|
Coryphodontidae
Coryphodontidae is an extinct family of pantodont mammals known from the Late Paleocene to the Middle Eocene of Eurasia and North America. The type genus '' Coryphodon'' is known from around the Paleocene-Eocene transition in Europe, western United States, northern Canada, and eastern Asia. The remaining genera are known exclusively from the middle Eocene of Asia. The coryphodontids are related to the pantolambdids. ''Coryphodon'' are large, derived pantodonts first described in the mid-19th century, but no intermediate stages leading to their unusual upper molars are known. The last known species of ''Coryphodon'' have bilophodont The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone toot ... molars similar to later, more derived coryphodontids, and, most likely, ''Coryphodon'' is the pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantodonta
Pantodonta is an extinct suborder (or, according to some, an Order (biology), order) of eutherian mammals. These herbivorous mammals were one of the first groups of large mammals to evolve (around 66 million years ago) after the K-T boundary, end of the Cretaceous. The last pantodonts died out at the end of the Eocene (around 34 million years ago). Pantodonta include some of the largest mammals of their time, but were a diversified group, with some primitive members weighing less than and the largest more than . The earliest and most primitive pantodonts, ''Bemalambda'' (with a skull probably the size of a dog) and ''Hypsilolambda'', appear in the early Paleocene Shanghuan Formation in China. All more derived families are collectively classified as Eupantodonta. The pantodonts appear in North America in the middle Paleocene, where ''Coryphodon'' survived into the middle Eocene. Pantodont teeth have been found in South America (''Alcidedorbignya'') and Antarctica, and footprin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
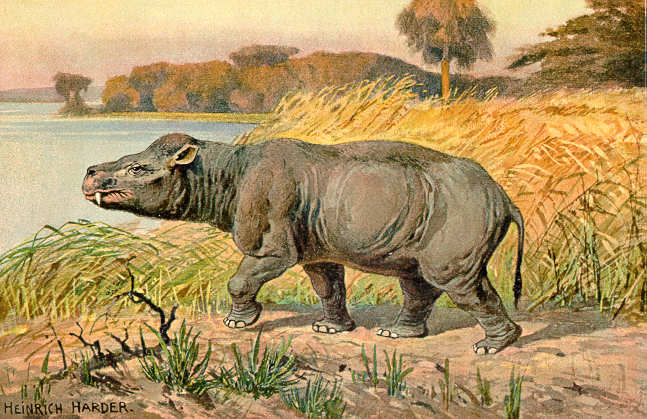
Coryphodon
''Coryphodon'' (from Greek , "point", and , "tooth", meaning ''peaked tooth'', referring to "the development of the angles of the ridges into points [on the molars].") is an extinct genus of pantodonts of the family Coryphodontidae. ''Coryphodon'' was a pantodont, a member of the world's first group of large browsing mammals. It migrated across what is now northern North America, replacing ''Barylambda'', an earlier pantodont. It is regarded as the ancestor of the genus ''Hypercoryphodon'' of Late Eocene Mongolia. ''Coryphodon'' is known from many specimens in North America and considerably fewer in Europe, Mongolia, and China. It is a small to medium-sized coryphodontid which differs from other members of the family in dental characteristics. Description At about at shoulder height and in body length, ''Coryphodon'' is one of the largest-known mammals of its time. The creature was very slow, with long upper limbs and short lower limbs, which were needed to support its weig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleocene First Appearances
The Paleocene ( ), or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palaiós'' meaning "old" and the Eocene Epoch (which succeeds the Paleocene), translating to "the old part of the Eocene". The epoch is bracketed by two major events in Earth's history. The K–Pg extinction event, brought on by an asteroid impact (Chicxulub impact) and possibly volcanism ( Deccan Traps), marked the beginning of the Paleocene and killed off 75% of species, most famously the non-avian dinosaurs. The end of the epoch was marked by the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM), which was a major climatic event wherein about 2,500–4,500 gigatons of carbon were released into the atmosphere and ocean systems, causing a spike in global temperatures and ocean acidification. In the Paleocene, the continents of the Northern Hemispher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
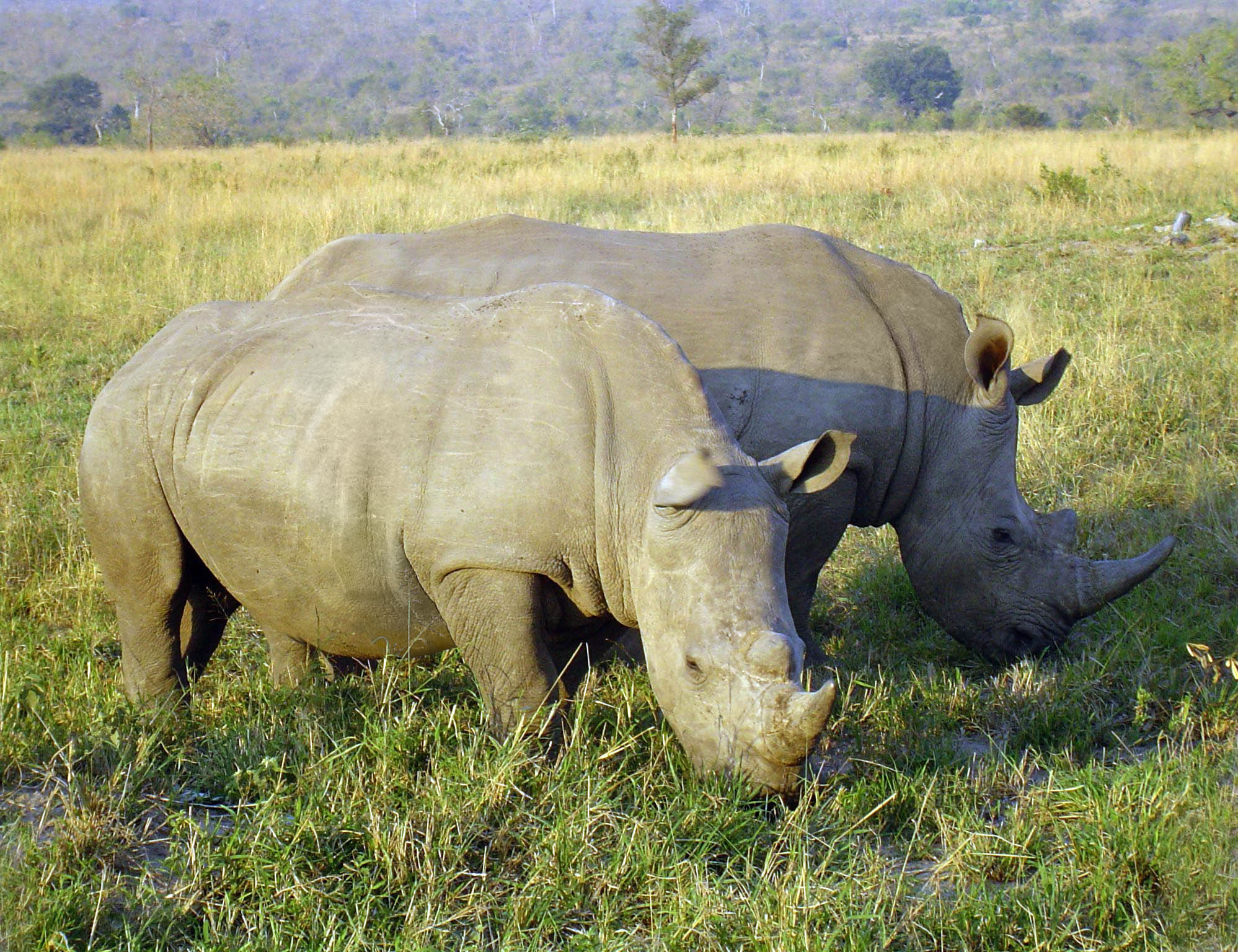
Ceratotherium Simum
The white rhinoceros, also known as the white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum''), is the largest extant species of rhinoceros and the most social of all rhino species, characterized by its wide mouth adapted for grazing. The species includes two subspecies with dramatically different conservation outlooks: the southern white rhinoceros, with an estimated 17,464 individuals in the wild as of the end of 2023, and the northern white rhinoceros. The northern subspecies is critically endangered and on the brink of extinction; its last known male, Sudan, died in March 2018, leaving behind only a very small number of females in captivity. Both subspecies have faced significant threats, primarily from poaching for their horns and habitat loss, which contribute to the species' overall conservation status of Near Threatened. Naming One popular, though widely discredited, theory for the origin of the name "white rhinoceros" is a mistranslation of the Dutch word "w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus Amphibius
The hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius;'' ; : hippopotamuses), often shortened to hippo (: hippos), further qualified as the common hippopotamus, Nile hippopotamus and river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus (''Choeropsis liberiensis'' or ''Hexaprotodon liberiensis''). Its name comes from the ancient Greek for "river horse" (). After elephants and rhinoceroses, the hippopotamus is the next largest land mammal. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl. Despite their physical resemblance to pigs and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar-like l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
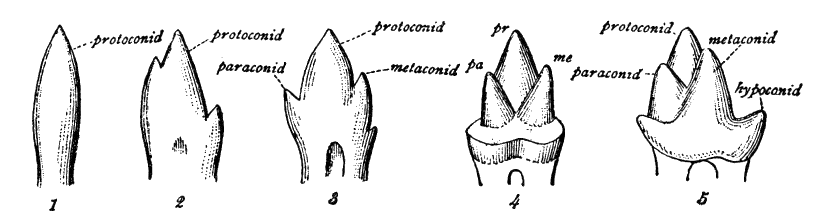
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygyny
Polygyny () is a form of polygamy entailing the marriage of a man to several women. The term polygyny is from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); . Incidence Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any other continent. Some scholars theorize that the History of slavery, slave trade's impact on the male-to-female sex ratio was a key factor in the emergence and fortification of polygynous practices in regions of Africa. Polygyny is most common in a region known as the "polygamy belt" in West Africa and Central Africa, with the countries estimated to have the highest polygamy prevalence in the world being Burkina Faso, Mali, Gambia, Niger and Nigeria. In the region of sub-Saharan Africa, polygyny is common and deeply rooted in the culture, with 11 percent of the population of sub-Saharan Africa living in such marriages (25 percent of the Muslim population and 3 percent of the Christian population, as of 2019). Polygyny is especially widespread in West Africa, with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molar (tooth)
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name ''molar'' derives from Latin, ''molaris dens'', meaning "millstone tooth", from ''mola'', millstone and ''dens'', tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial. Human anatomy In humans, the molar teeth have either four or five cusps. Adult humans have 12 molars, in four groups of three at the back of the mouth. The third, rearmost molar in each group is called a wisdom tooth. It is the last tooth to appear, breaking through the front of the gum at about the age of 20, although this varies among individuals and populations, and in many cases the tooth is missing. The human mouth contains upper (maxillary) and lower (mandibular) molars. They are: maxillary first molar, maxillary second molar, maxillary third mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantolambdidae
Pantolambdidae is an extinct family of pantodont mammal in the order Pantodonta Pantodonta is an extinct suborder (or, according to some, an Order (biology), order) of eutherian mammals. These herbivorous mammals were one of the first groups of large mammals to evolve (around 66 million years ago) after the K-T boundary, en .... References {{Taxonbar, from=Q25420770 Pantodonta Mammal families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Eocene
The Eocene ( ) is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (Ma). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''Ēṓs'', ' Dawn') and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch.See: *Letter from William Whewell to Charles Lyell dated 31 January 1831 in: * From p. 55: "The period next antecedent we shall call Eocene, from ήως, aurora, and χαινος, recens, because the extremely small proportion of living species contained in these strata, indicates what may be considered the first commencement, or ''dawn'', of the existing state of the animate creation." The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gobiatherium Major
''Gobiatherium'' (meaning "Beast of the Gobi Desert") was one of the last uintatheres, from the Mid Eocene of Mongolia. Unlike its North American cousins, ''Uintatherium'' or ''Eobasileus'', ''Gobiatherium'' lacked knob-like horns, or even fang-like tusks. Instead, it had enlarged cheekbone In the human skull, the zygomatic bone (from ), also called cheekbone or malar bone, is a paired irregular bone, situated at the upper and lateral part of the face and forming part of the lateral wall and floor of the orbit (anatomy), orbit, of t ...s and an almost spherical snout. Because of the noticeable lack of many diagnostic uintathere features (the horns and tusks), the genus is placed within its own subfamily, "Gobiatheriinae", though some experts prefer to rank it as the family "Gobiatheriidae". References *Cheng Jie & Ma Aneheng: ''New mammalian materials from the Eocene of the Liguanqiao basin.'' Vertebrata PalAsiatica 28, 1990, S. 228–244. * McKenna, M.C. & Bell, S.K. Cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |