|
Conservation Genetics
Conservation genetics is an interdisciplinary subfield of population genetics that aims to understand the dynamics of genes in a population for the purpose of natural resource management, conservation of genetic diversity, and the prevention of species extinction. Scientists involved in conservation genetics come from a variety of fields including population genetics, research in natural resource management, molecular ecology, molecular biology, evolutionary biology, and systematics. The genetic diversity within species is one of the three fundamental components of biodiversity (along with species diversity and ecosystem diversity), so it is an important consideration in the wider field of conservation biology. Genetic diversity Genetic diversity is the total amount of genetic variability within a species. It can be measured in several ways, including: observed heterozygosity, expected heterozygosity, the mean number of alleles per locus, the percentage of loci that are po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interdisciplinary
Interdisciplinarity or interdisciplinary studies involves the combination of multiple academic disciplines into one activity (e.g., a research project). It draws knowledge from several fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, economics, etc. It is related to an ''interdiscipline'' or an ''interdisciplinary field,'' which is an organizational unit that crosses traditional boundaries between Outline of academic disciplines, academic disciplines or School of thought, schools of thought, as new needs and professions emerge. Large engineering teams are usually interdisciplinary, as a power station or mobile phone or other project requires the melding of several specialties. However, the term "interdisciplinary" is sometimes confined to academic settings. The term ''interdisciplinary'' is applied within education and training pedagogies to describe studies that use methods and insights of several established disciplines or traditional fields of study. Interdisciplinarity in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
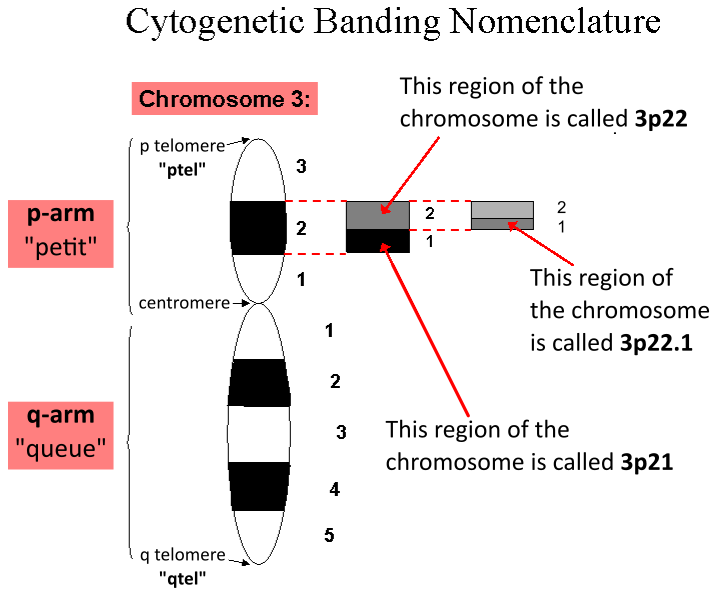
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (: loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of Human genome#Coding sequences (protein-coding genes), protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygote, homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygote, heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication ( translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from substitution, insertion or deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics ( phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer, and the development of the immune system, including junctional diversity. Mutati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
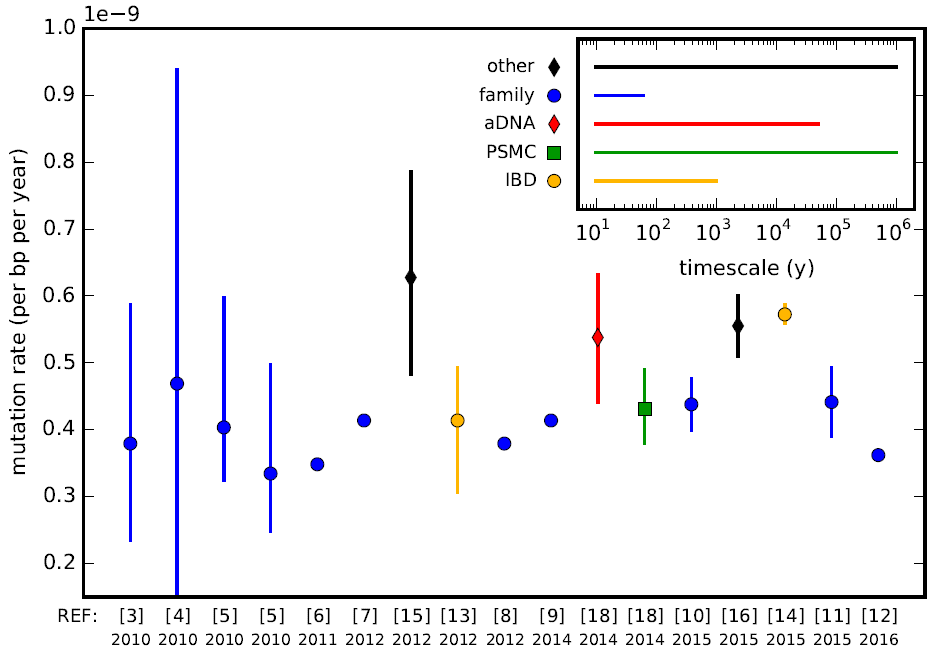
Mutation Rate
In genetics, the mutation rate is the frequency of new mutations in a single gene, nucleotide sequence, or organism over time. Mutation rates are not constant and are not limited to a single type of mutation; there are many different types of mutations. Mutation rates are given for specific classes of mutations. Point mutations are a class of mutations that are changes to a single base. Missense, nonsense, and synonymous mutations are three subtypes of point mutations. The rate of these types of substitutions can be further subdivided into a mutation spectrum, which describes the influence of the genetic context on the mutation rate. There are several natural units of time for each of these rates, with rates being characterized either as mutations per base pair per cell division, per gene per generation, or genome per generation. The mutation rate of an organism is an evolved characteristic and is strongly influenced by the genetics of each organism, in addition to a strong in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watterson Estimator
In population genetics, the Watterson estimator is a method for describing the genetic diversity in a population. It was developed by Margaret Wu and G. A. Watterson in the 1970s. It is estimated by counting the number of polymorphic sites. It is a measure of the "population mutation rate" (the product of the effective population size and the neutral mutation rate) from the observed nucleotide diversity of a population. \theta = 4N_e\mu, where N_e is the effective population size and \mu is the per-generation mutation rate of the population of interest ( ). The assumptions made are that there is a sample of n haploid individuals from the population of interest with effective size N_e, that n \ll N_e, and that there are infinitely many sites capable of varying (so that mutations never overlay or reverse one another). Because the number of segregating sites counted will increase with the number of sequences looked at, the correction factor a_n is used. The estimate of \theta, often d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosomal Crossover
Chromosomal crossover, or crossing over, is the exchange of genetic material during sexual reproduction between two homologous chromosomes' sister chromatids, non-sister chromatids that results in recombinant chromosomes. It is one of the final phases of genetic recombination, which occurs in the ''pachytene'' stage of prophase I of meiosis during a process called synapsis. Synapsis is usually initiated before the synaptonemal complex develops and is not completed until near the end of prophase I. Crossover usually occurs when matching regions on matching chromosomes break and then reconnect to the other chromosome, resulting in Chiasma (genetics), chiasma which are the visible evidence of crossing over. History of discovery Crossing over was described, in theory, by Thomas Hunt Morgan; the term crossover was coined by Morgan and Eleth Cattell. Hunt relied on the discovery of Frans Alfons Janssens who described the phenomenon in 1909 and had called it "chiasmatypie". Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmodium Falciparum
''Plasmodium falciparum'' is a Unicellular organism, unicellular protozoan parasite of humans and is the deadliest species of ''Plasmodium'' that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female ''Anopheles'' mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. ''P. falciparum'' is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer (Burkitt's lymphoma) and is classified as a List of IARC Group 2A carcinogens, Group 2A (probable) carcinogen. The species originated from the malarial parasite ''Laverania'' found in gorillas, around 10,000 years ago. Alphonse Laveran was the first to identify the parasite in 1880, and named it ''Oscillaria malariae''. Ronald Ross discovered its transmission by mosquito in 1897. Giovanni Battista Grassi elucidated the complete transmission from a female Anopheles, anopheline mosquito to humans in 1898. In 1897, William H. Welch create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inbreeding Depression
Inbreeding depression is the reduced biological fitness caused by loss of genetic diversity as a consequence of inbreeding, the breeding of individuals closely related genetically. This loss of genetic diversity results from small population size, often stemming from a population bottleneck. Biological fitness refers to an organism's ability to survive and perpetuate its genetic material. In general, the higher the genetic variation or gene pool within a breeding population, the less likely it is to suffer from inbreeding depression, though inbreeding and outbreeding depression can simultaneously occur. Inbreeding depression seems to be present in most populations of organisms, but varies across mating systems. Remarkably, hermaphroditic species often exhibit lower degrees of inbreeding depression than outcrossing species, as repeated generations of selfing is thought to purge deleterious alleles from populations. For example, the outcrossing nematode (roundworm) '' Caen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Flow
In population genetics, gene flow (also known as migration and allele flow) is the transfer of genetic variation, genetic material from one population to another. If the rate of gene flow is high enough, then two populations will have equivalent allele frequencies and therefore can be considered a single effective population. It has been shown that it takes only "one migrant per generation" to prevent populations from diverging due to Genetic drift, drift. Populations can diverge due to Natural selection, selection even when they are exchanging alleles, if the selection pressure is strong enough. Gene flow is an important mechanism for transferring genetic diversity among populations. Migrants change the distribution of genetic diversity among populations, by modifying allele frequencies (the proportion of members carrying a particular variant of a gene). High rates of gene flow can reduce the genetic differentiation between the two groups, increasing homogeneity. Gene flow has b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Population Size
In population genetics and population ecology, population size (usually denoted ''N'') is a countable quantity representing the number of individual organisms in a population. Population size is directly associated with amount of genetic drift, and is the underlying cause of effects like population bottlenecks and the founder effect. Genetic drift is the major source of decrease of genetic diversity within populations which drives fixation and can potentially lead to speciation events. Genetic drift Of the five conditions required to maintain Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium, infinite population size will always be violated; this means that some degree of genetic drift is always occurring. Smaller population size leads to increased genetic drift, it has been hypothesized that this gives these groups an evolutionary advantage for acquisition of genome complexity. An alternate hypothesis posits that while genetic drift plays a larger role in small populations developing complexity, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterozygosity
Zygosity (the noun, zygote, is from the Greek "yoked," from "yoke") () is the degree to which both copies of a chromosome or gene have the same genetic sequence. In other words, it is the degree of similarity of the alleles in an organism. Most eukaryotes have two matching sets of chromosomes; that is, they are diploid. Diploid organisms have the same locus (genetics), loci on each of their two sets of homologous chromosomes except that the sequences at these loci may differ between the two chromosomes in a matching pair and that a few chromosomes may be mismatched as part of a chromosomal Sex-determination system#Chromosomal determination, sex-determination system. If both alleles of a diploid organism are the same, the organism is #Homozygous, homozygous at that locus. If they are different, the organism is #Heterozygous, heterozygous at that locus. If one allele is missing, it is #Hemizygous, hemizygous, and, if both alleles are missing, it is #Nullizygous, nullizygous. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |