|
Contraharmonic Mean
In mathematics, a contraharmonic mean (or antiharmonic mean) is a function complementary to the harmonic mean. The contraharmonic mean is a special case of the Lehmer mean, L_p, where ''p'' = 2. Definition The contraharmonic mean of a set of positive real numbers is defined as the arithmetic mean of the squares of the numbers divided by the arithmetic mean of the numbers: \begin \operatorname\left(x_1, x_2, \dots, x_n\right) &= , \\[3pt] &= . \end Two-variable formulae From the formulas for the arithmetic mean and harmonic mean of two variables we have: \begin \operatorname(a, b) &= \\ \operatorname(a, b) &= = \\ \operatorname(a, b) &= 2 \cdot A(a ,b) - H(a, b) \\ &= a + b - = \\ &= \end Notice that for two variables the average of the harmonic and contraharmonic means is exactly equal to the arithmetic mean: As ''a'' gets closer to 0 then H(''a'', ''b'') also gets closer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Mean
In mathematics, the harmonic mean is a kind of average, one of the Pythagorean means. It is the most appropriate average for ratios and rate (mathematics), rates such as speeds, and is normally only used for positive arguments. The harmonic mean is the multiplicative inverse, reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of the reciprocals of the numbers, that is, the generalized f-mean with f(x) = \frac. For example, the harmonic mean of 1, 4, and 4 is :\left(\frac\right)^ = \frac = \frac = 2\,. Definition The harmonic mean ''H'' of the positive real numbers x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n is :H(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n) = \frac = \frac. It is the reciprocal of the arithmetic mean of the reciprocals, and vice versa: :\begin H(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n) &= \frac, \\ A(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n) &= \frac, \end where the arithmetic mean is A(x_1, x_2, \ldots, x_n) = \tfrac1n \sum_^n x_i. The harmonic mean is a Schur-concave function, and is greater than or equal to the minimum of its arguments: for positive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Variance
In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expected value of the squared deviation from the mean of a random variable. The standard deviation (SD) is obtained as the square root of the variance. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of numbers is spread out from their average value. It is the second central moment of a distribution, and the covariance of the random variable with itself, and it is often represented by \sigma^2, s^2, \operatorname(X), V(X), or \mathbb(X). An advantage of variance as a measure of dispersion is that it is more amenable to algebraic manipulation than other measures of dispersion such as the expected absolute deviation; for example, the variance of a sum of uncorrelated random variables is equal to the sum of their variances. A disadvantage of the variance for practical applications is that, unlike the standard deviation, its units differ from the random variable, which is why the standard devi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exponential Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the exponential distribution or negative exponential distribution is the probability distribution of the distance between events in a Poisson point process, i.e., a process in which events occur continuously and independently at a constant average rate; the distance parameter could be any meaningful mono-dimensional measure of the process, such as time between production errors, or length along a roll of fabric in the weaving manufacturing process. It is a particular case of the gamma distribution. It is the continuous analogue of the geometric distribution, and it has the key property of being memoryless. In addition to being used for the analysis of Poisson point processes it is found in various other contexts. The exponential distribution is not the same as the class of exponential families of distributions. This is a large class of probability distributions that includes the exponential distribution as one of its members, but also includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
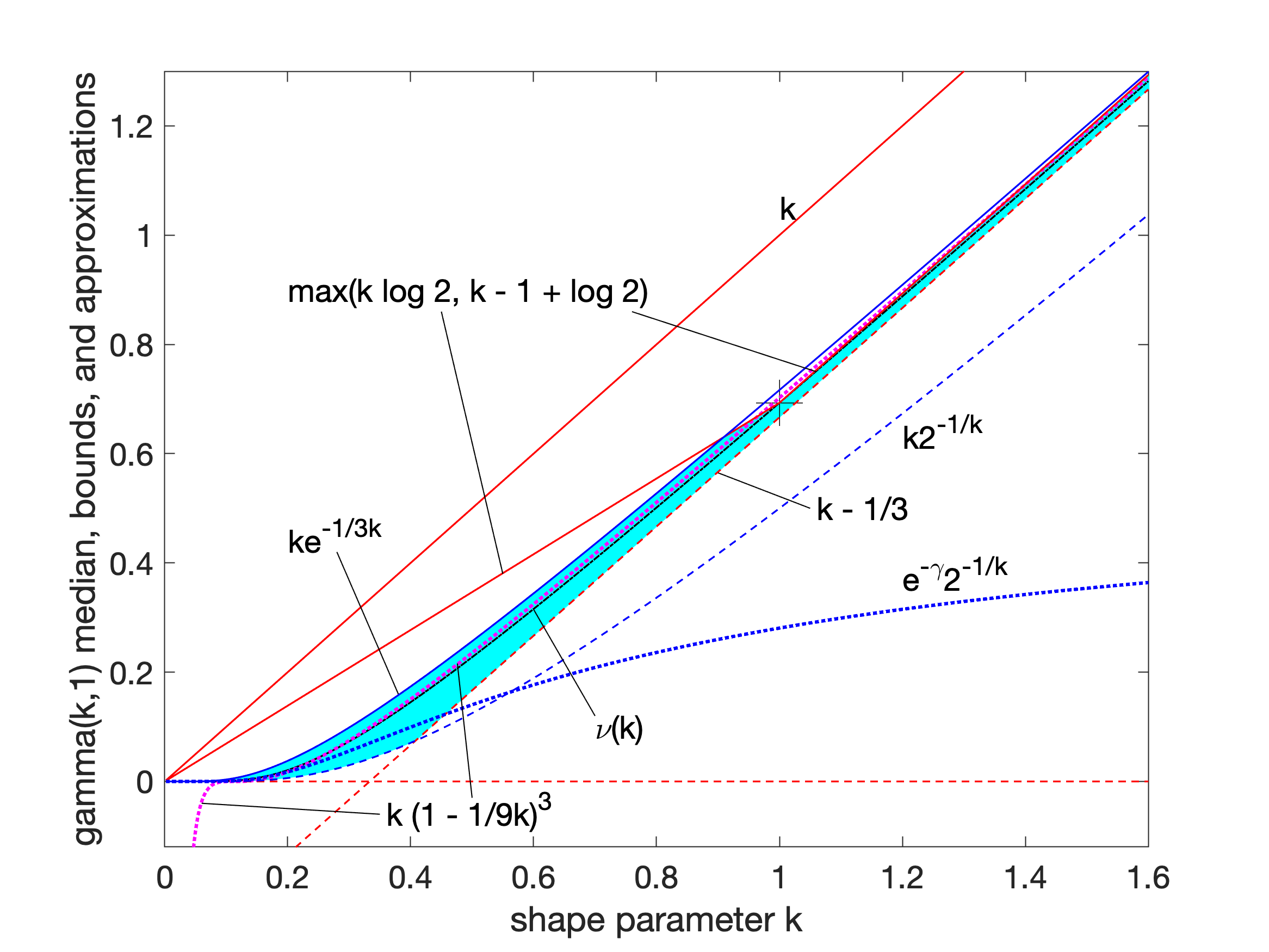
Gamma Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, the gamma distribution is a versatile two-parameter family of continuous probability distributions. The exponential distribution, Erlang distribution, and chi-squared distribution are special cases of the gamma distribution. There are two equivalent parameterizations in common use: # With a shape parameter and a scale parameter # With a shape parameter \alpha and a rate parameter In each of these forms, both parameters are positive real numbers. The distribution has important applications in various fields, including econometrics, Bayesian statistics, and life testing. In econometrics, the (''α'', ''θ'') parameterization is common for modeling waiting times, such as the time until death, where it often takes the form of an Erlang distribution for integer ''α'' values. Bayesian statisticians prefer the (''α'',''λ'') parameterization, utilizing the gamma distribution as a conjugate prior for several inverse scale parameters, facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Log Normal
Log most often refers to: * Trunk (botany), the stem and main wooden axis of a tree, called logs when cut ** Logging, cutting down trees for logs ** Firewood, logs used for fuel ** Lumber or timber, converted from wood logs * Logarithm, in mathematics Log, LOG or LoG may also refer to: Arts, entertainment and media * ''Log'' (magazine), an architectural magazine * ''The Log'', a boating and fishing newspaper published by the Duncan McIntosh Company * Lamb of God (band) or LoG, an American metal band * The Log, an electric guitar by Les Paul * Log, a fictional product in ''The Ren & Stimpy Show'' * The League of Gentlemen or LoG, a British comedy show. Places * Log, Russia, the name of several places * Log, Slovenia, the name of several places Science and mathematics *Logarithm, a mathematical function * Log file, a computer file in which events are recorded * Laplacian of Gaussian or LoG, an algorithm used in digital image processing Other uses * Logbook, or log, a record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, pixels are the smallest element that can be manipulated through software. Each pixel is a Sampling (signal processing), sample of an original image; more samples typically provide more accurate representations of the original. The Intensity (physics), intensity of each pixel is variable. In color imaging systems, a color is typically represented by three or four component intensities such as RGB color model, red, green, and blue, or CMYK color model, cyan, magenta, yellow, and black. In some contexts (such as descriptions of camera sensors), ''pixel'' refers to a single scalar element of a multi-component representation (called a ''photosite'' in the camera sensor context, although ''wikt:sensel, sensel'' is sometimes used), while in yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texas
Texas ( , ; or ) is the most populous U.S. state, state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. It borders Louisiana to the east, Arkansas to the northeast, Oklahoma to the north, New Mexico to the west, and has Mexico-United States border, an international border with the Mexican states of Chihuahua (state), Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas to the south and southwest. Texas has Texas Gulf Coast, a coastline on the Gulf of Mexico to the southeast. Covering and with over 31 million residents as of 2024, it is the second-largest state List of U.S. states and territories by area, by area and List of U.S. states and territories by population, population. Texas is nicknamed the ''Lone Star State'' for its former status as the independent Republic of Texas. Spain was the first European country to Spanish Texas, claim and control Texas. Following French colonization of Texas, a short-lived colony controlled by France, Mexico ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dallas
Dallas () is a city in the U.S. state of Texas and the most populous city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of Texas metropolitan areas, most populous metropolitan area in Texas and the Metropolitan statistical area, fourth-most populous metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 million people. It is the most populous city in and the county seat, seat of Dallas County, Texas, Dallas County, covering nearly 386 square miles into Collin County, Texas, Collin, Denton County, Texas, Denton, Kaufman County, Texas, Kaufman, and Rockwall County, Texas, Rockwall counties. With a 2020 United States census, 2020 census population of 1,304,379, it is the List of United States cities by population, ninth-most populous city in the U.S. and the List of cities in Texas by population, third-most populous city in Texas after Houston and San Antonio. Located in the North Texas region, the city of Dallas is the main core of the largest metropolitan area in the Southern Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Expected Value
In probability theory, the expected value (also called expectation, expectancy, expectation operator, mathematical expectation, mean, expectation value, or first Moment (mathematics), moment) is a generalization of the weighted average. Informally, the expected value is the arithmetic mean, mean of the possible values a random variable can take, weighted by the probability of those outcomes. Since it is obtained through arithmetic, the expected value sometimes may not even be included in the sample data set; it is not the value you would expect to get in reality. The expected value of a random variable with a finite number of outcomes is a weighted average of all possible outcomes. In the case of a continuum of possible outcomes, the expectation is defined by Integral, integration. In the axiomatic foundation for probability provided by measure theory, the expectation is given by Lebesgue integration. The expected value of a random variable is often denoted by , , or , with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montreal
Montreal is the List of towns in Quebec, largest city in the Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Quebec, the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, second-largest in Canada, and the List of North American cities by population, ninth-largest in North America. It was founded in 1642 as ''Fort Ville-Marie, Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", and is now named after Mount Royal, the triple-peaked mountain around which the early settlement was built. The city is centred on the Island of Montreal and a few, much smaller, peripheral islands, the largest of which is Île Bizard. The city is east of the national capital, Ottawa, and southwest of the provincial capital, Quebec City. the city had a population of 1,762,949, and a Census geographic units of Canada#Census metropolitan areas, metropolitan population of 4,291,732, making it the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, second-largest metropolitan area in Canada. French l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elemente Der Mathematik
''Elemente der Mathematik'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal covering mathematics. It is published by the European Mathematical Society Publishing House on behalf of the Swiss Mathematical Society. It was established in 1946 by Louis Locher-Ernst, and transferred to the Swiss Mathematical Society in 1976. Rather than publishing research papers, it focuses on survey papers aimed at a broad audience. History The journal ''Elemente der Mathematik'' was founded in 1946 by Louis Locher-Ernst under the patronage of the Swiss Mathematical Society (SMG) to disseminate pedagogical and expository articles in mathematics and physics. Locher-Ernst outlined the scope and objectives—emphasising support for secondary and tertiary instruction—in a letter to the SMG president in August 1945 and at the autumn members' meeting in Fribourg later that year. Early editorial responsibilities were assumed by Locher-Ernst alongside Erwin Voellmy, Ernst Trost and Paul Buchner, while an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Triple
A Pythagorean triple consists of three positive integers , , and , such that . Such a triple is commonly written , a well-known example is . If is a Pythagorean triple, then so is for any positive integer . A triangle whose side lengths are a Pythagorean triple is a right triangle and called a Pythagorean triangle. A primitive Pythagorean triple is one in which , and are coprime (that is, they have no common divisor larger than 1). For example, is a primitive Pythagorean triple whereas is not. Every Pythagorean triple can be scaled to a unique primitive Pythagorean triple by dividing by their greatest common divisor. Conversely, every Pythagorean triple can be obtained by multiplying the elements of a primitive Pythagorean triple by a positive integer (the same for the three elements). The name is derived from the Pythagorean theorem, stating that every right triangle has side lengths satisfying the formula a^2+b^2=c^2; thus, Pythagorean triples describe the three integer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |