|
Crescentin
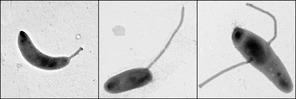
Crescentin is a protein which is a bacterial relative of the intermediate filaments found in eukaryotic cells. Just as tubulins and actins, the other major cytoskeletal proteins, have prokaryotic homologs in, respectively, the FtsZ and MreB proteins, intermediate filaments are linked to the crescentin protein. Some of its homologs are erroneously labelled Chromosome segregation protein ParA. This protein family is found in '' Caulobacter'' and '' Methylobacterium''. Role in cell shape Crescentin was discovered in 2009 by Christine Jacobs-Wagner in ''Caulobacter crescentus'' (now ''vibrioides''), an aquatic bacterium which uses its crescent-shaped cells for enhanced motility. The crescentin protein is located on the concave face of these cells and appears to be necessary for their shape, as mutants lacking the protein form rod-shaped cells. To influence the shape of the ''Caulobacter'' cells, the helices of crescentin filaments associate with the cytoplasmic side of the cell me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caulobacter Crescentus
''Caulobacter crescentus'' is a Gram-negative, oligotrophic bacterium widely distributed in fresh water lakes and streams. The taxon is more properly known as ''Caulobacter vibrioides'' (Henrici and Johnson 1935). ''C. crescentus'' is an important model organism for studying the regulation of the cell cycle, asymmetric cell division, and cellular differentiation. ''Caulobacter'' daughter cells have two very different forms. One daughter is a mobile "swarmer" cell that has a single flagellum at one cell pole that provides swimming motility for chemotaxis. The other daughter, called the "stalked" cell, has a tubular stalk structure protruding from one pole that has an adhesive holdfast material on its end, with which the stalked cell can adhere to surfaces. Swarmer cells differentiate into stalked cells after a short period of motility. Chromosome replication and cell division only occurs in the stalked cell stage. ''C. crescentus'' derives its name from its crescent shape, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intermediate Filaments
Intermediate filaments (IFs) are cytoskeletal structural components found in the cells of vertebrates, and many invertebrates. Homologues of the IF protein have been noted in an invertebrate, the cephalochordate ''Branchiostoma''. Intermediate filaments are composed of a family of related proteins sharing common structural and sequence features. Initially designated 'intermediate' because their average diameter (10 nm) is between those of narrower microfilaments (actin) and wider myosin filaments found in muscle cells, the diameter of intermediate filaments is now commonly compared to actin microfilaments (7 nm) and microtubules (25 nm). Animal intermediate filaments are subcategorized into six types based on similarities in amino acid sequence and protein structure. Most types are cytoplasmic, but one type, Type V is a nuclear lamin. Unlike microtubules, IF distribution in cells shows no good correlation with the distribution of either mitochondria or endop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a complex, dynamic network of interlinking protein filaments present in the cytoplasm of all cells, including those of bacteria and archaea. In eukaryotes, it extends from the cell nucleus to the cell membrane and is composed of similar proteins in the various organisms. It is composed of three main components: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules, and these are all capable of rapid growth and or disassembly depending on the cell's requirements. Cytoskeleton can perform many functions. Its primary function is to give the cell its shape and mechanical resistance to deformation, and through association with extracellular connective tissue and other cells it stabilizes entire tissues. The cytoskeleton can also contract, thereby deforming the cell and the cell's environment and allowing cells to migrate. Moreover, it is involved in many cell signaling pathways and in the uptake of extracellular material ( endocytosis), the segregation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christine Jacobs-Wagner
Christine Jacobs-Wagner is a microbial molecular biologist. She is the Dennis Cunningham Professor of Biology and Microbiology and Immunology at Stanford University. Jacobs-Wagner's research has shown that bacterial cells have a great deal of substructure, including analogs of microfilaments, and that proteins are directed by regulatory processes to locate to specific places within the bacterial cell. She was elected to the National Academy of Sciences in 2015 and has received a number of scientific awards. Early life and education Christine Jacobs-Wagner grew up in Belgium in a town near Liege. She thought of becoming a cyclist or a badminton Olympian, but was undecided about a career through high school. Jacobs-Wagner received her BS degree in biochemistry from the University of Liege; she also received her MS in 1991 and her PhD in 1996 from the University of Liege in the field of biochemistry. She subsequently worked with Lucy Shapiro at Stanford Medical School on a fello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutants
In biology, and especially in genetics, a mutant is an organism or a new genetic character arising or resulting from an instance of mutation, which is generally an alteration of the DNA sequence of the genome or chromosome of an organism. It is a characteristic that would not be observed naturally in a specimen. The term mutant is also applied to a virus with an alteration in its nucleotide sequence whose genome is in the nuclear genome. The natural occurrence of genetic mutations is integral to the process of evolution. The study of mutants is an integral part of biology; by understanding the effect that a mutation in a gene has, it is possible to establish the normal function of that gene. Mutants arise by mutation Mutants arise by mutations occurring in pre-existing genomes as a result of errors of DNA replication or errors of DNA repair. Errors of replication often involve translesion synthesis by a DNA polymerase when it encounters and bypasses a damaged base in the templ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of biological populations over successive generations. It occurs when evolutionary processes such as natural selection and genetic drift act on genetic variation, resulting in certain characteristics becoming more or less common within a population over successive generations. The process of evolution has given rise to biodiversity at every level of biological organisation. The scientific theory of evolution by natural selection was conceived independently by two British naturalists, Charles Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace, in the mid-19th century as an explanation for why organisms are adapted to their physical and biological environments. The theory was first set out in detail in Darwin's book '' On the Origin of Species''. Evolution by natural selection is established by observable facts about living organisms: (1) more offspring are often produced than can possibly survive; (2) traits vary among individuals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning ''in glass'', or ''in the glass'') Research, studies are performed with Cell (biology), cells or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called "test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, ''in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, known as clinical trials, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' (Latin language, Latin for "in glass"; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanosine Triphosphate
Guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) is a purine nucleoside triphosphate. It is one of the building blocks needed for the synthesis of RNA during the transcription process. Its structure is similar to that of the guanosine nucleoside, the only difference being that nucleotides like GTP have phosphates on their ribose sugar. GTP has the guanine nucleobase attached to the 1' carbon of the ribose and it has the triphosphate moiety attached to ribose's 5' carbon. It also has the role of a source of energy or an activator of substrates in metabolic reactions, like that of ATP, but more specific. It is used as a source of energy for protein synthesis and gluconeogenesis. GTP is essential to signal transduction, in particular with G-proteins, in second-messenger mechanisms where it is converted to guanosine diphosphate (GDP) through the action of GTPases. Uses Energy transfer GTP is involved in energy transfer within the cell. For instance, a GTP molecule is generated by one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is a nucleoside triphosphate that provides energy to drive and support many processes in living cell (biology), cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, it is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" for intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in a Metabolism, metabolic process, ATP converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. It is also a Precursor (chemistry), precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. An average adult human processes around 50 kilograms (about 100 mole (unit), moles) daily. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of three parts: a sugar, an amine base ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanobody
A single-domain antibody (sdAb), also known as a Nanobody, is an antibody fragment consisting of a single monomeric variable antibody domain. Like a whole antibody, it is able to bind selectively to a specific antigen. With a molecular weight of only 12–15 kDa, single-domain antibodies (sdAbs) are much smaller than common antibodies (150–160 kDa) which are composed of two heavy protein chains and two light chains, and even smaller than Fab fragments (~50 kDa, one light chain and half a heavy chain) and single-chain variable fragments (~25 kDa, two variable domains, one from a light and one from a heavy chain). The first single-domain antibodies were engineered from heavy-chain antibodies found in camelids at the Université Libre de Bruxelles; these are called VHH fragments. Cartilaginous fishes also have heavy-chain antibodies (IgNAR, 'immunoglobulin new antigen receptor'), from which single-domain antibodies called VNAR fragments can be obtained. An alternative approach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cryo-EM
Cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is a transmission electron microscopy technique applied to samples cooled to cryogenic temperatures. For biological specimens, the structure is preserved by embedding in an environment of vitreous ice. An aqueous sample solution is applied to a grid-mesh and plunge-frozen in liquid ethane or a mixture of liquid ethane and propane. While development of the technique began in the 1970s, recent advances in detector technology and software algorithms have allowed for the determination of biomolecular structures at near-atomic resolution. This has attracted wide attention to the approach as an alternative to X-ray crystallography or NMR spectroscopy in the structural biology field. In 2017, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Jacques Dubochet, Joachim Frank, and Richard Henderson "for developing cryo-electron microscopy for the high-resolution structure determination of biomolecules in solution." '' Nature Methods'' also named cryo- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
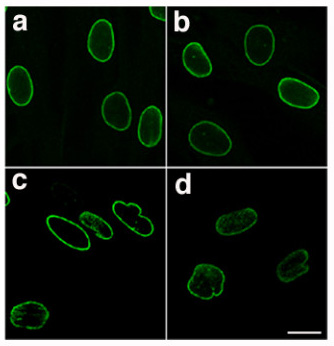
Lamin
Lamins, also known as nuclear lamins, are fibrous proteins in Intermediate filament#Type V – nuclear lamins, type V intermediate filaments, providing structural function and Transcription (biology), transcriptional regulation in the cell nucleus. Nuclear lamins interact with inner nuclear membrane proteins to form the nuclear lamina on the interior of the nuclear envelope. Lamins have elastic and mechanosensitive properties, and can alter Regulation of gene expression, gene regulation in a feedback response to mechanical cues. Lamins are present in all animals but are not found in microorganisms, plants or Fungus, fungi. Lamin proteins are involved in the disassembling and reforming of the nuclear envelope during mitosis, the positioning of nuclear pores, and programmed cell death. Mutations in lamin genes can result in several Genetic disorder, genetic Laminopathy, laminopathies, which may be life-threatening. History Lamins were first identified in the cell nucleus, using E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |