|
Conductive Textile
A conductive textile is a fabric which can conduct electricity. Conductive textiles known as lamé are made with guipé thread or yarn that is conductive because it is composed of metallic fibers wrapped around a non-metallic core or has a metallic coating. A different way of achieving conductivity is to weave metallic strands into the textile. Some historic fabrics use yarns of solid metals, most commonly gold. Alternatively, novel materials such as nanomaterials (including graphene, and carbon nanotubes) or conducting polymers may also be used as the conducting materials. There is also an interest in semiconducting textiles, made by impregnating normal textiles with carbon- or metal-based powders. Conductive fibers consist of a non-conductive or less conductive substrate, which is then either coated or embedded with electrically conductive elements, often carbon, nickel, copper, gold, silver, titanium or PEDOT. Metals may be deposited chemically with Autocatalysis, autocat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Vapor Deposition
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polymers. PVD is characterized by a process in which the material transitions from a condensed phase to a vapor phase and then back to a thin film condensed phase. The most common PVD processes are Sputter coating, sputtering and Evaporation (deposition), evaporation. PVD is used in the manufacturing of items which require thin films for optical, mechanical, electrical, acoustic or chemical functions. Examples include semiconductor devices such as thin-film solar cells, microelectromechanical devices such as thin film bulk acoustic resonator, aluminized Polyethylene terephthalate, PET film for food packaging and balloons, and titanium nitride coated cutting tools for metalworking. Besides PVD tools for fabrication, special smaller tools used mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or a gas). In electrochemical cells, electrodes are essential parts that can consist of a variety of materials (chemicals) depending on the type of cell. An electrode may be called either a cathode or anode according to the direction of the electric current, unrelated to the potential difference between electrodes. Michael Faraday coined the term "" in 1833; the word recalls the Greek ἤλεκτρον (, "amber") and ὁδός (, "path, way"). The electrophore, invented by Johan Wilcke in 1762, was an early version of an electrode used to study static electricity. Anode and cathode in electrochemical cells Electrodes are an essential part of any battery. The first electrochemical battery was devised by Alessandro Volta and was aptly named the Voltaic cell. This battery consisted of a stack of copper and zinc electrodes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamé (fencing)
In modern fencing, a lamé is an electrically conductive jacket worn by foil and sabre fencers in order to define the scoring area and register contact with it. Lamés are wired by use of a body cord to a scoring machine, which allows the other person's weapon to register touches when their tips (or blades, in sabre) contact the lamé. Lamés generally consist of a polyester jacket overlain with a thin, interwoven metal, usually steel or copper. This gives the lamés a metallic, gray appearance, but colored foil lamés have become increasingly popular. Lamés used in higher-level competitions usually have the last name and country of their owner printed in blue across the back. Because the scoring area is different for each weapon, the lamé may cover more or less of the body depending on which weapon the fencer uses. In foil, the lamé extends on the torso from the shoulders to the groin area, including the back. In sabre, the lamé covers both arms, the torso from the shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fencing
Fencing is a combat sport that features sword fighting. It consists of three primary disciplines: Foil (fencing), foil, épée, and Sabre (fencing), sabre (also spelled ''saber''), each with its own blade and set of rules. Most competitive fencers specialise in one of these disciplines. The modern sport gained prominence near the end of the 19th century, evolving from historical European swordsmanship. The Italian school of swordsmanship, Italian school altered the Historical European martial arts, historical European martial art of classical fencing, and the French school of fencing, French school later refined that system. Scoring points in a fencing competition is done by making contact with the opponent with one's sword. The 1904 Olympic Games featured a fourth discipline of fencing known as singlestick, but it was dropped after that year and is not a part of modern fencing. Competitive fencing was one of the first sports to be featured in the Olympics and, along with Athl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heating Element
A heating element is a device used for conversion of electric energy into heat, consisting of a heating resistor and accessories. Heat is generated by the passage of electric current through a resistor through a process known as Joule heating. Heating elements are used in household appliances, industrial equipment, and scientific instruments enabling them to perform tasks such as cooking, warming, or maintaining specific temperatures higher than the ambient. Heating elements may be used to transfer heat via Thermal conduction, conduction, convection, or radiation. They are different from devices that generate heat from electrical energy via the Peltier effect, and have no dependence on the direction of electrical current. Principles of operation Resistance & resistivity Materials used in heating elements have a relatively high Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical resistivity, which is a measure of the material's ability to resist electric current. The Electri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrical Resistance
The electrical resistance of an object is a measure of its opposition to the flow of electric current. Its reciprocal quantity is , measuring the ease with which an electric current passes. Electrical resistance shares some conceptual parallels with mechanical friction. The SI unit of electrical resistance is the ohm (), while electrical conductance is measured in siemens (S) (formerly called the 'mho' and then represented by ). The resistance of an object depends in large part on the material it is made of. Objects made of electrical insulators like rubber tend to have very high resistance and low conductance, while objects made of electrical conductors like metals tend to have very low resistance and high conductance. This relationship is quantified by resistivity or conductivity. The nature of a material is not the only factor in resistance and conductance, however; it also depends on the size and shape of an object because these properties are extensive rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostatics
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies slow-moving or stationary electric charges. Since classical antiquity, classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after triboelectric effect, rubbing. The Greek language, Greek word (), meaning 'amber', was thus the Root (linguistics), root of the word ''electricity''. Electrostatic phenomena arise from the forces that electric charges exert on each other. Such forces are described by Coulomb's law. There are many examples of electrostatic phenomena, from those as simple as the attraction of plastic wrap to one's hand after it is removed from a package, to the apparently spontaneous explosion of grain silos, the damage of electronic components during manufacturing, and photocopier and laser printing, laser printer operation. The electrostatic model accurately predicts electrical phenomena in "classical" cases where the velocities are low and the system is macroscopic so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbon Tape Used For Stun Gun Proof Clothing
Carbon () is a chemical element; it has symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—meaning that its atoms are able to form up to four covalent bonds due to its valence shell exhibiting 4 electrons. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon makes up about 0.025 percent of Earth's crust. Three isotopes occur naturally, C and C being stable, while C is a radionuclide, decaying with a half-life of 5,700 years. Carbon is one of the few elements known since antiquity. Carbon is the 15th most abundant element in the Earth's crust, and the fourth most abundant element in the universe by mass after hydrogen, helium, and oxygen. Carbon's abundance, its unique diversity of organic compounds, and its unusual ability to form polymers at the temperatures commonly encountered on Earth, enables this element to serve as a common element of all known life. It is the second most abundant element in the human body by mass (about 18.5%) after oxygen. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
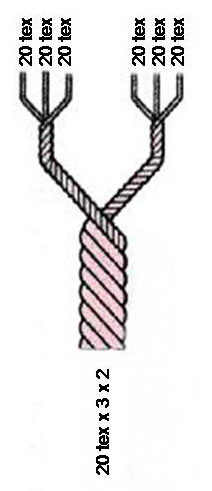
Units Of Textile Measurement
Textile fibers, threads, yarns and fabrics are measured in a multiplicity of units. * A fiber, a single filament of natural material, such as cotton, linen or wool, or artificial material such as nylon, polyester, metal or mineral fiber, or human-made cellulosic fibre like viscose, Modal, Lyocell or other rayon fiber is measured in terms of linear mass density, the weight of a given length of fiber. Various units are used to refer to the measurement of a fiber, such as: the denier and tex (linear mass density of fibers), super S (fineness of wool fiber), worsted count, woolen count, linen count (wet spun) (or Number English (Ne)), cotton count (or Number English (Ne)), Number metric (Nm) and yield (the reciprocal of denier and tex). * A yarn, a spun agglomeration of fibers used for knitting, weaving or sewing, is measured in terms of cotton count and yarn density. * Thread, usually consisting of multiple yarns plied together producing a long, thin strand used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel, also known as inox, corrosion-resistant steel (CRES), or rustless steel, is an iron-based alloy that contains chromium, making it resistant to rust and corrosion. Stainless steel's resistance to corrosion comes from its chromium content of 11% or more, which forms a Passivation (chemistry), passive film that protects the material and can self-healing material, self-heal when exposed to oxygen. It can be further alloyed with elements like molybdenum, carbon, nickel and nitrogen to enhance specific properties for various applications. The alloy's properties, such as luster and resistance to corrosion, are useful in many applications. Stainless steel can be rolled into Sheet metal, sheets, plates, bars, wire, and tubing. These can be used in cookware, cutlery, surgical instruments, major appliances, vehicles, construction material in large buildings, industrial equipment (e.g., in paper mills, chemical plants, water treatment), and storage tanks and tankers for ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |