|
Corporate
A corporation or body corporate is an individual or a group of people, such as an association or company, that has been authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law as "born out of statute"; a legal person in a legal context) and recognized as such in law for certain purposes. Early incorporated entities were established by charter (i.e., by an '' ad hoc'' act granted by a monarch or passed by a parliament or legislature). Most jurisdictions now allow the creation of new corporations through registration. Corporations come in many different types but are usually divided by the law of the jurisdiction where they are chartered based on two aspects: whether they can issue stock, or whether they are formed to make a profit. Depending on the number of owners, a corporation can be classified as ''aggregate'' (the subject of this article) or '' sole'' (a legal entity consisting of a single incorporated office occupied ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporate Law
Corporate law (also known as company law or enterprise law) is the body of law governing the rights, relations, and conduct of persons, companies, organizations and businesses. The term refers to the legal practice of law relating to corporations, or to the theory of corporations. Corporate law often describes the law relating to matters which derive directly from the life-cycle of a corporation.John Armour, Henry Hansmann, Reinier Kraakman, Mariana Pargendler "What is Corporate Law?" in ''The Anatomy of Corporate Law: A Comparative and Functional Approach''(Eds Reinier Kraakman, John Armour, Paul Davies, Luca Enriques, Henry Hansmann, Gerard Hertig, Klaus Hopt, Hideki Kanda, Mariana Pargendler, Wolf-Georg Ringe, and Edward Rock, Oxford University Press 2017)1.1 It thus encompasses the formation, funding, governance, and death of a corporation. While the minute nature of corporate governance as personified by share ownership, capital market, and business culture rules diff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Company Registers
This is a list of official business registers around the world. There are many types of official business registers, usually maintained for various purposes by a state authority, such as a government agency, or a court of law. In some cases, it may also be devolved to self-governing bodies, either commercial (a chamber of commerce) or professional (a regulatory college); or to a dedicated, highly regulated company (i.e., operator of a stock exchange, a multilateral trading facility, a central securities depository or an alternative trading system). The following is an incomplete list of official business registers by country. Types of registers A business register may include data on entities, as well as on their status for various purposes. Examples of such registers include: * company register — a register of legal entities in the jurisdiction they operate under, for the purpose of establishing, dissolving, acquisition of legal capacity and (in some cases) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Directors
A board of directors is a governing body that supervises the activities of a business, a nonprofit organization, or a government agency. The powers, duties, and responsibilities of a board of directors are determined by government regulations (including the jurisdiction's corporate law) and the organization's own constitution and by-laws. These authorities may specify the number of members of the board, how they are to be chosen, and how often they are to meet. In an organization with voting members, the board is accountable to, and may be subordinate to, the organization's full membership, which usually elect the members of the board. In a stock corporation, non-executive directors are elected by the shareholders, and the board has ultimate responsibility for the management of the corporation. In nations with codetermination (such as Germany and Sweden), the workers of a corporation elect a set fraction of the board's members. The board of directors appoints the ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limited Liability
Limited liability is a legal status in which a person's financial Legal liability, liability is limited to a fixed sum, most commonly the value of a person's investment in a corporation, company, or joint venture. If a company that provides limited liability to its investors is sued, then the claimants are generally entitled to collect only against the assets of the company, not the assets of its shareholders or other investors. A shareholder in a corporation or Limited company, limited liability company is not personally liable for any of the debts of the company, other than for the amount already invested in the company and for any unpaid amount on the shares in the company, if any—except under special and rare circumstances that permit "piercing the corporate veil." The same is true for the members of a limited liability partnership and the limited partners in a limited partnership. By contrast, sole proprietors and partners in general partnerships are each liable for all the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Person
In law, a legal person is any person or legal entity that can do the things a human person is usually able to do in law – such as enter into contracts, lawsuit, sue and be sued, ownership, own property, and so on. The reason for the term "''legal'' person" is that some legal persons are not human persons: Company, companies and corporations (i.e., business entities) are ''persons'', legally speaking (they can legally do most of the things an ordinary person can do), but they are not, in a literal sense, human beings. Legal personhood is a prerequisite to capacity (law), legal capacity (the ability of any legal person to amend – i.e. enter into, transfer, etc. – rights and Law of obligations, obligations): it is a prerequisite for an international organization being able to sign treaty, international treaties in its own legal name, name. History The concept of legal personhood for organizations of people is at least as old as Ancient Rome: a variety of Coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporation Sole
A corporation sole is a legal entity consisting of a single ("sole") incorporated office, occupied by a single ("sole") natural person.Technical Manual Insolvencydirect.bis.gov.uk This structure allows corporations (often religious corporations or Commonwealth governments) to pass without interruption from one officeholder to the next, giving positions legal continuity with subsequent officeholders having identical powers and possessions to their predecessors. A corporation sole is one of two types of |
Natural Person
In jurisprudence, a natural person (also physical person in some Commonwealth countries, or natural entity) is a person (in legal meaning, i.e., one who has its own legal personality) that is an individual human being, distinguished from the broader category of a legal person, which may be a private (i.e., business entity or non-governmental organization) or public (i.e., government) organization. Historically, a human being was not necessarily considered a natural person in some jurisdictions where slavery existed (subject of a property right) rather than a person. Definitions According to Maria Helena Diniz, an individual or natural person "is the human being considered as a subject of rights and obligations". Every human being is endowed with legal personality and, therefore, is a subject of law. According to Sílvio de Salvo Venosa, "legal personality is a projection of the intimate, psychic personality of each person; it is a social projection of the psychic personalit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiduciary
A fiduciary is a person who holds a legal or ethical relationship of trust with one or more other parties (legal person or group of persons). Typically, a fiduciary prudently takes care of money or other assets for another person. One party, for example, a corporate trust company or the trust department of a bank, acts in a fiduciary capacity to another party, who, for example, has entrusted funds to the fiduciary for safekeeping or investment. Likewise, financial advisers, financial planners, and asset managers, including managers of pension plans, endowments, and other tax-exempt assets, are considered fiduciaries under applicable statutes and laws. In a fiduciary relationship, one person, in a position of vulnerability, justifiably vests confidence, good faith, reliance, and trust in another whose aid, advice, or protection is sought in some matter... In such a relation, good conscience requires the fiduciary to act at all times for the sole benefit and interest of the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
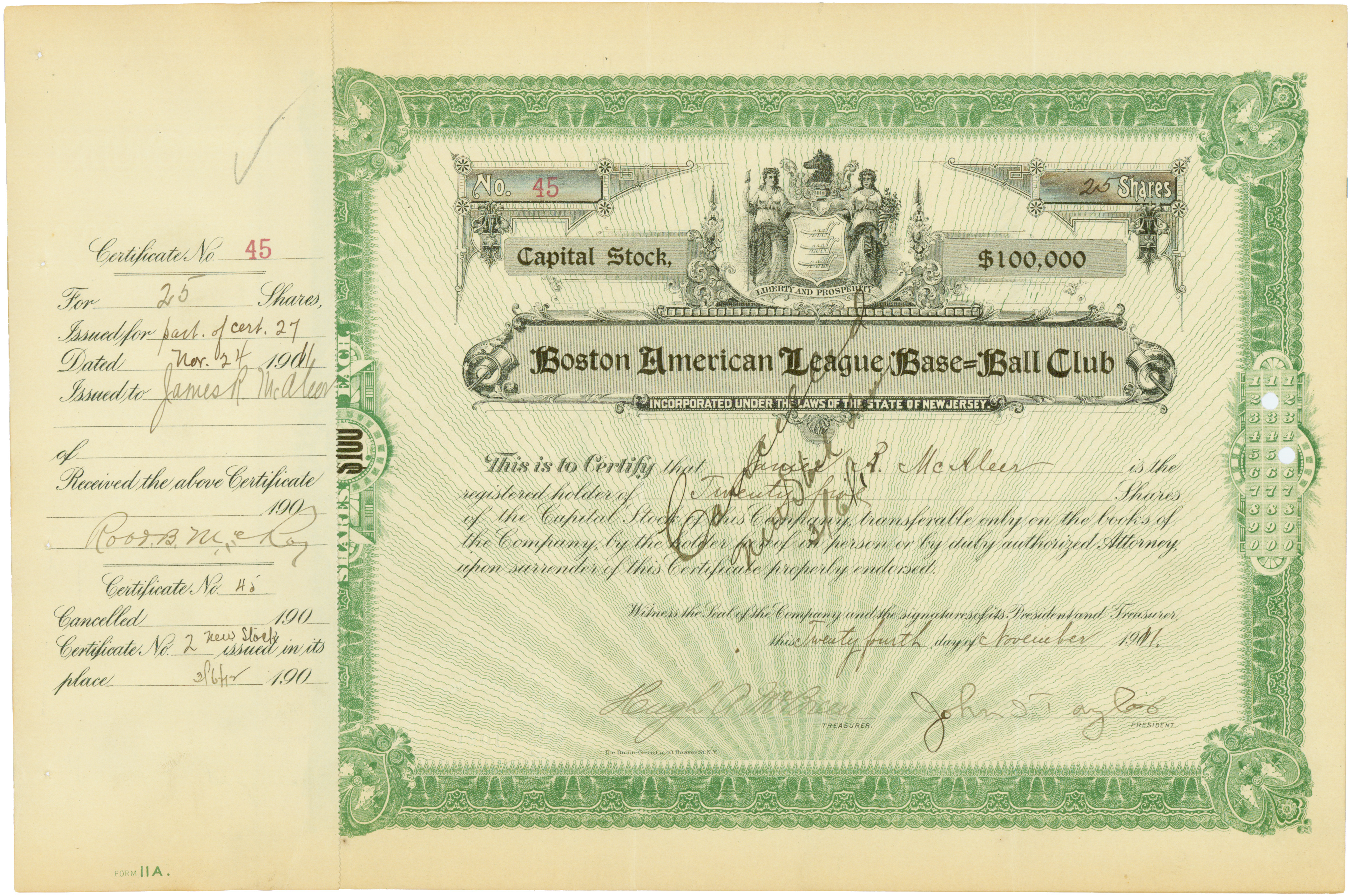
Shareholder
A shareholder (in the United States often referred to as stockholder) of corporate stock refers to an individual or legal entity (such as another corporation, a body politic, a trust or partnership) that is registered by the corporation as the legal owner of shares of the share capital of a public or private corporation. Shareholders may be referred to as members of a corporation. A person or legal entity becomes a shareholder in a corporation when their name and other details are entered in the corporation's register of shareholders or members, and unless required by law the corporation is not required or permitted to enquire as to the beneficial ownership of the shares. A corporation generally cannot own shares of itself. The influence of shareholders on the business is determined by the shareholding percentage owned. Shareholders of corporations are legally separate from the corporation itself. They are generally not liable for the corporation's debts, and the shareholders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Share Capital
A corporation's share capital, commonly referred to as capital stock in the United States, is the portion of a corporation's equity that has been derived by the issue of shares in the corporation to a shareholder, usually for cash. ''Share capital'' may also denote the number and types of shares that compose a corporation's share structure. Definition In accounting, the share capital of a corporation is the nominal value of issued shares (that is, the sum of their par values, sometimes indicated on share certificates). If the allocation price of shares is greater than the par value, as in a rights issue, the shares are said to be sold at a premium (variously called share premium, additional paid-in capital or paid-in capital in excess of par). This equation shows the constituents that make up a company's real share capital: : \sum\text \times \text This is differentiated from share capital in the accounting sense, as it presents nominal share capital and does not take t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stock
Stocks (also capital stock, or sometimes interchangeably, shares) consist of all the Share (finance), shares by which ownership of a corporation or company is divided. A single share of the stock means fractional ownership of the corporation in proportion to the total number of shares. This typically entitles the shareholder (stockholder) to that fraction of the company's earnings, proceeds from liquidation of assets (after discharge of all Seniority (financial), senior claims such as secured and unsecured debt), or Voting interest, voting power, often dividing these up in proportion to the number of like shares each stockholder owns. Not all stock is necessarily equal, as certain classes of stock may be issued, for example, without voting rights, with enhanced voting rights, or with a certain priority to receive profits or liquidation proceeds before or after other classes of Shareholder, shareholders. Stock can be bought and sold over-the-counter (finance), privately or on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State (polity)
A state is a politics, political entity that regulates society and the population within a definite territory. Government is considered to form the fundamental apparatus of contemporary states. A country often has a single state, with various administrative divisions. A state may be a unitary state or some type of federation, federal union; in the latter type, the term "state" is sometimes used to refer to the federated state, federated polities that make up the federation, and they may have some of the attributes of a sovereign state, except being under their federation and without the same capacity to act internationally. (Other terms that are used in such federal systems may include "province", "Region#Administrative regions, region" or other terms.) For most of prehistory, people lived in stateless societies. The earliest forms of states arose about 5,500 years ago. Over time societies became more Social stratification, stratified and developed institutions leading to Centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |