|
Connexin 30
Gap junction beta-6 protein (GJB6), also known as connexin 30 (Cx30) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GJB6'' gene. Connexin 30 (Cx30) is one of several gap junction proteins expressed in the inner ear. Mutations in gap junction genes have been found to lead to both syndromic and nonsyndromic deafness. Mutations in this gene are associated with Clouston syndrome (i.e., hydrotic ectodermal dysplasia). Function The connexin gene family codes for the protein subunits of gap junction channels that mediate direct diffusion of ions and metabolites between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells. Connexins span the plasma membrane 4 times, with amino- and carboxy-terminal regions facing the cytoplasm. Connexin genes are expressed in a cell type-specific manner with overlapping specificity. The gap junction channels have unique properties depending on the type of connexins constituting the channel.[supplied by OMIM] Connexin 30 is prevalent in the two distinct gap junction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ Of Corti
The organ of Corti, or spiral organ, is the receptor organ for hearing and is located in the mammalian cochlea. This highly varied strip of epithelial cells allows for transduction of auditory signals into nerve impulses' action potential. Transduction occurs through vibrations of structures in the inner ear causing displacement of cochlear fluid and movement of hair cells at the organ of Corti to produce electrochemical signals.The Ear Pujol, R., Irving, S., 2013 Italian anatomist Alfonso Giacomo Gaspare Corti (1822–1876) discovered the organ of Corti in 1851. The structure evolved from the basilar p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connexin 30
Gap junction beta-6 protein (GJB6), also known as connexin 30 (Cx30) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GJB6'' gene. Connexin 30 (Cx30) is one of several gap junction proteins expressed in the inner ear. Mutations in gap junction genes have been found to lead to both syndromic and nonsyndromic deafness. Mutations in this gene are associated with Clouston syndrome (i.e., hydrotic ectodermal dysplasia). Function The connexin gene family codes for the protein subunits of gap junction channels that mediate direct diffusion of ions and metabolites between the cytoplasm of adjacent cells. Connexins span the plasma membrane 4 times, with amino- and carboxy-terminal regions facing the cytoplasm. Connexin genes are expressed in a cell type-specific manner with overlapping specificity. The gap junction channels have unique properties depending on the type of connexins constituting the channel.[supplied by OMIM] Connexin 30 is prevalent in the two distinct gap junction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
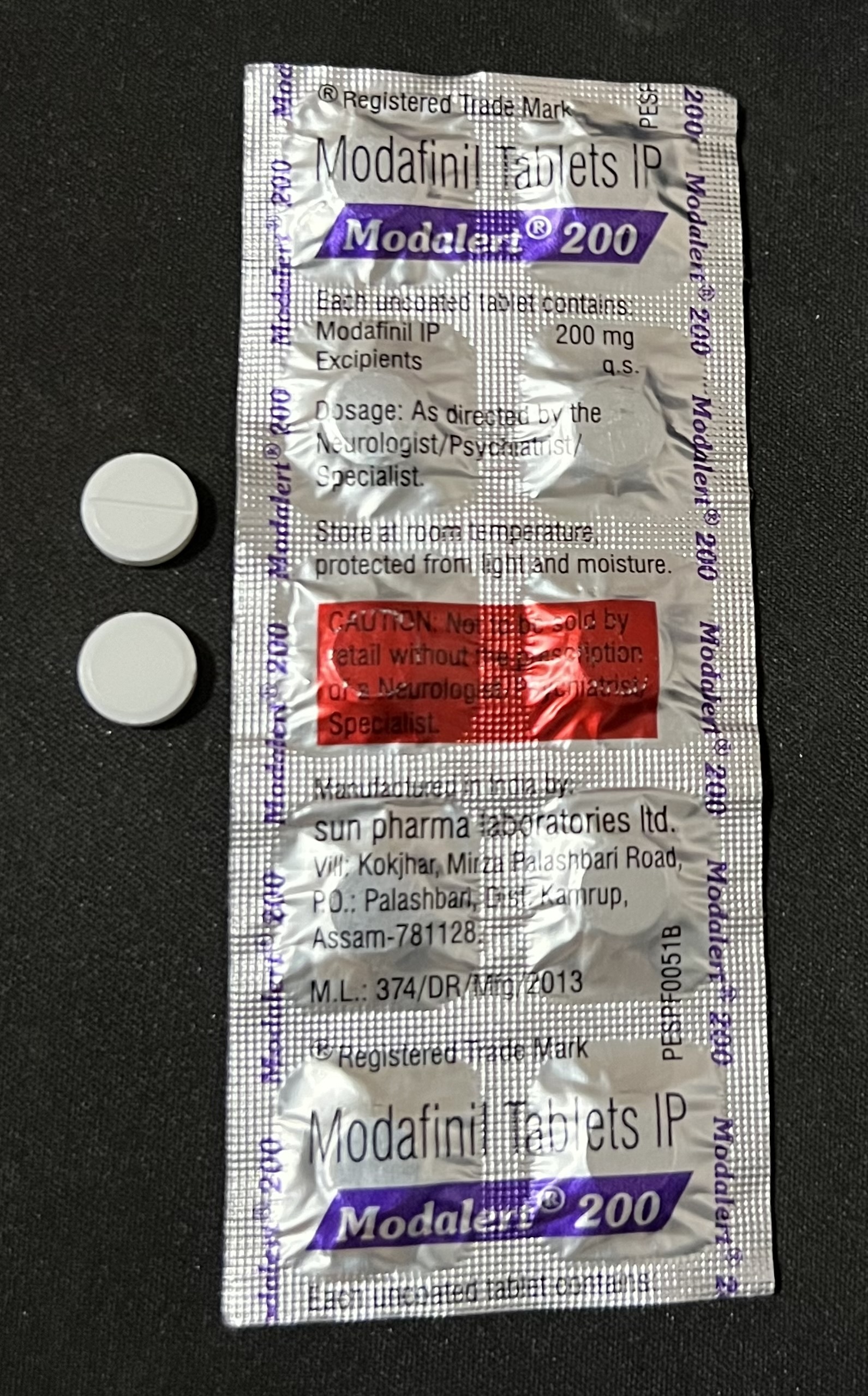
Modafinil
Modafinil, sold under the brand name Provigil among others, is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant and wakefulness-promoting agent, eugeroic (wakefulness promoter) medication used primarily to treat narcolepsy, a sleep disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness and sudden Microsleep, sleep attacks. Modafinil is also approved for stimulating wakefulness in people with sleep apnea and shift work sleep disorder. It is taken by mouth. Modafinil is not approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in people under 17 years old. Common side effects of Modafinil include anxiety, insomnia, dizziness, and headache. Modafinil has potential for causing severe allergic reactions, Psychiatry, psychiatric effects, hypersensitivity, adverse effect, adverse drug interaction, interactions with prescription drugs, and misuse or drug abuse, abuse. Modafinil may harm the fetus if taken during or two months prior to pregnancy. While modafinil is used as a Nootropi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
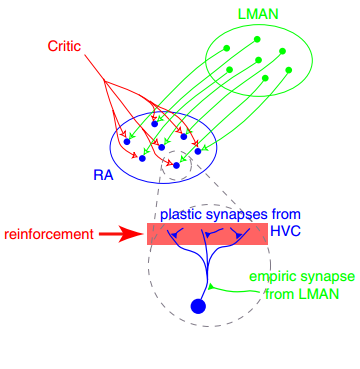
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to Chemical synapse#Synaptic strength, strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memory, memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both Excitatory synapse, excitatory and Inhibitory synapse, inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus
The hippocampus (: hippocampi; via Latin from Ancient Greek, Greek , 'seahorse'), also hippocampus proper, is a major component of the brain of humans and many other vertebrates. In the human brain the hippocampus, the dentate gyrus, and the subiculum are components of the hippocampal formation located in the limbic system. The hippocampus plays important roles in the Memory consolidation, consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables Navigation#Navigation in spatial cognition, navigation. In humans, and other primates the hippocampus is located in the archicortex, one of the three regions of allocortex, in each cerebral hemisphere, hemisphere with direct neural projections to, and reciprocal indirect projections from the neocortex. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extracellular Matrix
In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM. The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest. Each type of connective tissue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Critical Period
In developmental psychology and developmental biology, a critical period is a maturational stage in the lifespan of an organism during which the nervous system is especially sensitive to certain environmental stimuli. If, for some reason, the organism does not receive the appropriate stimulus during this "critical period" to learn a given skill or trait, it may be difficult, ultimately less successful, or even impossible, to develop certain associated functions later in life. Functions that are indispensable to an organism's survival, such as vision, are particularly likely to develop during critical periods. "Critical period" also relates to the ability to acquire one's first language. Researchers found that people who passed the "critical period" without having developed communication skills would not acquire their first language fluently. Some researchers differentiate between 'strong critical periods' and 'weak critical periods' (also known as 'sensitive' periods)—defining ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism. The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, catalytic activity of their own (usually as a cofactor to an enzyme), defense, and interactions with other organisms (e.g. pigments, odorants, and pheromones). A primary metabolite is directly involved in normal "growth", development, and reproduction. Ethylene exemplifies a primary metabolite produced large-scale by industrial microbiology. A secondary metabolite is not directly involved in those processes, but usually has an important ecological function. Examples include antibiotics and pigments such as resins and terpenes etc. Some antibiotics use primary metabolites as precursors, such as actinomycin, which is created from the primary metabolite tryptophan. Some sugars are metabolites, such as fructose or glucose, which ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hair Cell
Hair cells are the sensory receptors of both the auditory system and the vestibular system in the ears of all vertebrates, and in the lateral line organ of fishes. Through mechanotransduction, hair cells detect movement in their environment. In mammals, the auditory hair cells are located within the spiral organ of Corti on the thin basilar membrane in the cochlea of the inner ear. They derive their name from the tufts of stereocilia called ''hair bundles'' that protrude from the apical surface of the cell into the fluid-filled cochlear duct. The stereocilia number from fifty to a hundred in each cell while being tightly packed together and decrease in size the further away they are located from the kinocilium. Mammalian cochlear hair cells are of two anatomically and functionally distinct types, known as outer, and inner hair cells. Damage to these hair cells results in decreased hearing sensitivity, and because the inner ear hair cells cannot regenerate, this damag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |