|
Culture Of El Salvador
The culture of El Salvador is a Central American culture nation influenced by the clash of ancient Mesoamerica and medieval Iberian Peninsula. Salvadoran culture is influenced by Native American culture (Lenca people, Cacaopera people, Maya peoples, Pipil people) as well as Latin American culture (Latin America, Hispanic America, Ibero-America). Mestizo culture, Afro-Latin culture and the Catholic Church dominates the country. Although the Romance language, Castilian Spanish, is the official and dominant language spoken in El Salvador, Salvadoran Spanish which is part of Central American Spanish has influences of Native American languages of El Salvador such as Lencan languages, Cacaopera language, Mayan languages and Pipil language, which are still spoken in some regions of El Salvador. Native Homeland File:Departments of El Salvador named.svg, Modern El Salvador map Salvadorans inhabit the lush Central American nation of El Salvador. El Salvador is one of seven countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
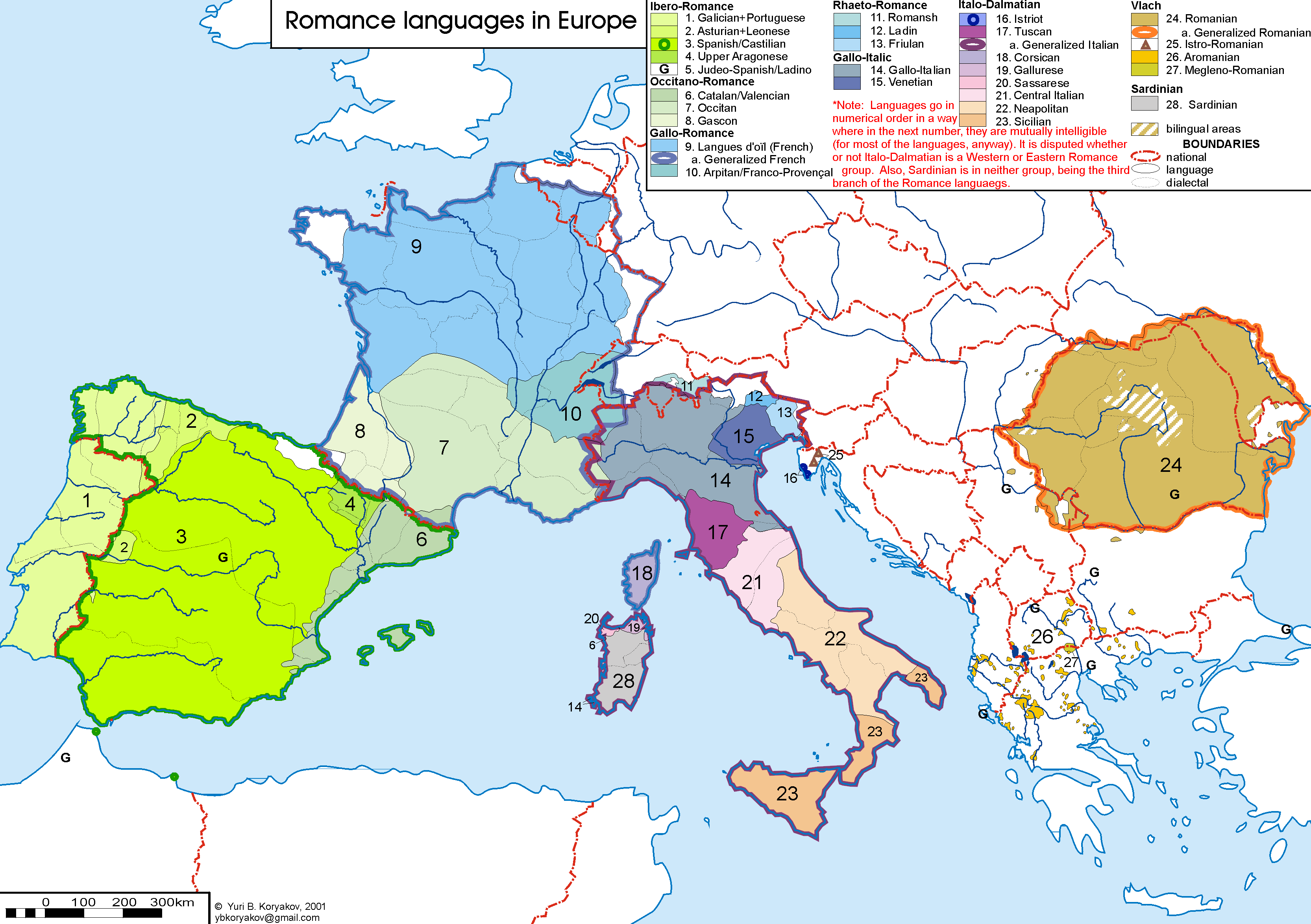
Romance Languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Salvador National Anthem
EL, El or el may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in the Superman dynasty * E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film '' Road Trip'' Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él ''(Lucerito album), a 1982 album by Lucerito * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from the album '' Caminando'' * "Él" (Lucía song), the Spanish entry performed by Lucía in the Eurovision Song Contest 1982 Other media * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (film), a 1953 film by Luis Buñuel based on the 1926 novel * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 1991 Japanese adult visual novel * EL TV, an Azerbaijani regional television channel Companies and organizations * Estée Lauder Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Anthem Of El Salvador
The National Anthem of El Salvador () was adopted on 15 September 1879 and officially approved on 11 December 1953. The lyrics were written by General Juan José Cañas in 1856, with music composed by the Italian Juan Aberle in 1879. The composition has been likened to "William Tell Overture" by critics. History 1866 anthem In 1866, at the initiative of doctor Francisco Dueñas, who at the time was President of El Salvador, President of the Republic, the first national anthem of El Salvador was created by Cuban doctor Tomás M. Muñoz, who wrote the lyrics, and Salvadoran musician Rafael Orozco, who composed the music. This national anthem was legally adopted through Executive Agreement of 8 October 1866, being published in the state newspaper ''El Constitucional'' No. 31, Volume 2, of 11 October 1866, to be officially released on 24 January 1867. This anthem was sung until the overthrow of President Dueñas through a coup d'état in 1871. 1879 anthem Later, in 1879 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorido Nacional
The scene subculture is a youth subculture that emerged during the early 2000s in the United States from the pre-existing emo subculture. The subculture became popular with adolescents from the mid 2000s to the early 2010s. Members of the scene subculture are referred to as scene kids, trendies, or scenesters. Scene fashion consists of skinny jeans, bright-colored clothing, a signature hairstyle consisting of straight, flat hair with long Bangs (hair), fringes covering the forehead, and bright-colored hair dye. Music genres associated with the scene subculture include metalcore, crunkcore, deathcore, electronic music, and pop punk. From the mid-2000s to early 2010s, scene fashion gained popularity among teens and the music associated with the subculture achieved commercial success in both the underground and the mainstream. Groups like Bring Me the Horizon, Asking Alexandria, Pierce the Veil, and Metro Station (band), Metro Station garnered mainstream attention and large audien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipil Language
Nawat (academically Pipil, also known as Nahuat) is a Nahuan language native to Central America. It is the southernmost extant member of the Uto-Aztecan family. Before Spanish colonization it was spoken in several parts of present-day Central America, most notably El Salvador and Nicaragua, but now is mostly confined to western El Salvador. It has been on the verge of extinction in El Salvador, and has already gone extinct elsewhere in Central America. In 2012, a large number of new Nawat speakers started to appear. As of today, the language is currently going through a revitalization. In El Salvador, Nawat (Nahuat) was the language of several groups: Nonualcos, Cuscatlecos, Izalcos and is known to be the Nahua variety of migrating Toltec. The name ''Pipil'' for this language is mostly used by the international scholarly community to differentiate it more clearly from Nahuatl. In Nicaragua it was spoken by the Nicarao people who split from the Pipil around 1200 CE when they ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mayan Languages
The Mayan languages In linguistics, it is conventional to use ''Mayan'' when referring to the languages, or an aspect of a language. In other academic fields, ''Maya'' is the preferred usage, serving as both a singular and plural noun, and as the adjective, adjectival form. form a language family spoken in Mesoamerica, both in the south of Mexico and northern Central America. Mayan languages are spoken by at least six million Maya peoples, Maya people, primarily in Guatemala, Mexico, Belize, El Salvador and Honduras. In 1996, Guatemala formally recognized 21 Mayan languages by name,Achiʼ is counted as a variant of Kʼicheʼ by the Guatemalan government. and Mexico Languages of Mexico, recognizes eight within its territory. The Mayan language family is one of the best-documented and most studied in the south Americas. Modern Mayan languages descend from the Proto-Mayan language, thought to have been spoken at least 5,000 years ago; it has been partially historical linguistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacaopera Language
Cacaopera is an extinct language belonging to the Misumalpan family, formerly spoken in the department of Morazán in El Salvador by the Cacaopera people. It was closely related to Matagalpa, and slightly more distantly to Sumo, but was geographically separated from other Misumalpan languages. The last semi-speakers of Cacaopera lived in the 1970s. All native speakers had died before this time. Phonology Consonants Vowels References External links Recording of a semi-speaker of Cacaoperafrom 1973, from the MesoAmerican Languageof Lyle Campbell at the Archive of the Indigenous Languages of Latin America The Archive of the Indigenous Languages of Latin America (AILLA) is a digital repository housed in LLILAS Benson Latin American Studies and Collections at the University of Texas at Austin. AILLA is a digital language archive dedicated to the digi .... Misumalpan languages Languages of El Salvador Extinct languages of North America Languages extinct in the 20th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lencan Languages
The Lencan languages are a small linguistic family from Central America, whose speakers before the Spanish conquest spread throughout El Salvador and Honduras. But by the beginning of the 20th century, only two languages of the family survived, Salvadoran Lenca or Potón and Honduran Lenca, which were described and studied academically; Of them, only Salvadoran Lenca still has current speakers, despite the fact that indigenous people belonging to the Lenca ethnic group exceed between 37,000 and 100,000 people. Languages There are two attested Lencan languages: * Salvadoran Lencan was spoken in Chilanga and Guatajigua. Lencans had arrived in El Salvador about 2,295 years B.P. and founded the site of Quelepa. One speaker remains. * Honduran Lencan was spoken with minor dialect differences in Intibucá, Opatoro, Guajiquiro, Similatón (modern Cabañas), and Santa Elena. Some phrases survive; it is not known if the entire language still exists. The languages are not close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Languages Of The Americas
The Indigenous languages of the Americas are the languages that were used by the Indigenous peoples of the Americas before the arrival of non-Indigenous peoples. Over a thousand of these languages are still used today, while many more are now extinct. The Indigenous languages of the Americas are not all related to each other; instead, they are classified into a hundred or so language families and isolates, as well as several extinct languages that are unclassified due to the lack of information on them. Many proposals have been made to relate some or all of these languages to each other, with varying degrees of success. The most widely reported is Joseph Greenberg's Amerind hypothesis, which, however, nearly all specialists reject because of severe methodological flaws; spurious data; and a failure to distinguish cognation, contact, and coincidence. According to UNESCO, most of the Indigenous languages of the Americas are critically endangered, and many are dormant (wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |