|
Crank Journal
A crankpin or crank pin, also known as a rod bearing journal, is a mechanical device in an engine which connects the crankshaft to the connecting rod for each cylinder. It has a cylindrical surface, to allow the crankpin to rotate relative to the "big end" of the connecting rod. The most common configuration is for a crankpin to serve one cylinder. However, many V engines have each crankpin shared by each pair of cylinders. Design The crankpin connects to the larger end of the connecting rod for each cylinder. This end of the connecting rod is called the "big end", as opposed to the "small end" or "little end" (which connects to the wrist/gudgeon pin in the piston). The bearing which allows the crankpin to rotate around its shaft is called the "rod bearing". In automotive engines, the most common type of rod bearing is the plain bearing, however bushings or roller bearings are also used in some engines. Configurations In a single-cylinder engine, straight engine or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radial Engine
The radial engine is a reciprocating engine, reciprocating type internal combustion engine, internal combustion engine configuration in which the cylinder (engine), cylinders "radiate" outward from a central crankcase like the spokes of a wheel. It resembles a stylized Star polygon, star when viewed from the front, and is called a "star engine" in some other languages. The radial configuration was commonly used for aircraft engines before gas turbine engines became predominant. Engine operation Since the axes of the cylinders are coplanar, the connecting rods cannot all be directly attached to the crankshaft unless mechanically complex forked connecting rods are used, none of which have been successful. Instead, the pistons are connected to the crankshaft with a master-and-articulating-rod assembly. One piston, the uppermost one in the animation, has a master rod with a direct attachment to the crankshaft. The remaining pistons pin their connecting rods' attachments to rings ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slider-crank Linkage
A slider-crank linkage (also commonly referred to as a crank-slider linkage) is a four-link mechanism with three revolute joint, revolute joints and one prismatic joint, prismatic (sliding) joint. The naming convention of slider-crank and crank-slider is generally used to refer to the functional [input]-[output] of the linkage. In a crank-slider, the rotation of the crank (mechanism), crank drives the linear movement of the slider, and in a slider-crank, the expansion of gases against a sliding piston in a cylinder can drive the rotation of the crank. There are two types of slider-cranks: in-line and offset. # In-line: An in-line slider-crank has its slider positioned so the line of travel of the hinged joint of the slider passes through the base joint of the crank. This creates a symmetric slider movement back and forth as the crank rotates. # Offset: If the line of travel of the hinged joint of the slider does not pass through the base pivot of the crank, the slider movemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crank (mechanism)
A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod). The term often refers to a human-powered crank which is used to manually turn an axle, as in a bicycle crankset or a brace and bit drill. In this case a person's arm or leg serves as the connecting rod, applying reciprocating force to the crank. There is usually a bar perpendicular to the other end of the arm, often with a freely rotatable handle or pedal attached. Examples Familiar examples include: Hand-powered cranks * Spinning wheel * Mechanical pencil sharpener * Fishing reel and other reels for cables, wires, ropes, etc. *Starti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piston (technology)
A piston is a component of reciprocating engines, reciprocating pumps, gas compressors, hydraulic cylinders and pneumatic cylinders, among other similar mechanisms. It is the moving component that is contained by a cylinder (engine), cylinder and is made gas-tight by piston rings. In an engine, its purpose is to transfer force from expanding gas in the cylinder to the crankshaft via a piston rod and/or connecting rod. In a pump, the function is reversed and force is transferred from the crankshaft to the piston for the purpose of compressing or ejecting the fluid in the cylinder. In some engines, the piston also acts as a valve by covering and uncovering Porting (engine)#Two-stroke porting, ports in the cylinder. __TOC__ Piston engines Internal combustion engines An internal combustion piston engine, internal combustion engine is acted upon by the pressure of the expanding combustion gases in the combustion chamber space at the top of the cylinder. This force then acts dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroke (mechanics)
In the context of an internal combustion engine, the term stroke has the following related meanings: * A phase of the engine's cycle (e.g. compression stroke, exhaust stroke), during which the piston travels from top to bottom or vice versa. * The type of power cycle used by a piston engine (e.g. two-stroke engine, four-stroke engine). * "Stroke length", the distance travelled by the piston during each cycle. The stroke length, along with bore (engine), bore diameter, determines the engine's engine displacement, displacement. Phases in the power cycle Commonly used engine phases or strokes (i.e. those used in a four-stroke engine) are described below. Other types of engines can have very different phases. Induction-intake stroke The induction stroke is the first phase in a four-stroke (e.g. Otto cycle or Diesel cycle) engine. It involves the downward movement of the piston, creating a partial vacuum that draws an air-fuel mixture (or air alone, in the case of a direct injec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crank Drive
A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod). The term often refers to a human-powered crank which is used to manually turn an axle, as in a bicycle crankset or a brace and bit drill. In this case a person's arm or leg serves as the connecting rod, applying reciprocating force to the crank. There is usually a bar perpendicular to the other end of the arm, often with a freely rotatable handle or pedal attached. Examples Familiar examples include: Hand-powered cranks * Spinning wheel * Mechanical pencil sharpener * Fishing reel and other reels for cables, wires, ropes, etc. *Starting handl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
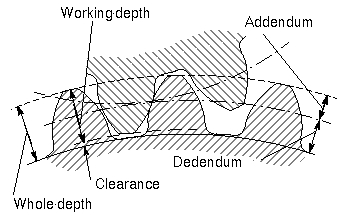
Offset (gears)
This page lists the standard US nomenclature used in the description of mechanical gear construction and function, together with definitions of the terms. The terminology was established by the American Gear Manufacturers Association (AGMA), under accreditation from the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Addendum The addendum is the height by which a tooth of a gear projects beyond (outside for external, or inside for internal) the standard pitch circle or pitch line; also, the radial distance between the pitch diameter and the outside diameter. Addendum angle Addendum angle in a bevel gear, is the angle between face cone and pitch cone. Addendum circle The addendum circle coincides with the tops of the teeth of a gear and is concentric with the standard (reference) pitch circle and radially distant from it by the amount of the addendum. For external gears, the addendum circle lies on the outside cylinder while on internal gears the addendum circle lies on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steel
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon that demonstrates improved mechanical properties compared to the pure form of iron. Due to steel's high Young's modulus, elastic modulus, Yield (engineering), yield strength, Fracture, fracture strength and low raw material cost, steel is one of the most commonly manufactured materials in the world. Steel is used in structures (as concrete Rebar, reinforcing rods), in Bridge, bridges, infrastructure, Tool, tools, Ship, ships, Train, trains, Car, cars, Bicycle, bicycles, Machine, machines, Home appliance, electrical appliances, furniture, and Weapon, weapons. Iron is always the main element in steel, but other elements are used to produce various grades of steel demonstrating altered material, mechanical, and microstructural properties. Stainless steels, for example, typically contain 18% chromium and exhibit improved corrosion and Redox, oxidation resistance versus its carbon steel counterpart. Under atmospheric pressures, steels generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheel
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle Bearing (mechanical), bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the Simple machine, six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be moved easily facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Wheels are also used for other purposes, such as a ship's wheel, steering wheel, potter's wheel, and flywheel. Common examples can be found in transport applications. A wheel reduces friction by facilitating motion by rolling together with the use of axles. In order for a wheel to rotate, a Moment (physics), moment must be applied to the wheel about its axis, either by gravity or by the application of another external force or torque. Terminology The English word '':wikt:wheel, wheel'' comes from the Old English word , from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cylinder (engine)
In an engine, the cylinder is the space in which a piston travels. The inner surface of the cylinder is formed from either a thin metallic liner (also called "sleeve") or a surface coating applied to the engine block. A piston is seated inside each cylinder by several metal piston rings, which also provide seals for compression and the lubricating oil. The piston rings do not actually touch the cylinder walls, instead they ride on a thin layer of lubricating oil. Steam engines The cylinder in a steam engine is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in cast iron and later in steel. The cylinder casting can include other features such as valve ports and mounting feet. Internal combustion engines The cylinder is the space through which the piston travels, propelled by the energy generated from the combustion of the air/fuel mixture in the combustion chamber. In an air-cooled e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the crankshaft. The connecting rod is required to transmit the compressive and tensile forces from the piston. In its most common form, in an internal combustion engine, it allows pivoting on the piston end and rotation on the shaft end. The predecessor to the connecting rod is a mechanic linkage used by water mills to convert rotating motion of the water wheel into reciprocating motion. The most common usage of connecting rods is in internal combustion engines or on steam engines. __TOC__ Origins A connecting rod crank has been found in the Celtic Oppida at Paule in Brittany, dated to 69 BC. The predecessor to the connecting length is the mechanical linkage used by Roman-era watermills. An early example of this linkage has been found at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |