|
Corticotropin Releasing Hormone
Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) (also known as corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) or corticoliberin; corticotropin may also be spelled corticotrophin) is a peptide hormone involved in stress (biology), stress responses. It is a releasing hormone that belongs to corticotropin-releasing factor family. In humans, it is encoded by the ''CRH'' gene. Its main function is the stimulation of the pituitary synthesis of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), as part of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA axis). Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) is a 41-amino acid peptide derived from a 196-amino acid preprohormone. CRH is secreted by the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus in response to stress (biological), stress. Increased CRH production has been observed to be associated with Alzheimer's disease and major depression, and autosomal recessive hypothalamic corticotropin deficiency has multiple and potentially fatal metabolic consequences including hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peptide
Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have a molecular mass of 10,000 Da or more are called proteins. Chains of fewer than twenty amino acids are called oligopeptides, and include dipeptides, tripeptides, and tetrapeptides. Peptides fall under the broad chemical classes of biological polymers and oligomers, alongside nucleic acids, oligosaccharides, polysaccharides, and others. Proteins consist of one or more polypeptides arranged in a biologically functional way, often bound to ligands such as coenzymes and cofactors, to another protein or other macromolecule such as DNA or RNA, or to complex macromolecular assemblies. Amino acids that have been incorporated into peptides are termed residues. A water molecule is released during formation of each amide bond.. All peptides except cyclic peptides have an N-terminal (amine group) and C-terminal (carboxyl g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parturition
Birth is the act or process of bearing or bringing forth offspring, also referred to in technical contexts as parturition. In mammals, the process is initiated by hormones which cause the muscular walls of the uterus to contract, expelling the fetus at a developmental stage when it is ready to feed and breathe. In some species, the offspring is precocial and can move around almost immediately after birth but in others, it is altricial and completely dependent on parenting. In marsupials, the fetus is born at a very immature stage after a short gestation and develops further in its mother's womb pouch. It is not only mammals that give birth. Some reptiles, amphibians, fish and invertebrates carry their developing young inside them. Some of these are ovoviviparous, with the eggs being hatched inside the mother's body, and others are viviparous, with the embryo developing inside their body, as in the case of mammals. Human childbirth Humans usually produce a single offspri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucocorticoids
Glucocorticoids (or, less commonly, glucocorticosteroids) are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau of "glucose", "cortex", and "steroid" and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure (see structure below). Glucocorticoids are part of the feedback mechanism in the immune system, which reduces certain aspects of immune function, such as inflammation. They are therefore used in medicine to treat diseases caused by an overactive immune system, such as allergies, asthma, autoimmune diseases, and sepsis. Glucocorticoids have many diverse effects such as pleiotropy, including potentially harmful side effects. They also interfere with some of the abnormal mechanisms in cancer cells, so they are used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone in the glucocorticoid class of hormones and a stress hormone. When used as medication, it is known as hydrocortisone. Cortisol is produced in many animals, mainly by the ''zona fasciculata'' of the adrenal cortex in an adrenal gland. In other tissues, it is produced in lower quantities. By a Circadian rhythm, diurnal cycle, cortisol is released and increases in response to Stress (biology), stress and a low Blood sugar, blood-glucose concentration. It functions to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis, suppress the immune system, and aid in the metabolism of calories. It also decreases bone formation. These stated functions are carried out by cortisol binding to glucocorticoid or mineralocorticoid receptors inside a cell, which then bind to DNA to affect gene expression. Health effects Metabolic response Metabolism of glucose Cortisol plays a crucial role in regulating glucose metabolism and promotes gluconeogenesis (glucose synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH; also adrenocorticotropin, corticotropin) is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced by and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is also used as a medication and diagnostic agent. ACTH is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and is often produced in response to biological stress (along with its precursor corticotropin-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus). Its principal effects are increased production and release of cortisol and androgens by the zona fasiculata and zona reticularis, respectively. ACTH is also related to the circadian rhythm in many organisms. Deficiency of ACTH is an indicator of secondary adrenal insufficiency (suppressed production of ACTH due to an impairment of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus, cf. hypopituitarism) or tertiary adrenal insufficiency (disease of the hypothalamus, with a decrease in the release of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH)). Conversely, chronically ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corticotrope
Corticotropic cells, (corticotropes or corticotrophs) are basophilic cells in the anterior pituitary that produce pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) which undergoes cleavage to adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), β-lipotropin (β-LPH), and melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH). These cells are stimulated by corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) and make up 15–20% of the cells in the anterior pituitary. The release of ACTH from the corticotropic cells is controlled by CRH, which is formed in the cell bodies of parvocellular neurosecretory cells within the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus and passes to the corticotropes in the anterior pituitary via the hypophyseal portal system. Adrenocorticotropin hormone stimulates the adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids and plays an important role in the stress response. Function The primary function of the corticotropic cells is to produce the prohormone POMC in response to the release of CRH from the hypothalamus. POMC is cleaved in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
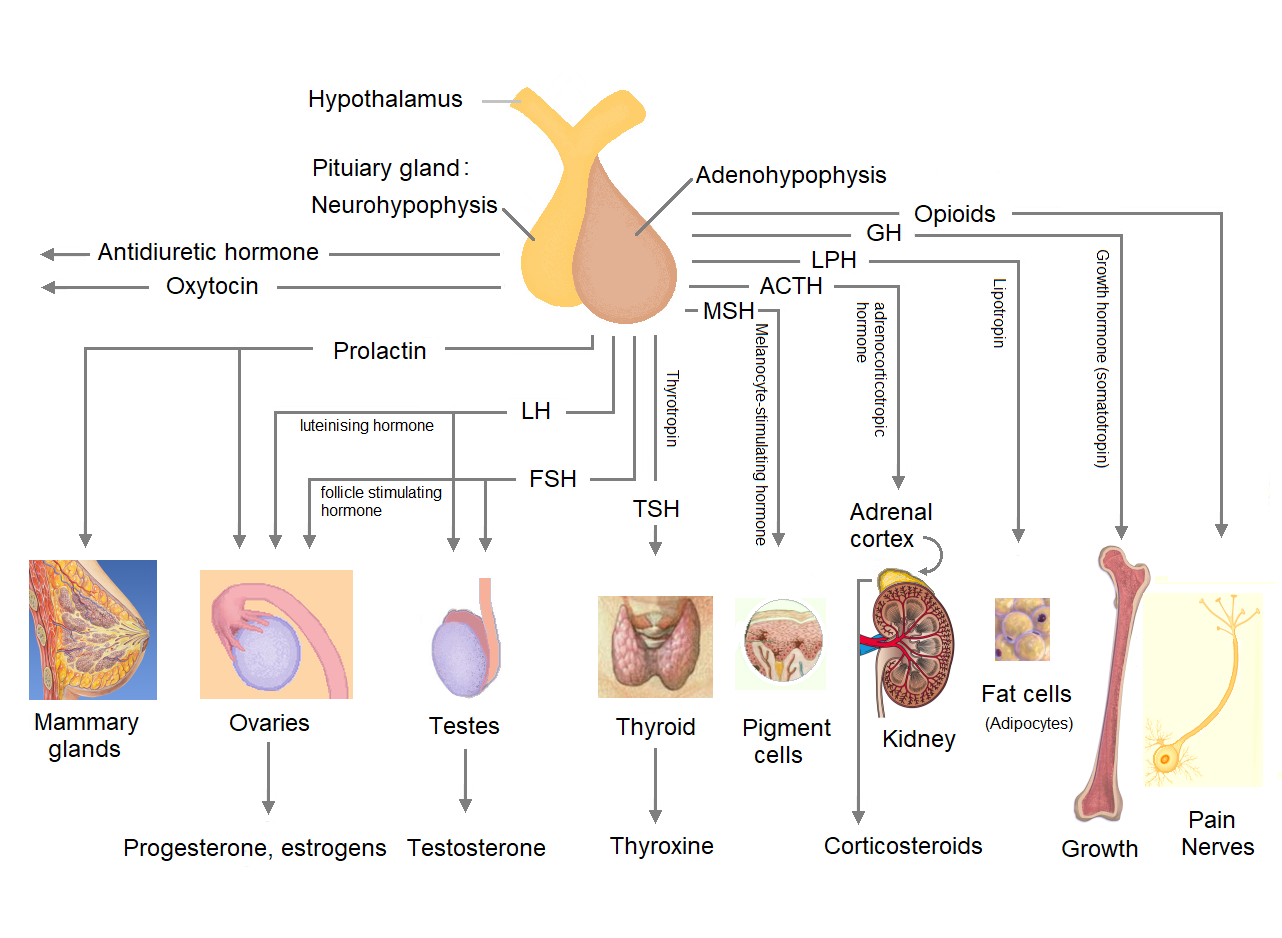
Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland or hypophysis is an endocrine gland in vertebrates. In humans, the pituitary gland is located at the base of the human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The pituitary gland and the hypothalamus control much of the body's endocrine system. It is seated in part of the sella turcica a fossa (anatomy), depression in the sphenoid bone, known as the hypophyseal fossa. The human pituitary gland is ovoid, oval shaped, about 1 cm in diameter, in weight on average, and about the size of a kidney bean. Digital version. There are two main lobes of the pituitary, an anterior pituitary, anterior lobe, and a posterior pituitary, posterior lobe joined and separated by a small intermediate lobe. The anterior lobe (adenohypophysis) is the glandular part that produces and secretes several hormones. The posterior lobe (neurohypophysis) secretes neurohypophysial hormones produced in the hypothalamus. Both lobes have different origins and they are both co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Pituitary
The anterior pituitary (also called the adenohypophysis or pars anterior) is a major Organ (anatomy), organ of the endocrine system. The anterior pituitary is the glandular, Anatomical terms of location#Usage in human anatomy, anterior lobe that together with the posterior pituitary (or neurohypophysis) makes up the pituitary gland (hypophysis) which, in humans, is located at the base of the Human brain, brain, protruding off the bottom of the hypothalamus. The anterior pituitary regulates several physiological processes, including stress (medicine), stress, Human development (biology), growth, reproduction, and lactation. Proper functioning of the anterior pituitary and of the organs it regulates can often be ascertained via blood tests that measure hormone levels. Structure The pituitary gland sits in a protective bony enclosure called the sella turcica (''Turkish chair/saddle''). It is composed of three lobes: the anterior, intermediate, and posterior lobes. In many animals, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypothalamo-hypophyseal Portal System
The hypophyseal portal system is a system of blood vessels in the microcirculation at the base of the brain, connecting the hypothalamus with the anterior pituitary. Its main function is to quickly transport and exchange hormones between the hypothalamus arcuate nucleus and anterior pituitary gland. The capillaries in the portal system are fenestrated (have many small channels with high vascular permeability) which allows a rapid exchange between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. The main hormones transported by the system include gonadotropin-releasing hormone, corticotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone–releasing hormone, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Structure The blood supply and direction of flow in the hypophyseal portal system has been studied over many years on laboratory animals and human cadaver specimens with injection and vascular corrosion casting methods. Short portal vessels between the neural and anterior pituitary lobes provide an avenue for rapid h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Median Eminence
The median eminence is generally defined as the portion of the ventral hypothalamus from which the portal vessels arise. The median eminence is a small swelling on the tuber cinereum, posterior to and on top of the pituitary stalk; it lies in the area roughly bounded on its posterolateral region by the cerebral peduncles, and on its anterolateral region by the optic chiasm. As one of the seven areas of the brain devoid of a blood–brain barrier, the median eminence is a circumventricular organ having permeable capillaries. Its main function is as a gateway for release of hypothalamic hormones, although it does share contiguous perivascular spaces with the adjacent hypothalamic arcuate nucleus, indicating a potential sensory role. __TOC__ Physiology The median eminence is a part of the hypothalamus from which regulatory hormones are released. It is integral to the hypophyseal portal system, which connects the hypothalamus with the pituitary gland. The pars nervosa (part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parvocellular Neurosecretory Cell
Parvocellular neurosecretory cells are small neurons that produce hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones. The cell bodies of these neurons are located in various nuclei of the hypothalamus or in closely related areas of the basal brain, mainly in the medial zone of the hypothalamus. All or most of the axons of the parvocellular neurosecretory cells project to the median eminence, at the base of the brain, where their nerve terminals release the hypothalamic hormones. These hormones are then immediately absorbed into the blood vessels of the hypothalamo-pituitary portal system, which carry them to the anterior pituitary gland, where they regulate the secretion of hormones into the systemic circulation. __TOC__ Types The parvocellular neurosecretory cells include those that make: * Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), which acts as the primary regulator of TSH and a regulator of prolactin * Corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), which acts as the primary regulator of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |