|
Cretic
A cretic ( ), also known as an amphimacer ( ) and sometimes paeon diagyios, is a metrical foot containing three syllables: long, short, long (– ᴗ –). In Greek poetry, lines made entirely of cretic feet are less common than other metres. An example is Alcman 58. However, any line mixing iambs and trochees could employ a cretic foot as a transition. In other words, a poetic line might have two iambs and two trochees, with a cretic foot in between. In later poets the cretic foot could be resolved into a paeonic (ᴗ ᴗ ᴗ – or – ᴗ ᴗ ᴗ) or sometimes even five short syllables (ᴗ ᴗ ᴗ ᴗ ᴗ).West (1987), p. 39. In Latin, cretics were used for composition both in comedy and tragedy. They are fairly frequent in Plautus but rarer in Terence. (See Metres of Roman comedy.) Words which include a cretic (e.g. Latin '' cīvitās'' and its various inflections) cannot be used in works composed in dactylic hexameter or dactylic pentameter. For Romance language poetry, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metres Of Roman Comedy
Roman comedy is mainly represented by two playwrights, Plautus (writing between c.205 and 184 BC) and Terence (writing c.166-160 BC). The works of other Latin playwrights such as Livius Andronicus, Naevius, Ennius, and Caecilius Statius are now lost except for a few lines quoted in other authors. 20 plays of Plautus survive complete, and 6 of Terence. Various metres are used in the plays. The most common are iambic senarii and trochaic septenarii. As far as is known, iambic senarii were spoken without music; trochaic septenarii (and also iambic septenarii and trochaic and iambic octonarii)Fortson (2008), p. 22. were chanted or recited (or possibly sung) to the sound of a pair of pipes known as (the equivalent of the Greek aulos), played by a ("piper"); and other metres were sung, possibly in an operatic style, to the same . In Plautus about 37% of lines are unaccompanied iambic senarii,A.S. Gratwick (1982), in ''The Cambridge History of Classical Literature'', vol. 2 part 1, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metrical Foot
The foot is the basic repeating rhythmic unit that forms part of a line of verse in most Indo-European traditions of poetry, including English accentual-syllabic verse and the quantitative meter of classical ancient Greek and Latin poetry. The unit is composed of syllables, and is usually two, three, or four syllables in length. The most common feet in English are the iamb, trochee, dactyl, and anapaest. The foot might be compared to a bar, or a beat divided into pulse groups, in musical notation. A metrical foot is, in classical poetry, a combination of two or more short or long syllables in a specific order; although this "does not provide an entirely reliable standard of measurement" in heavily accented Germanic languages such as English. In these languages it is defined as a combination of one stressed and one or two unstressed syllables in a specific order. In general, lines of verse can be classified according to the number of feet they contain, using the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Poetry
Folk poetry (sometimes referred to as ''poetry in action'') is poetry that is part of a society's folklore, usually part of their oral tradition. When sung, folk poetry becomes a folk song. Description Folk poetry in general has several characteristics. It may be informal and unofficial, generally lacks an owner and may "belong" to the society, and its telling may be an implicitly social activity. The term can refer to poems of an oral tradition that may date back many years; that is, it is information that has been transmitted over time (between generations) ''only'' in spoken (and non-written) form. Thus as an oral tradition folk poetry requires a performer to promulgate it over generations. The definition can also be extended to include not just oral epics, but latrinalia, many forms of childlore (skipping-rope rhymes, the words of counting-out games etc.), and limericks; as well as including anonymous or improvised poems. Narrative folk poetry is often characterized by repetit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Advertising
Advertising is the practice and techniques employed to bring attention to a Product (business), product or Service (economics), service. Advertising aims to present a product or service in terms of utility, advantages, and qualities of interest to Consumer, consumers. It is typically used to promote a specific good or service, but there are a wide range of uses, the most common being commercial advertisement. Commercial advertisements often seek to generate increased Consumption (economics), consumption of their products or services through "Branding (promotional), branding", which associates a product name or image with certain qualities in the minds of consumers. On the other hand, ads that intend to elicit an immediate sale are known as Direct marketing, direct-response advertising. Non-commercial entities that advertise more than consumer products or services include Political party, political parties, Interest group, interest groups, Religious organization, religious o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antithesis
Antithesis (: antitheses; Greek for "setting opposite", from "against" and "placing") is used in writing or speech either as a proposition that contrasts with or reverses some previously mentioned proposition, or when two opposites are introduced together for contrasting effect. Antithesis can be defined as "a figure of speech involving a seeming contradiction of ideas, words, clauses, or sentences within a balanced grammatical structure. Parallelism of expression serves to emphasize opposition of ideas". An antithesis must always contain two ideas within one statement. The ideas may not be structurally opposite, but they serve to be functionally opposite when comparing two ideas for emphasis. According to Aristotle, the use of an antithesis makes the audience better understand the point the speaker is trying to make. Further explained, the comparison of two situations or ideas makes choosing the correct one simpler. Aristotle states that antithesis in rhetoric is similar to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 23 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's national poet and the "Bard of River Avon, Warwickshire, Avon" or simply "the Bard". His extant works, including William Shakespeare's collaborations, collaborations, consist of some Shakespeare's plays, 39 plays, Shakespeare's sonnets, 154 sonnets, three long narrative poems and a few other verses, some of uncertain authorship. His plays List of translations of works by William Shakespeare, have been translated into every major modern language, living language and are performed more often than those of any other playwright. Shakespeare remains arguably the most influential writer in the English language, and his works continue to be studied and reinterpreted. Shakespeare was born and raised in Stratford-upon-Avon, Warwickshire. At the age of 18 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dimeter
In poetry, a dimeter is a metrical line of verse with two feet. The particular foot The foot (: feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is an organ at the terminal part of the leg made up o ... can vary. Consider Thomas Hood's " Bridge of Sighs," in which the first line of a pair is of two feet, each composed of three syllables, and the subsequent line is of two feet, each of two syllables. :Take her up \\ tenderly, :Lift her \\ with care, :Fashioned so \\ slenderly, :Young and \\ so fair. Also, the first line of William Wordsworth's "We Are Seven": :A simp \\ le Child References Types of verses {{Poetry-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Renaissance
The English Renaissance was a Cultural movement, cultural and Art movement, artistic movement in England during the late 15th, 16th and early 17th centuries. It is associated with the pan-European Renaissance that is usually regarded as beginning in Italy in the late 14th century. As in most of the rest of Northern Europe, England saw little of these developments until more than a century later within the Northern Renaissance. Renaissance style and ideas were slow to penetrate England, and the Elizabethan era in the second half of the 16th century is usually regarded as the height of the English Renaissance. Many scholars see its beginnings in the early 16th century during the reign of Henry VIII. Others argue the Renaissance was already present in England in the late 15th century. The English Renaissance is different from the Italian Renaissance in several ways. The dominant art forms of the English Renaissance were literature and music. Visual arts in the English Renaissance w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Poetry
This article focuses on poetry from the United Kingdom written in the English language. The article does not cover poetry from other countries where the English language is spoken, including the Republic of Ireland after December 1922. The earliest surviving English poetry, written in Old English language, Anglo-Saxon, the direct predecessor of modern English, may have been composed as early as the 7th century. The earliest English poetry The earliest known English poem is a hymn on the creation; Bede attributes this to C√¶dmon (floruit, fl. 658–680), who was, according to legend, an illiterate herdsman who produced extemporaneous poetry at a monastery at Whitby. This is generally taken as marking the beginning of Old English poetry, Anglo-Saxon poetry. Much of the poetry of the period is difficult to date, or even to arrange chronologically; for example, estimates for the date of the great epic ''Beowulf'' range from A.D. 608 right through to A.D. 1000, and there has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proverb
A proverb (from ) or an adage is a simple, traditional saying that expresses a perceived truth based on common sense or experience. Proverbs are often metaphorical and are an example of formulaic speech, formulaic language. A proverbial phrase or a proverbial expression is a type of a conventional saying similar to proverbs and transmitted by oral tradition. The difference is that a proverb is a fixed expression, while a proverbial phrase permits alterations to fit the grammar of the context. Collectively, they form a folklore genre, genre of folklore. Some proverbs exist in more than one language because people borrow them from languages and cultures with which they are in contact. In the West, the Bible (including, but not limited to the Book of Proverbs) and medieval Latin (aided by the work of Erasmus) have played a considerable role in distributing proverbs. Not all Biblical proverbs, however, were distributed to the same extent: one scholar has gathered evidence to show th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dactylic Pentameter
The dactylic pentameter is a verse-form which, in classical Greek and Latin poetry, follows a dactylic hexameter to make up an elegiac couplet. It features two halves, each consisting of two dactyls, for which spondees can be substituted in the first half only, followed by a longum. Thus the line most normally looks as follows (note that "—" marks a long syllable, "∪" a short syllable and " ∪ ∪ " either one long or two shorts): , — ∪ ∪ , — ∪ ∪ , — , , — ∪ ∪ , — ∪ ∪ , — As in all classical verse-forms, the phenomenon of brevis in longo is observed, so the last syllable can actually be short or long. Also, the line has a diaeresis, where a word boundary must occur, after the first half-line, here marked , , . "Pentameter" may seem a slightly strange term for this meter, as it seems to have six parts, but the reason is that each half of the line has two and a half feet, the two together thus making up five. Each half-line is call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
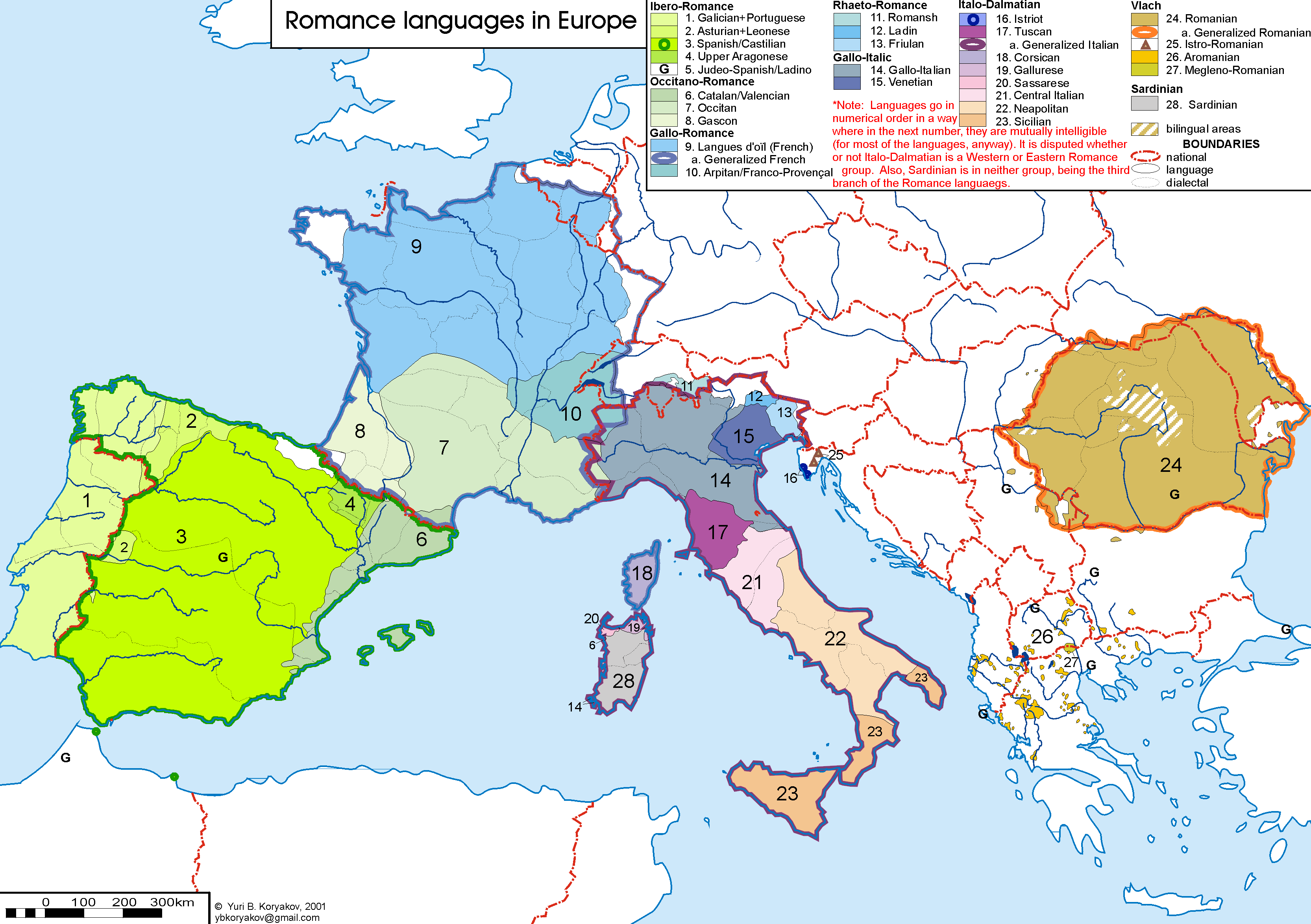
Romance Language
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. The five list of languages by number of native speakers, most widely spoken Romance languages by number of native speakers are: * Spanish language, Spanish (489 million): official language in Spain, Mexico, Equatorial Guinea, the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, SADR, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Puerto Rico and most of Central America, Central and South America * French language, French (310 million): official in 26 countries * Portuguese language, Portuguese (240 million): official in Portugal, Brazil, Portuguese-speaking African countries, Portuguese-speaking Africa, Timor-Leste and Macau * Italian language, Italian (67 million): official in Italy, Vatican City, San Marino, Switzerland; mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |