|
Covarion
{, class="wikitable" align="right" , - ! ! colspan=4 , Rate = 1 ! colspan=4 , Rate = 0 , - , , A1 , G1 , C1 , T1 , A0 , G0 , C0 , T0 , - , A1 , – , α , β , γ , δ , 0 , 0 , 0 , - , G1 , α , – , γ , β , 0 , δ , 0 , 0 , - , C1 , β , γ , – , α , 0 , 0 , δ , 0 , - , T1 , γ , β , α , – , 0 , 0 , 0 , δ , - , A0 , κδ , 0 , 0 , 0 , – , 0 , 0 , 0 , - , G0 , 0 , κδ , 0 , 0 , 0 , – , 0 , 0 , - , C0 , 0 , 0 , κδ , 0 , 0 , 0 , – , 0 , - , T0 , 0 , 0 , 0 , κδ , 0 , 0 , 0 , – , - The method of covarions, or ''co''ncomitantly ''vari''able cod''ons'', is a technique in computational phylogenetics that allows the hypothesized rate of molecular evolution at individual codons in a set of nucleotide sequences to vary in an autocorrelated manner. Under the covarion model, the rates of evolution on different branches of a hypothesized phylogenetic tree vary in an auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Phylogenetics
Computational phylogenetics, phylogeny inference, or phylogenetic inference focuses on computational and optimization algorithms, Heuristic (computer science), heuristics, and approaches involved in Phylogenetics, phylogenetic analyses. The goal is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of genes, species, or taxa. Maximum likelihood estimation, Maximum likelihood, Maximum parsimony (phylogenetics), parsimony, Bayesian inference in phylogeny, Bayesian, and minimum evolution are typical optimality criteria used to assess how well a phylogenetic tree topology describes the sequence data. Nearest Neighbour Interchange (NNI), Subtree Prune and Regraft (SPR), and Tree Bisection and Reconnection (TBR), known as tree rearrangements, are deterministic algorithms to search for optimal or the best phylogenetic tree. The space and the landscape of searching for the optimal phylogenetic tree is known as phylogeny search space. Maximum Likelihood (al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterotachy
Heterotachy refers to variations in lineage-specific evolutionary rates over time. In the field of molecular evolution, the principle of heterotachy states that the substitution rate of sites in a gene can change through time. It has been proposed that the positions that show switches in substitution rate over time (that is, heterotachous sites) are good indicators of functional divergence. However, it appears that heterotachy is a much more general process, since most variable sites of homologous proteins with no evidence of functional shift are heterotachous. The covarion hypothesis is a specific form of heterotachy. Some studies have proposed functional divergence models that are also heterotachous. Additionally, some mixture models that do not explicitly account for rate-shift, but site-partitions evolving at different relative substitution rates across lineages are mathematically heterotachous. Failure to take heterotachy into account in phylogenetic reconstructions may lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Evolution
Molecular evolution describes how Heredity, inherited DNA and/or RNA change over evolutionary time, and the consequences of this for proteins and other components of Cell (biology), cells and organisms. Molecular evolution is the basis of phylogenetics, phylogenetic approaches to describing the Tree of life (biology), tree of life. Molecular evolution overlaps with population genetics, especially on shorter timescales. Topics in molecular evolution include the origins of new genes, the genetic nature of complex traits, the genetic basis of adaptation and speciation, the Evolutionary developmental biology, evolution of development, and patterns and processes underlying genome, genomic changes during evolution. History The history of molecular evolution starts in the early 20th century with comparative biochemistry, and the use of "fingerprinting" methods such as immune assays, gel electrophoresis, and paper chromatography in the 1950s to explore homologous proteins. The advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codon
Genetic code is a set of rules used by living cells to translate information encoded within genetic material (DNA or RNA sequences of nucleotide triplets or codons) into proteins. Translation is accomplished by the ribosome, which links proteinogenic amino acids in an order specified by messenger RNA (mRNA), using transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules to carry amino acids and to read the mRNA three nucleotides at a time. The genetic code is highly similar among all organisms and can be expressed in a simple table with 64 entries. The codons specify which amino acid will be added next during protein biosynthesis. With some exceptions, a three-nucleotide codon in a nucleic acid sequence specifies a single amino acid. The vast majority of genes are encoded with a single scheme (see the RNA codon table). That scheme is often called the canonical or standard genetic code, or simply ''the'' genetic code, though variant codes (such as in mitochondria) exist. History Efforts to understan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide Sequence
A nucleic acid sequence is a succession of bases within the nucleotides forming alleles within a DNA (using GACT) or RNA (GACU) molecule. This succession is denoted by a series of a set of five different letters that indicate the order of the nucleotides. By convention, sequences are usually presented from the 5' end to the 3' end. For DNA, with its double helix, there are two possible directions for the notated sequence; of these two, the sense strand is used. Because nucleic acids are normally linear (unbranched) polymers, specifying the sequence is equivalent to defining the covalent structure of the entire molecule. For this reason, the nucleic acid sequence is also termed the primary structure. The sequence represents genetic information. Biological deoxyribonucleic acid represents the information which directs the functions of an organism. Nucleic acids also have a secondary structure and tertiary structure. Primary structure is sometimes mistakenly referred to as "prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autocorrelation
Autocorrelation, sometimes known as serial correlation in the discrete time case, measures the correlation of a signal with a delayed copy of itself. Essentially, it quantifies the similarity between observations of a random variable at different points in time. The analysis of autocorrelation is a mathematical tool for identifying repeating patterns or hidden periodicities within a signal obscured by noise. Autocorrelation is widely used in signal processing, time domain and time series analysis to understand the behavior of data over time. Different fields of study define autocorrelation differently, and not all of these definitions are equivalent. In some fields, the term is used interchangeably with autocovariance. Various time series models incorporate autocorrelation, such as unit root processes, trend-stationary processes, autoregressive processes, and moving average processes. Autocorrelation of stochastic processes In statistics, the autocorrelation of a real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogenetic Tree
A phylogenetic tree or phylogeny is a graphical representation which shows the evolutionary history between a set of species or taxa during a specific time.Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA. In other words, it is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. In evolutionary biology, all life on Earth is theoretically part of a single phylogenetic tree, indicating common ancestry. Phylogenetics is the study of phylogenetic trees. The main challenge is to find a phylogenetic tree representing optimal evolutionary ancestry between a set of species or taxa. Computational phylogenetics (also phylogeny inference) focuses on the algorithms involved in finding optimal phylogenetic tree in the phylogenetic landscape. Phylogenetic trees may be rooted or unrooted. In a ''rooted'' p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sequence Alignment
In bioinformatics, a sequence alignment is a way of arranging the sequences of DNA, RNA, or protein to identify regions of similarity that may be a consequence of functional, structural biology, structural, or evolutionary relationships between the sequences. Aligned sequences of nucleotide or amino acid residues are typically represented as rows within a matrix (mathematics), matrix. Gaps are inserted between the Residue (chemistry), residues so that identical or similar characters are aligned in successive columns. Sequence alignments are also used for non-biological sequences such as calculating the Edit distance, distance cost between strings in a natural language, or to display financial data. Interpretation If two sequences in an alignment share a common ancestor, mismatches can be interpreted as point mutations and gaps as indels (that is, insertion or deletion mutations) introduced in one or both lineages in the time since they diverged from one another. In sequence ali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probability Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a probability distribution is a Function (mathematics), function that gives the probabilities of occurrence of possible events for an Experiment (probability theory), experiment. It is a mathematical description of a Randomness, random phenomenon in terms of its sample space and the Probability, probabilities of Event (probability theory), events (subsets of the sample space). For instance, if is used to denote the outcome of a coin toss ("the experiment"), then the probability distribution of would take the value 0.5 (1 in 2 or 1/2) for , and 0.5 for (assuming that fair coin, the coin is fair). More commonly, probability distributions are used to compare the relative occurrence of many different random values. Probability distributions can be defined in different ways and for discrete or for continuous variables. Distributions with special properties or for especially important applications are given specific names. Introduction A prob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
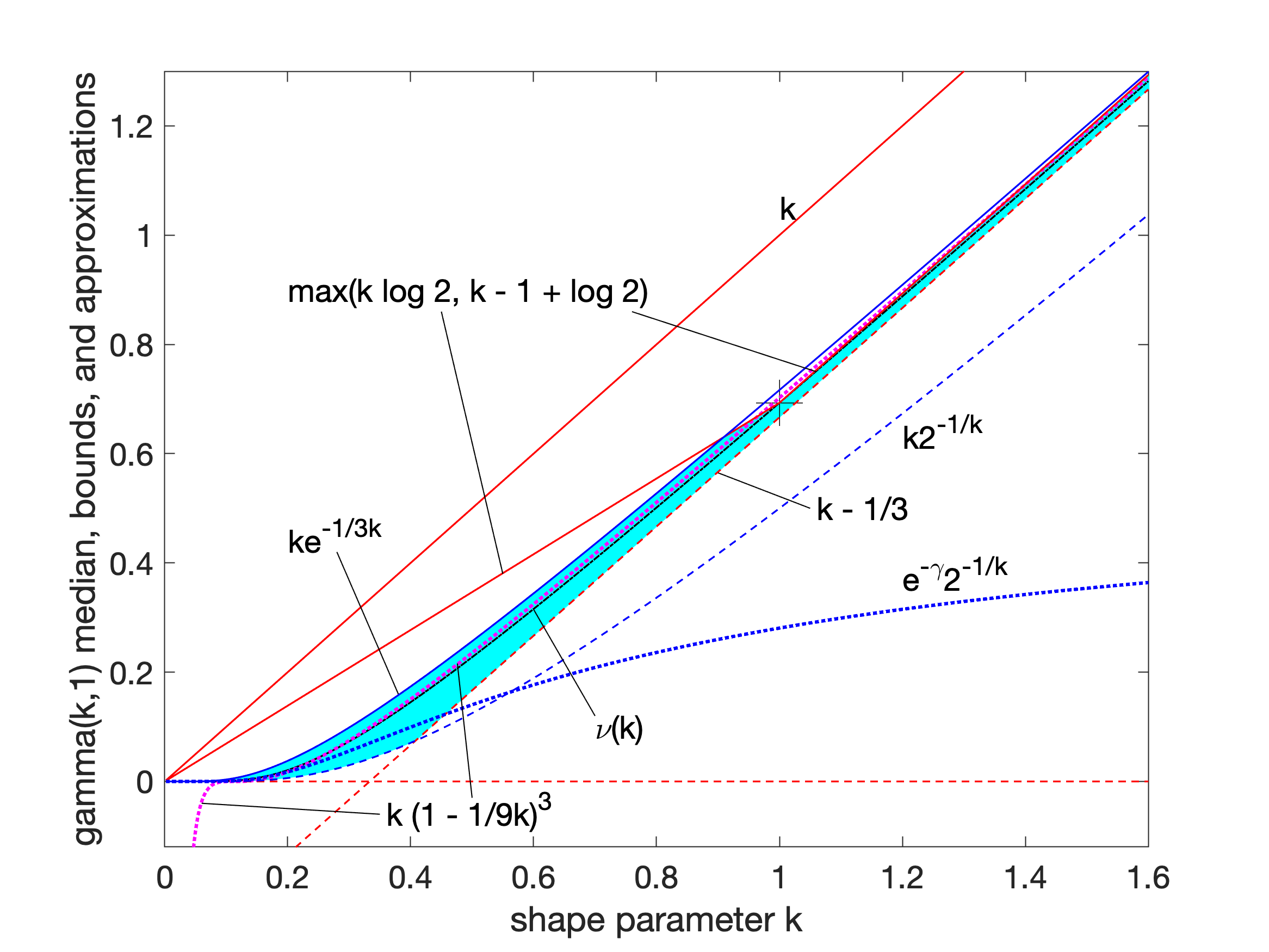
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a versatile two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-squared distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: # With a shape parameter and a scale parameter # With a shape parameter \alpha and a rate parameter In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The distribution has important applications in various fields, including econometrics, Bayesian statistics, and life testing. In econometrics, the (''α'', ''θ'') parameterization is common for modeling waiting times, such as the time until death, where it often takes the form of an Erlang distribution for integer ''α'' values. Bayesian statisticians prefer the (''α'',''λ'') parameterization, utilizing the gamma distribution as a conjugate prior for several inverse scale parameters, facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stochastic
Stochastic (; ) is the property of being well-described by a random probability distribution. ''Stochasticity'' and ''randomness'' are technically distinct concepts: the former refers to a modeling approach, while the latter describes phenomena; in everyday conversation, however, these terms are often used interchangeably. In probability theory, the formal concept of a '' stochastic process'' is also referred to as a ''random process''. Stochasticity is used in many different fields, including image processing, signal processing, computer science, information theory, telecommunications, chemistry, ecology, neuroscience, physics, and cryptography. It is also used in finance (e.g., stochastic oscillator), due to seemingly random changes in the different markets within the financial sector and in medicine, linguistics, music, media, colour theory, botany, manufacturing and geomorphology. Etymology The word ''stochastic'' in English was originally used as an adjective with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |