a metal bell, such as an agogô, gankoqui, or cowbell, or a hollowed piece of wood, or wooden claves. In band music, bell patterns are also played on the metal shell of the timbales, and drum kit cymbals. Sub-Saharan African music Gerhard Kubik notes that key patterns are not universally found in sub-Saharan Africa: "Their geographical distribution mainly covers those parts of Africa where I.A.4 (Kwa languages) and the ' western stream' of the I.A.5 (Benue–Congo languages), or ' Bantu' languages are spoken, with offshoots into the Lower Zambezi valley and the Nyasa/Ruvu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
African Diaspora
The African diaspora is the worldwide collection of communities descended from List of ethnic groups of Africa, people from Africa. The term most commonly refers to the descendants of the native West Africa, West and Central Africans who were slavery, enslaved and shipped to the Americas via the Atlantic slave trade between the 16th and 19th centuries, with their largest populations in Brazil, the United States, and Haiti. The term can also be used to refer to Demographics of Africa, African descendants who immigrated to other parts of the world. Scholars identify "four circulatory phases" of this migration out of Africa. The phrase ''African diaspora'' gradually entered common usage at the turn of the 21st century. The term ''diaspora'' originates from the Greek (''diaspora'', "scattering") which gained popularity in English in reference to the Jewish diaspora before being more broadly applied to other populations. Less commonly, the term has been used in scholarship to refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cell (music)
The 1957 ''Encyclopédie Larousse''quoted in Nattiez, Jean-Jacques (1990). ''Music and Discourse: Toward a Semiology of Music'' (''Musicologie générale et sémiologue'', 1987). Translated by Carolyn Abbate (1990). . defines a cell in music as a "small rhythmic and melodic design that can be isolated, or can make up one part of a theme (music), thematic context". The cell may be distinguished from the figure (music), figure or motif (music), motif: the 1958 ''Encyclopédie Fasquelle'' defines a cell as "the smallest indivisible unit", unlike the motif, which may be divisible into more than one cell. "A cell can be musical development, developed, independent of its context, as a melodic fragment, it can be used as a developmental motif. It can be the source for the whole musical form, structure of the work; in that case it is called a generative cell." A rhythmic cell is a cell without melodic connotations. It may be entirely percussive or applied to different melodic segments. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |