|
Crawlspace
A crawl space or crawlspace is an unoccupied, unfinished, narrow space within a building, between the ground and the first (or ground) floor. The crawl space is so named because there is typically only enough room to crawl rather than stand; anything larger than about and beneath the ground floor would tend to be considered a basement. Uses In the USA, a crawl space is often built when building a basement would be impractical. A crawl space can also substitute for a concrete slab foundation that would hinder building inspections. The crawl space's functions include providing access to repair plumbing, electrical wiring, and heating and cooling systems without the need for excavation. Building insulation can also be installed in a crawl space. The crawl space can provide a protective buffer between the damp ground and the wooden parts of a home and, with adequate sealing, help with radon mitigation. Crawl spaces are also sometimes used for storage of items such as canned goo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radon Mitigation
Radon mitigation is any process used to reduce radon gas concentrations in the breathing zones of occupied buildings, or radon from water supplies. Radon is a significant contributor to environmental radioactivity and indoor air pollution. Exposure to radon can cause serious health problems such as lung cancer. Mitigation of radon in the air by active soil depressurization is most effective. Concrete slabs, sub-floors, and/or crawlspaces are sealed, an air pathway is then created to exhaust radon above the roof-line, and a radon mitigation fan is installed to run permanently. In particularly troublesome dwellings, air exchangers can be used to reduce indoor radon concentrations. Treatment systems using aeration or activated charcoal are available to remove radon from domestic water supplies. There is no proven link between radon in water and gastrointestinal cancers; however, extremely high radon concentrations in water can be aerosolized by faucets and shower heads and contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete Slab
A concrete slab is a common structural element of modern buildings, consisting of a flat, horizontal surface made of cast concrete. Steel- reinforced slabs, typically between 100 and 500 mm thick, are most often used to construct floors and ceilings, while thinner ''mud slabs'' may be used for exterior paving . In many domestic and industrial buildings, a thick concrete slab supported on foundations or directly on the subsoil, is used to construct the ground floor. These slabs are generally classified as ''ground-bearing'' or ''suspended''. A slab is ground-bearing if it rests directly on the foundation, otherwise the slab is suspended. For multi-story buildings, there are several common slab designs : * Beam and block, also referred to as ''rib and block'', is mostly used in residential and industrial applications. This slab type is made up of pre-stressed beams and hollow blocks and are temporarily propped until set, typically after 21 days. * A hollow core slab which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dehumidifier
A dehumidifier is an air conditioning device which reduces and maintains the level of humidity in the air. This is done usually for health or thermal comfort reasons or to eliminate musty odor and to prevent the growth of mildew by extracting water from the air. It can be used for household, commercial, or industrial applications. Large dehumidifiers are used in commercial buildings such as indoor ice rinks and swimming pools, as well as manufacturing plants or storage warehouses. Typical air conditioning systems combine dehumidification with cooling, by operating cooling coils below the dewpoint and draining away the water that condensation, condenses. Dehumidifiers extract water from air that passes through the unit. There are two common types of dehumidifiers: condensate dehumidifiers and desiccation , desiccant dehumidifiers, and there are also other emerging designs. Condensate dehumidifiers use a refrigeration cycle to collect water known as condensate, which is normally co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
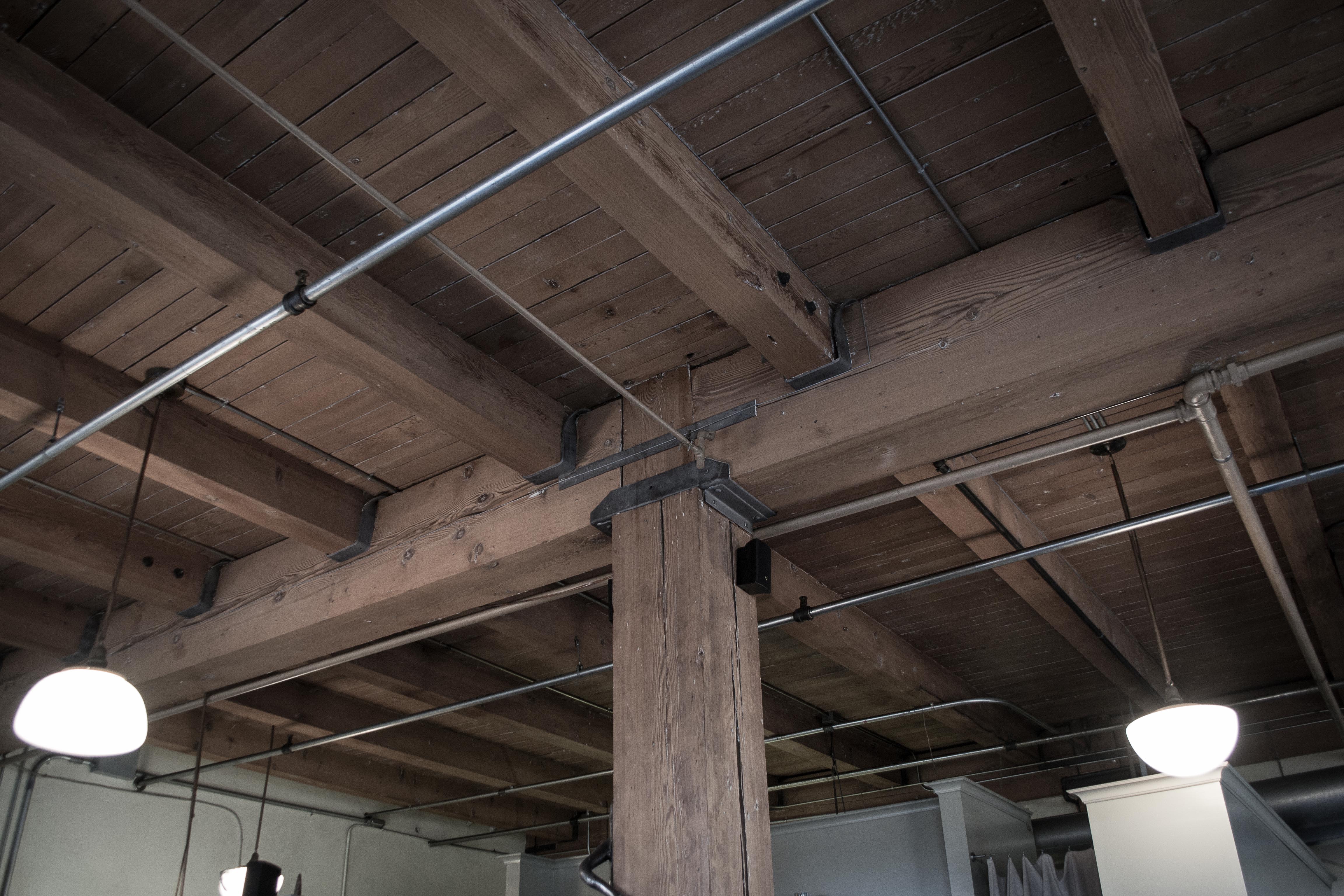
Joist
A joist is a horizontal structural member used in Framing (construction), framing to span an open space, often between Beam (structure), beams that subsequently transfer loads to vertical members. When incorporated into a floor framing system, joists serve to provide stiffness to the subfloor sheathing, allowing it to function as a horizontal Diaphragm (structural system), diaphragm. Joists are often doubled or tripled, placed side by side, where conditions warrant, such as where wall partitions require support. Joists are either made of wood, engineered wood, or steel, each of which has unique characteristics. Typically, wood joists have the Cross section (geometry), cross section of a Plank (wood), plank with the longer faces positioned vertically. However, engineered wood joists may have a cross section resembling the Roman capital letter ""; these joists are referred to as I-joist, -joists. Steel joists can take on various shapes, resembling the Roman capital letters "C", "", " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, dew, or fog to be present. Humidity depends on the temperature and pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is the dew point. The amount of water vapor needed to achieve saturation increases as the temperature increases. As the temperature of a parcel of air decreases it will eventually reach the saturation point without adding or losing water mass. The amount of water vapor contained within a parcel of air can vary significantly. For example, a parcel of air near saturation may contain 8 g of water per cubic metre of air at , and 28 g of water per cubic metre of air at Three primary measurements of humidity are widely employed: abso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
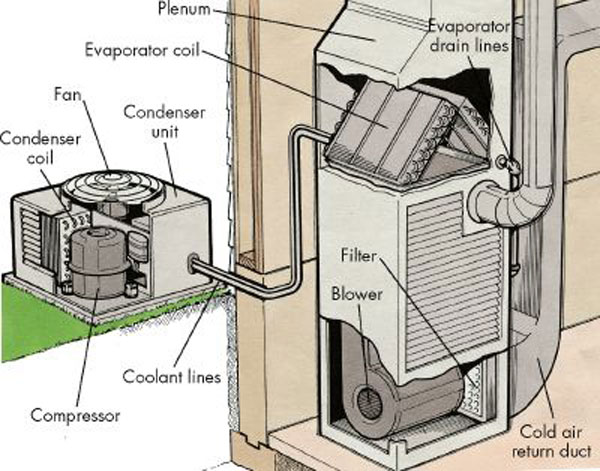
HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC ) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HVAC system design is a subdiscipline of mechanical engineering, based on the principles of thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and heat transfer. "Refrigeration" is sometimes added to the field's abbreviation as HVAC&R or HVACR, or "ventilation" is dropped, as in HACR (as in the designation of HACR-rated circuit breakers). HVAC is an important part of residential structures such as single family homes, apartment buildings, hotels, and senior living facilities; medium to large industrial and office buildings such as skyscrapers and hospitals; vehicles such as cars, trains, airplanes, ships and submarines; and in marine environments, where safe and healthy building conditions are regulated with respect to temperature and humidity, using fres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
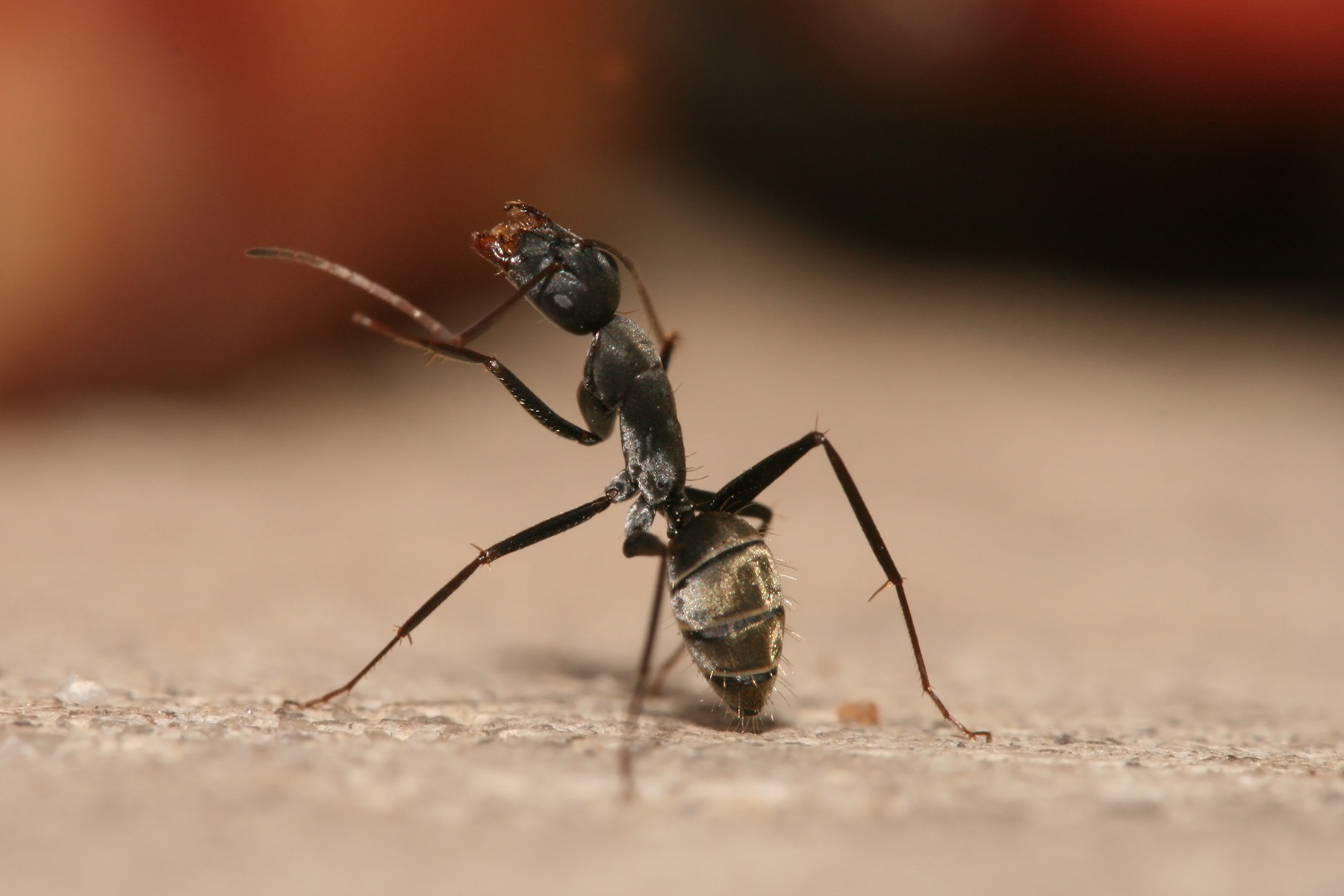
Carpenter Ant
Carpenter ants (''Camponotus'' spp.) are a genus of large ants (workers ) indigenous to many parts of the world. True carpenter ants build nests inside wood, consisting of galleries chewed out with their mandibles or jaws, preferably in dead, damp wood. However, unlike termites, they do not consume wood, but instead discard a material that resembles sawdust outside their nest. Sometimes, carpenter ants hollow out sections of trees. They also commonly infest wooden buildings and structures, causing a widespread problem: they are a major cause of structural damage. Nevertheless, their ability to excavate wood helps in forest decomposition. The genus includes over 1,000 species. They also farm aphids. In their farming, the ants protect the aphids from predators (usually other insects) while they excrete a sugary fluid called honeydew, which the ants get by stroking the aphids with their antennae. Description Carpenter ants are generally large ants: workers are usually 4–7&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Termite
Termites are a group of detritivore, detritophagous Eusociality, eusocial cockroaches which consume a variety of Detritus, decaying plant material, generally in the form of wood, Plant litter, leaf litter, and Humus, soil humus. They are distinguished by their moniliform antennae and the soft-bodied, unpigmented worker caste for which they have been commonly termed "white ants"; however, they are not ants but highly Apomorphy and synapomorphy, derived cockroaches. About 2,997 extant species are currently described, 2,125 of which are members of the family Termitidae. Termites comprise the infraorder Isoptera, or alternatively the Taxonomic rank#All ranks, epifamily Termitoidae, within the order Blattodea (the cockroaches). Termites were once classified in a separate Order (biology), order from cockroaches, but recent phylogenetic studies indicate that they evolved from cockroaches, as they are deeply nested within the group, and the sister group to wood-eating cockroaches of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
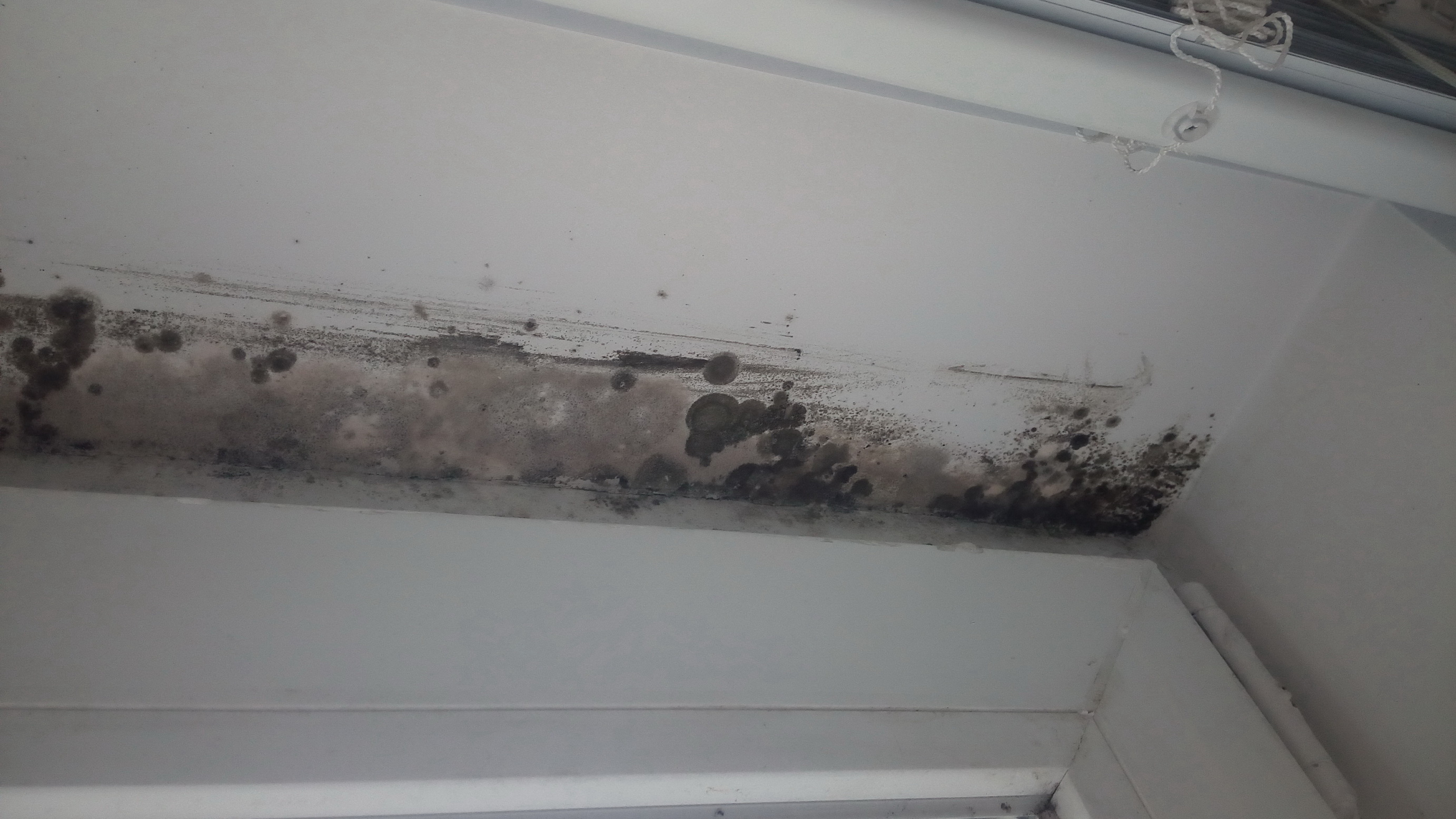
Indoor Mold
Indoor mold (American English) or indoor mould (British English), also sometimes referred to as mildew, is a fungal growth that develops on wet materials in interior spaces. Mold is a natural, ubiquitous part of the environment and plays an important part in nature by breaking down dead organic matter such as fallen leaves and dead trees; indoors, mold growth should be avoided as it can affect the structural integrity of buildings and pose potential health risks to susceptible individuals. Mold reproduces by means of tiny spores, which range in size from 1 to 40 microns. The spores are like seeds, but invisible to the naked eye, that float through the air and deposit on surfaces. When the temperature, moisture, and available nutrient conditions are correct, the spores can form into new mold colonies where they are deposited. There are many types of mold, but all require moisture and a food source for growth. Common indoor molds include Aspergillus, Cladosporium, Penicillium, and St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |