|
Crotaline
The Crotalinae, commonly known as pit vipers,Mehrtens JM (1987). ''Living Snakes of the World in Color''. New York: Sterling Publishers. 480 pp. . or pit adders, are a subfamily of vipers found in Asia and the Americas. Like all other vipers, they are venomous. They are distinguished by the presence of a heat-sensing pit organ located between the eye and the nostril on both sides of the head. Currently, 23 genera and 155 species are recognized: These are also the only viperids found in the Americas. The groups of snakes represented here include rattlesnakes, lanceheads, and Asian pit vipers. The type genus for this subfamily is '' Crotalus'', of which the type species is the timber rattlesnake, ''C. horridus''. These snakes range in size from the diminutive hump-nosed viper, '' Hypnale hypnale'', that grows to a typical total length (including tail) of only , to the bushmaster, ''Lachesis muta'', a species known to reach a maximum total length of in length. This subfami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rattlesnake
Rattlesnakes are venomous snakes that form the genus, genera ''Crotalus'' and ''Sistrurus'' of the subfamily Crotalinae (the pit vipers). All rattlesnakes are vipers. Rattlesnakes are predators that live in a wide array of habitats, hunting small animals such as birds and rodents. Rattlesnakes receive their name from the #Rattle, rattle located at the end of their tails, which makes a loud rattling noise when tail vibration, vibrated that deters predators. Rattlesnakes are the leading contributor to snakebite injuries in North America, but rarely bite unless provoked or threatened; if treated promptly, the bites are seldom fatal. The 36 known List of rattlesnake species and subspecies, species of rattlesnakes have between 65 and 70 subspecies, all native to the Americas, ranging from central Argentina to southern Canada. The largest rattlesnake, the Eastern diamondback rattlesnake, eastern diamondback, can measure up to in length. Rattlesnakes are preyed upon by hawks, wease ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Sensing In Snakes
The ability to sense infrared thermal radiation evolved independently in three different groups of snakes, consisting of the families of Boidae (boas), Pythonidae (pythons), and the subfamily Crotalinae (pit vipers). What is commonly called a pit organ allows these animals to essentially "see" radiant heat at wavelengths between 5 and 30 μm. The more advanced infrared sense of pit vipers allows these animals to strike prey accurately even in the absence of light, and detect warm objects from several meters away. It was previously thought that the organs evolved primarily as prey detectors, but recent evidence suggests that it may also be used in thermoregulation and predator detection, making it a more general-purpose sensory organ than was supposed.Greene HW. 1992. The ecological and behavioral context for pitviper evolution. ''In'' Campbell JA, Brodie ED Jr. 1992. Biology of the Pitvipers. Texas: Selva. 467 pp. 17 plates. . Phylogeny and evolution The facial pit underwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loreal Pit
The loreal pit is the deep depression, or fossa, in the Lore (anatomy), loreal area on either side of the head in pit vipers (crotaline snakes). The area is located behind the nostril and in front of the eye, but below the line that runs between the centers of each. It is the external opening to an extremely sensitive Infrared sensing in snakes, infrared detecting organ. The loreal pit is bordered by lacunal scales. The loreal pit also functions as part of a thermal regulating system, enabling pit vipers to maintain their body temperature. References Snake anatomy {{snake-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Radiation
Infrared (IR; sometimes called infrared light) is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than that of visible light but shorter than microwaves. The infrared spectral band begins with the waves that are just longer than those of red light (the longest waves in the visible spectrum), so IR is invisible to the human eye. IR is generally (according to ISO, CIE) understood to include wavelengths from around to . IR is commonly divided between longer-wavelength thermal IR, emitted from terrestrial sources, and shorter-wavelength IR or near-IR, part of the solar spectrum. Longer IR wavelengths (30–100 μm) are sometimes included as part of the terahertz radiation band. Almost all black-body radiation from objects near room temperature is in the IR band. As a form of EMR, IR carries energy and momentum, exerts radiation pressure, and has properties corresponding to both those of a wave and of a particle, the photon. It was long known that fires emit i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timber Rattlesnake
The timber rattlesnake (''Crotalus horridus''), also known Common name, commonly as the canebrake rattlesnake and the banded rattlesnake,Albert Hazen WWright AH, species:Anna Allen WWright AA (1957). ''Handbook of Snakes of the United States and Canada''. Ithaca and London: Comstock Publishing Associates, a division of Cornell University Press. (7th printing, 1985). 1,105 pp. (in two volumes). . (''Crotalus horridus'', pp. 956–966.) is a species of Crotalinae, pit viper in the Family (biology), family Viperidae. The species is native to the eastern United States. Like all other pit vipers, it is Venomous snake, venomous, with a very toxic bite. Its venom is extremely potent, both hemorrhagic and neurotoxic venom are present depending on population and location. ''C. horridus'' is the only rattlesnake species in most of the populous Northeastern United States and is second only to its relatives to the west, the Crotalus viridis, prairie rattlesnake, as the most northerly distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebraska
Nebraska ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwest; and Wyoming to the west. Nebraska is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 16th-largest state by land area, with just over . With a population of over 2 million as of 2024, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by population, 38th-most populous state and the List of states and territories of the United States by population density, eighth-least densely populated. Its List of capitals in the United States, capital is Lincoln, Nebraska, Lincoln, and its List of municipalities in Nebraska, most populous city is Omaha, Nebraska, Omaha, which is on the Missouri River. Nebraska was admitted into the United States in 1867, two years after the end of the American Civil War. The Nebras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Miocene
The Early Miocene (also known as Lower Miocene) is a sub-epoch of the Miocene epoch (geology), Epoch made up of two faunal stage, stages: the Aquitanian age, Aquitanian and Burdigalian stages. The sub-epoch lasted from 23.03 ± 0.05 annum, Ma to 15.97 ± 0.05 Ma (million years ago). It was preceded by the Oligocene epoch. As the climate started to get cooler, the landscape started to change. New mammals evolved to replace the extinct animals of the Oligocene epoch. The first members of the hyena and weasel family started to evolve to replace the extinct ''Hyaenodon'', entelodonts and bear-dogs. The chalicotheres survived the Oligocene epoch. A new genus of entelodont called ''Daeodon'' evolved in order to adapt to the new habitats and hunt the new prey animals of the Early Miocene epoch; it quickly became the top predator of North America. But it became extinct due to competition from ''Amphicyon'', a newcomer from Eurasia. ''Amphicyon'' bested ''Daeodon'' because the bear-dog's la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rangefinder
A rangefinder (also rangefinding telemeter, depending on the context) is a device used to Length measurement, measure distances to remote objects. Originally optical devices used in surveying, they soon found applications in other fields, such as photography, the military, and space travel. They were especially useful for finding the range of a target, such as in naval gunnery and anti-aircraft artillery. The word ''telemeter'' is derived . Designs The first rangefinder telemeter was invented by James Watt in 1769 and put to use in 1771 in surveying canals. Watt called his instrument a micrometer, a term now used with a different meaning in engineering (the micrometer screw gauge). It consisted of two parallel reticle, hairs in the focal plane of a telescope eyepiece crossing an upright hair. At the point to be measured, two sliding targets on a surveyor's rod were adjusted to align with the hairs in the telescope. The distance to the rod could then be determined from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
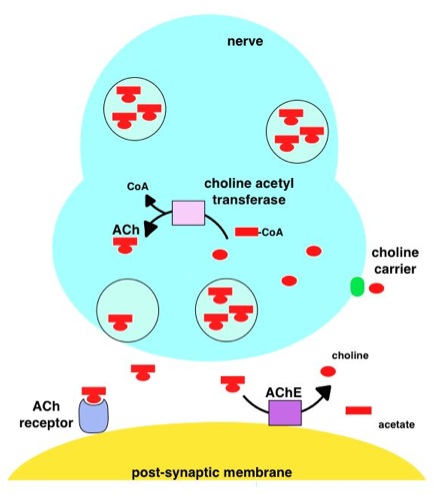
Acetylcholine Esterase
Acetylcholinesterase ( HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate cholinergic synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechanism AChE is a hydrolase that hydrolyzes choline esters. It has a very high catalytic activity—each molecule of AChE degrades about 5,000 molecules of acetylcholine (ACh) per second, approaching the limit allowed by diffusion of the substrate. The active site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Esterase
In biochemistry, an esterase is a class of enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis (and as such, it is a type of hydrolase). A wide range of different esterases exist that differ in their substrate specificity, their protein structure, and their biological function. EC classification/list of enzymes * ''EC 3.1.1'': Carboxylic ester hydrolases ** Acetylesterase (EC 3.1.1.6), splits off acetyl groups *** Cholinesterase **** Acetylcholinesterase, inactivates the neurotransmitter acetylcholine **** Pseudocholinesterase, broad substrate specificity, found in the blood plasma and in the liver ** Pectinesterase (EC 3.1.1.11), clarifies fruit juices * ''EC 3.1.2'': Thiolester hydrolases ** Thioesterase *** Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 * ''EC 3.1.3'': Phosphoric monoester hydrolases ** Phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.x), hydrolyses phosphoric acid monoesters into a phosphate ion and an alcohol *** Alkaline phosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoamine Oxidase
Monoamine oxidases (MAO) () are a family of enzymes that catalyze the oxidation of monoamines, employing oxygen to clip off their amine group. They are found bound to the outer membrane of mitochondria in most cell types of the body. The first such enzyme was discovered in 1928 by Mary Bernheim in the liver and was named tyramine oxidase. The MAOs belong to the protein family of flavin-containing amine oxidoreductases. MAOs are important in the breakdown of monoamines ingested in food, and also serve to inactivate monoamine neurotransmitters. Because of the latter, they are involved in a number of psychiatric and neurological diseases, some of which can be treated with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) which block the action of MAOs. Subtypes and tissue distribution In humans there are two types of MAO: MAO-A and MAO-B. * Both are found in neurons and astroglia. * Outside the central nervous system: ** MAO-A is also found in the liver, pulmonary vascular end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |