|
Cubitus Valgus
Cubitus valgus is a medical deformity in which the forearm is angled away from the body to a greater degree than normal when fully extended. A small degree of cubitus valgus (known as the carrying angle) is acceptable and occurs in the general population. When present at birth, it can be an indication of Turner syndromeChapter on Amenorrhea in: or Noonan syndrome. It can also be acquired through fracture or other trauma. The physiological cubitus valgus varies from 3° to 29°. Women usually have a more pronounced Cubitus valgus than men. The deformity can also occur as a complication of fracture of the lateral condyle of the humerus, which may lead to tardy/delayed ulnar nerve palsy. The opposite condition is cubitus varus (). See also * Valgus deformity * Varus deformity A varus deformity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubitus Varus
Cubitus varus is a varus deformity in which the extended forearm is deviated towards midline of the body. Cubitus varus is often referred to as "Gunstock deformity", due to the crooked nature of the healing. The "opposite" condition is cubitus valgus. Signs and symptoms Complications Instances in which the medial epicondyle of the distal humerus is malformed due to the initial fracture at the humeral endplate may result in subluxation (snapping) of the ulnar nerve over the medial epicondyle with active flexion and extension of the elbow. In such instances, conductance of the ulnar nerve may be compromised due to chronic irritation, potentially resulting in irreversible ulnar neuropathy. Causes A common cause is a supracondylar fracture of the humerus. It can be corrected via a corrective osteotomy of the humerus and either internal or external fixation of the bone until union. Rüdiger Döhler: ''Suprakondyläre Korrekturosteotomie beim posttraumatischen Cubitus varus''. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valgus Deformity
A valgus deformity is a condition in which the bone segment distal to a joint is angled outward, that is, angled laterally, away from the body's midline. The opposite deformation, where the twist or angulation is directed medially, toward the center of the body, is called varus. Knee arthritis with valgus knee Rheumatoid knee commonly presents as valgus knee. Osteoarthritis knee may also sometimes present with valgus deformity though varus deformity is common. Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) to correct valgus deformity is surgically difficult and requires specialized implants called constrained condylar knees. Examples * Ankle: ''talipes valgus'' (from Latin ''talus'' = ankle and ''pes'' = foot) – outward turning of the heel, resulting in a 'flat foot' presentation. * Elbows: '' cubitus valgus'' (from Latin ''cubitus'' = elbow) – forearm is angled away from the body. * Foot: ''pes valgus'' (from Latin ''pes'' = foot) – a medial deviation of the foot at subtalar join ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
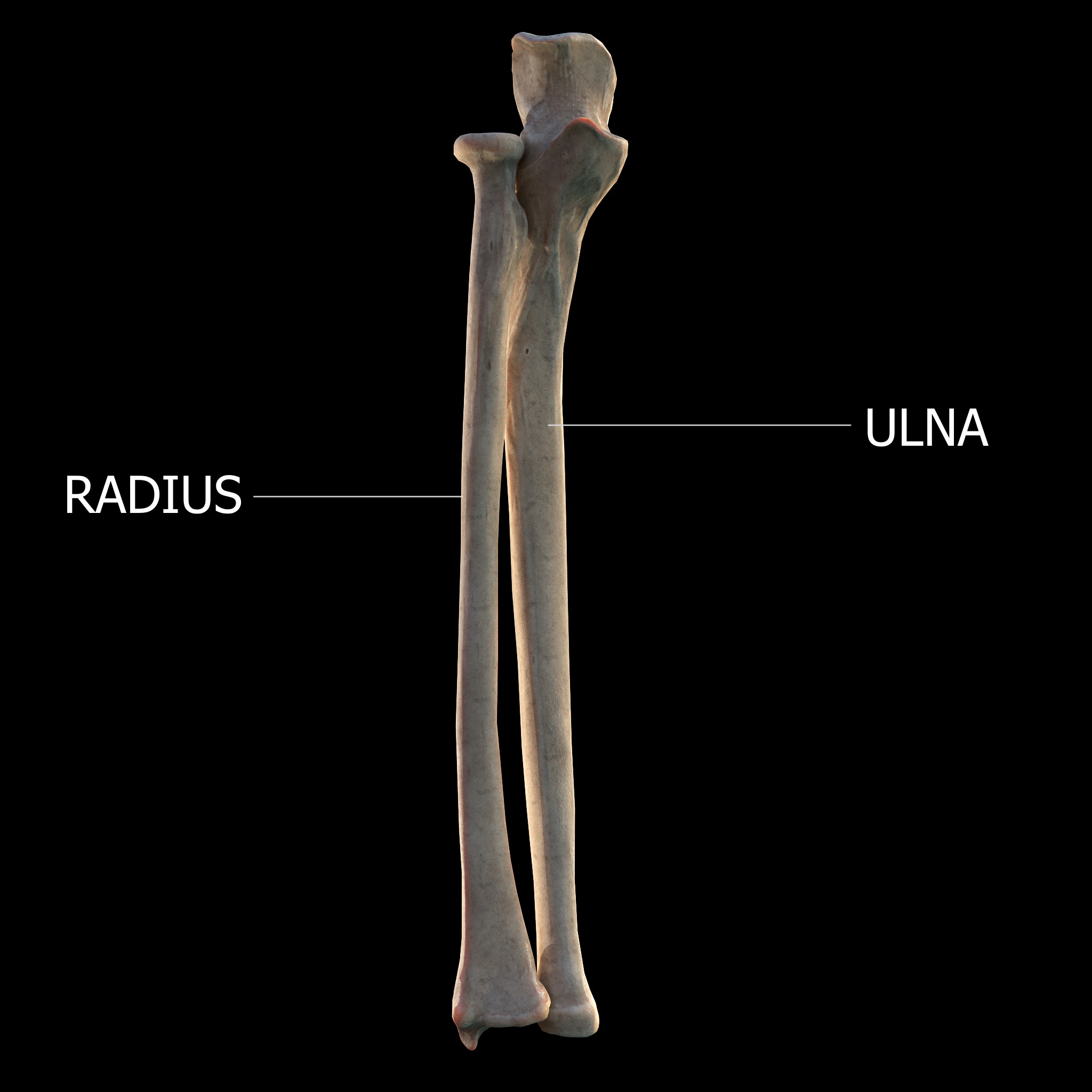
Forearm
The forearm is the region of the upper limb between the elbow and the wrist. The term forearm is used in anatomy to distinguish it from the arm, a word which is used to describe the entire appendage of the upper limb, but which in anatomy, technically, means only the region of the upper arm, whereas the lower "arm" is called the forearm. It is homologous to the region of the leg that lies between the knee and the ankle joints, the crus. The forearm contains two long bones, the radius and the ulna, forming the two radioulnar joints. The interosseous membrane connects these bones. Ultimately, the forearm is covered by skin, the anterior surface usually being less hairy than the posterior surface. The forearm contains many muscles, including the flexors and extensors of the wrist, flexors and extensors of the digits, a flexor of the elbow ( brachioradialis), and pronators and supinators that turn the hand to face down or upwards, respectively. In cross-section, the forearm can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elbow-joint
The elbow is the region between the arm, upper arm and the forearm that surrounds the elbow joint. The elbow includes prominent landmarks such as the olecranon, the cubital fossa (also called the chelidon, or the elbow pit), and the Lateral epicondyle of the humerus, lateral and the Medial epicondyle of the humerus, medial epicondyles of the humerus. The elbow joint is a hinge joint between the arm and the forearm; more specifically between the humerus in the upper arm and the radius (bone), radius and ulna in the forearm which allows the forearm and hand to be moved towards and away from the body. The term ''elbow'' is specifically used for primate, humans and other primates, and in other vertebrates it is not used. In those cases, forelimb plus joint is used. The name for the elbow in Latin is ''cubitus'', and so the word cubital is used in some elbow-related terms, as in ''cubital nodes'' for example. Structure Joint The elbow joint has three different portions surrounded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turner Syndrome
Turner syndrome (TS), commonly known as 45,X, or 45,X0,Also written as 45,XO. is a chromosomal disorder in which cells of females have only one X chromosome instead of two, or are partially missing an X chromosome (sex chromosome monosomy) leading to the complete or partial deletion of the pseudoautosomal regions (PAR1, PAR2) in the affected X chromosome. Typically, people have two sex chromosomes (XX for females or XY for males). The chromosomal abnormality is often present in just some cells, in which case it is known as Turner syndrome with mosaicism. 45,X0 with mosaicism can occur in males or females, but Turner syndrome without mosaicism only occurs in females. Signs and symptoms vary among those affected but often include additional skin folds on the neck, arched palate, low-set ears, low hairline at the nape of the neck, short stature, and lymphedema of the hands and feet. Those affected do not normally develop menstrual periods or mammary glands without hormone trea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noonan Syndrome
Noonan syndrome (NS) is a genetic disorder that may present with mildly unusual facial features, short height, congenital heart disease, bleeding problems, and skeletal malformations. Facial features include widely spaced eyes, light-colored eyes, low-set ears, a short neck, and a small lower jaw. Heart problems may include pulmonary valve stenosis. The breast bone may either protrude or be sunken, while the spine may be abnormally curved. Intelligence is often normal. Complications of NS can include leukemia. Some of NS' symptoms are shared with Watson syndrome, a related genetic condition. A number of genetic mutations can result in Noonan syndrome. The condition may be inherited as an autosomal dominant condition or occur as a new mutation. Noonan syndrome is a type of RASopathy, the underlying mechanism for which involves sustained activation of the RAS/MAPK cell signaling pathway. The diagnosis may be suspected based on symptoms, medical imaging, and blood test ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulnar Nerve Palsy
The ulna or ulnar bone (: ulnae or ulnas) is a long bone in the forearm stretching from the elbow to the wrist. It is on the same side of the forearm as the little finger, running parallel to the radius, the forearm's other long bone. Longer and thinner than the radius, the ulna is considered to be the smaller long bone of the lower arm. The corresponding bone in the lower leg is the fibula. Structure The ulna is a long bone found in the forearm that stretches from the elbow to the wrist, and when in standard anatomical position, is found on the medial side of the forearm. It is broader close to the elbow, and narrows as it approaches the wrist. Close to the elbow, the ulna has a bony process, the olecranon process, a hook-like structure that fits into the olecranon fossa of the humerus. This prevents hyperextension and forms a hinge joint with the trochlea of the humerus. There is also a radial notch for the head of the radius, and the ulnar tuberosity to which muscles attac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubitus Varus
Cubitus varus is a varus deformity in which the extended forearm is deviated towards midline of the body. Cubitus varus is often referred to as "Gunstock deformity", due to the crooked nature of the healing. The "opposite" condition is cubitus valgus. Signs and symptoms Complications Instances in which the medial epicondyle of the distal humerus is malformed due to the initial fracture at the humeral endplate may result in subluxation (snapping) of the ulnar nerve over the medial epicondyle with active flexion and extension of the elbow. In such instances, conductance of the ulnar nerve may be compromised due to chronic irritation, potentially resulting in irreversible ulnar neuropathy. Causes A common cause is a supracondylar fracture of the humerus. It can be corrected via a corrective osteotomy of the humerus and either internal or external fixation of the bone until union. Rüdiger Döhler: ''Suprakondyläre Korrekturosteotomie beim posttraumatischen Cubitus varus''. Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varus Deformity
A varus deformity is an excessive inward angulation ( medial angulation, that is, towards the body's midline) of the distal segment of a bone or joint. The opposite of varus is called valgus. The terms varus and valgus always refer to the direction that the distal segment of the joint points. For example, in a valgus deformity of the knee, the distal part of the leg below the knee is deviated ''outward, in relation to the femur,'' resulting in a '' knock-kneed'' appearance. Conversely, a ''varus'' deformity at the knee results in a '' bowlegged'' with the distal part of the leg deviated ''inward, in relation to the femur''. However, in relation to the mid-line of the body, the knee joint is deviated towards the mid-line. Terminology The terminology is made confusing by the etymology of these words. * The terms ''varus'' and ''valgus'' are both Latin, but confusingly, their Latin meanings conflict with their current usage. In current usage, as noted above, a varus deformity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |