|
Conotoxin
A conotoxin is one of a group of neurotoxic peptides isolated from the venom of the marine cone snail, genus '' Conus''. Conotoxins, which are peptides consisting of 10 to 30 amino acid residues, typically have one or more disulfide bonds. Conotoxins have a variety of mechanisms of actions, most of which have not been determined. However, it appears that many of these peptides modulate the activity of ion channels. Over the last few decades conotoxins have been the subject of pharmacological interest. The LD50 of conotoxin ranges from 5-25 μg/kg. Hypervariability Conotoxins are hypervariable even within the same species. They do not act within a body where they are produced (endogenously) but act on other organisms. Therefore, conotoxin genes experience less selection against mutations (like gene duplication and nonsynonymous substitution), and mutations remain in the genome longer, allowing more time for potentially beneficial novel functions to arise. Variability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
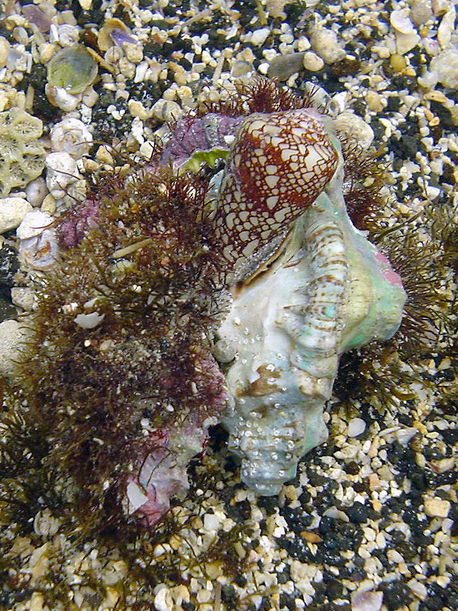
Cone Snail
Cone snails, or cones, are highly venomous sea snails that constitute the family Conidae. ''Conidae'' is a taxonomic family (previously subfamily) of predatory marine gastropod molluscs in the superfamily Conoidea. The 2014 classification of the superfamily Conoidea groups only cone snails in the family Conidae. Some previous classifications grouped the cone snails in a subfamily, Coninae. As of March 2015 Conidae contained over 800 recognized species, varying widely in size from lengths of 1.3 cm to 21.6 cm. Working in 18th-century Europe, Carl Linnaeus knew of only 30 species that are still considered valid. Fossils of cone snails have been found from the Eocene to the Holocene epochs. Cone snail species have shells that are roughly conical in shape. Many species have colorful patterning on the shell surface. Cone snails are almost exclusively tropical in distribution. All cone snails are venomous and capable of stinging. Cone snails use a modified radula tooth and a venom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Channel
Ion channels are pore-forming membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through the channel pore. Their functions include establishing a resting membrane potential, shaping action potentials and other electrical signals by Gating (electrophysiology), gating the flow of ions across the cell membrane, controlling the flow of ions across secretion, secretory and epithelial cells, and regulating cell (biology), cell volume. Ion channels are present in the membranes of all cells. Ion channels are one of the two classes of ionophore, ionophoric proteins, the other being ion transporters. The study of ion channels often involves biophysics, electrophysiology, and pharmacology, while using techniques including voltage clamp, patch clamp, immunohistochemistry, X-ray crystallography, fluoroscopy, and RT-PCR. Their classification as molecules is referred to as channelomics. Basic features There are two distinctive features of ion channels that differentiate them from other types of ion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium Channel
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell (biology), cell's cell membrane, membrane. They belong to the Cation channel superfamily, superfamily of cation channels. Classification They are classified into 2 types: Function In excitable cells such as neurons, muscle, myocytes, and certain types of glia, sodium channels are responsible for the Action potential#Stimulation and rising phase, rising phase of action potentials. These channels go through three different states called resting, active and inactive states. Even though the resting and inactive states would not allow the ions to flow through the channels the difference exists with respect to their structural conformation. Selectivity Sodium channels are highly selective for the transport of ions across cell membranes. The high selectivity with respect to the sodium ion is achieved in many different ways. All involve encapsulation of the sodium ion in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage-dependent Sodium Channels
Sodium channels are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na+) through a cell's membrane. They belong to the superfamily of cation channels. Classification They are classified into 2 types: Function In excitable cells such as neurons, myocytes, and certain types of glia, sodium channels are responsible for the rising phase of action potentials. These channels go through three different states called resting, active and inactive states. Even though the resting and inactive states would not allow the ions to flow through the channels the difference exists with respect to their structural conformation. Selectivity Sodium channels are highly selective for the transport of ions across cell membranes. The high selectivity with respect to the sodium ion is achieved in many different ways. All involve encapsulation of the sodium ion in a cavity of specific size within a larger molecule. Voltage-gated sodium channels Structure Sodium chann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orientations Of Proteins In Membranes Database
Orientations of Proteins in Membranes (OPM) database provides spatial positions of membrane protein protein structure, structures with respect to the lipid bilayer. Positions of the proteins are calculated using an Implicit solvation, implicit solvation model of the lipid bilayer. The results of calculations were verified against experimental studies of spatial arrangement of transmembrane protein, transmembrane and peripheral membrane protein, peripheral proteins in membranes. Proteins structures are taken from the Protein Data Bank. OPM also provides structural classification of membrane-associated proteins into families and superfamilies, membrane topology, quaternary structure of proteins in membrane-bound state, and the type of a destination Biological membrane, membrane for each protein. The coordinate files with calculated membrane boundaries are downloadable. The site allows visualization of protein structures with membrane boundary planes through Jmol. The database w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are Receptor (biochemistry), receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the Sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trefoil Knot Fold
The trefoil knot fold is a protein fold in which the protein backbone is twisted into a trefoil knot shape. "Shallow" knots in which the tail of the polypeptide chain only passes through a loop by a few residues are uncommon, but "deep" knots in which many residues are passed through the loop are extremely rare. Deep trefoil knots have been found in the SPOUT superfamily. including methyltransferase proteins involved in posttranscriptional RNA modification in all three domains of life, including bacterium ''Thermus thermophilus'' and proteins, in archaea and in eukaryota. In many cases the trefoil knot is part of the active site or a ligand-binding site and is critical to the activity of the enzyme in which it appears. Before the discovery of the first knotted protein, it was believed that the process of protein folding could not efficiently produce deep knots in protein backbones. Studies of the folding kinetics of a dimeric protein from ''Haemophilus influenzae'' have rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
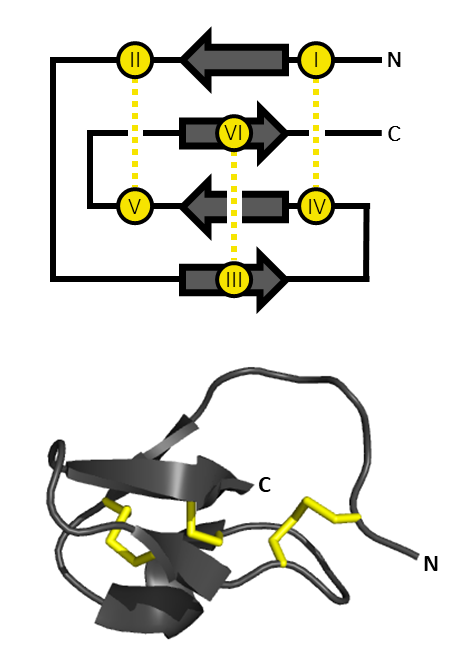
Inhibitor Cystine Knot
An inhibitor cystine knot (also known as ICK or Knottin) is a protein structural motif containing three disulfide bridges. Knottins are one of three folds in the cystine knot motif; the other closely related knots are the growth factor cystine knot (GFCK) and the cyclic cystine knot (CCK; cyclotide). Types include a) cyclic mobius, b) cyclic bracelet, c) acyclic inhibitor knottins. Cystine knot motifs are found frequently in nature in a plethora of plants, animals, and fungi and serve diverse functions from appetite suppression to anti-fungal activity. Along with the sections of polypeptide between them, two disulfides form a loop through which the third disulfide bond (linking the 3rd and 6th cysteine in the sequence) passes, forming a knot. The motif is common in invertebrate toxins such as those from arachnids and molluscs. The motif is also found in some inhibitor proteins found in plants, but the plant and animal motifs are thought to be a product of convergent evolution. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphine
Morphine, formerly also called morphia, is an opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin produced by drying the latex of opium poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as an analgesic (pain medication). There are multiple methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual administration, sublingual; via inhalation; intramuscular, injection into a muscle, Subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin, or injection into the spinal cord area; transdermal; or via rectal administration, rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during Childbirth, labor. Its maximum effect is reached after about 20 minutes when administ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analgesic
An analgesic drug, also called simply an analgesic, antalgic, pain reliever, or painkiller, is any member of the group of drugs used for pain management. Analgesics are conceptually distinct from anesthetics, which temporarily reduce, and in some instances eliminate, sensation, although analgesia and anesthesia are neurophysiologically overlapping and thus various drugs have both analgesic and anesthetic effects. Analgesic choice is also determined by the type of pain: For neuropathic pain, recent research has suggested that classes of drugs that are not normally considered analgesics, such as tricyclic antidepressants and anticonvulsants may be considered as an alternative. Various analgesics, such as many NSAIDs, are available over the counter in most countries, whereas various others are prescription drugs owing to the substantial risks and high chances of overdose, misuse, and addiction in the absence of medical supervision. Etymology The word ''analgesic'' derive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pain
Pain is a distressing feeling often caused by intense or damaging Stimulus (physiology), stimuli. The International Association for the Study of Pain defines pain as "an unpleasant sense, sensory and emotional experience associated with, or resembling that associated with, actual or potential tissue damage." Pain motivates organisms to withdraw from damaging situations, to protect a damaged body part while it heals, and to avoid similar experiences in the future. Congenital insensitivity to pain may result in reduced life expectancy. Most pain resolves once the noxious stimulus is removed and the body has healed, but it may persist despite removal of the stimulus and apparent healing of the body. Sometimes pain arises in the absence of any detectable stimulus, damage or disease. Pain is the most common reason for physician consultation in most developed countries. It is a major symptom in many medical conditions, and can interfere with a person's quality of life and general fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algesia
Hyperalgesia ( or ; ''hyper'' from Greek ὑπέρ (''huper'') 'over' + ''-algesia'' from Greek ἄλγος (algos) 'pain') is an abnormally increased sensitivity to pain, which may be caused by damage to nociceptors or peripheral nerves and can cause hypersensitivity to stimulus. Prostaglandins E and F are largely responsible for sensitizing the nociceptors. Temporary increased sensitivity to pain also occurs as part of sickness behavior, the evolved response to infection. Types Hyperalgesia can be experienced in focal, discrete areas, or as a more diffuse, body-wide form. Conditioning studies have established that it is possible to experience a learned hyperalgesia of the latter, diffuse form. The focal form is typically associated with injury, and is divided into two subtypes: * ''Primary hyperalgesia'' describes pain sensitivity that occurs directly in the damaged tissues. * ''Secondary hyperalgesia'' describes pain sensitivity that occurs in surrounding undamaged tissues. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |