|
Concentric Hypertrophy
Concentric hypertrophy is a hypertrophic growth of a hollow organ without overall enlargement, in which the walls of the organ are thickened and its capacity or volume is diminished. Sarcomeres are added in parallel, as for example occurs in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In the heart, concentric hypertrophy is related to increased pressure overload of the heart, often due to hypertension and/or aortic stenosis. The consequence is a decrease in ventricular compliance and diastolic dysfunction Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the ..., followed eventually by ventricular failure and systolic dysfunction. Laplace's law for a sphere states wall stress (T) is proportionate to the product of the transmural pressure (P) and cavitary radius (r) and inversely proportionate to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
|
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number. Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy. Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart. Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel). Gallery Gould Pyle 234.jpg, Breasts Hypertrophied clitoris.jpg, Clitoris Head of a boy with hypertrophy of the ear Wellcome L0062496.j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Ventricular Failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood. Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically presents with shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and bilateral leg swelling. The severity of the heart failure is mainly decided based on ejection fraction and also measured by the severity of symptoms. Other conditions that have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering the structure or the function of the heart or in some cases both. There are different types of heart failure: right-sided heart failure, which affects the righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Tissues (biology)
Tissue may refer to: Biology * Tissue (biology), an ensemble of similar (or dissimilar in structure but same in origin) cells that together carry out a specific function * ''Triphosa haesitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue moth") found in North America * ''Triphosa dubitata'', a species of geometer moth ("tissue") found in Afro-Eurasia Paper products * Tissue paper, a type of thin, gauzy translucent paper used for wrapping and cushioning items * Tissue (cloth), a thin, transparent, and lightweight fabric * Facial tissue, tissue paper used for cleaning the face * Japanese tissue, tissue paper from Japan made of vegetable fibers * Toilet paper, tissue paper used for cleaning the anus * Wrapping tissue, tissue paper used for wrapping and cushioning items Other * Aerial tissue, an acrobatic art form and one of the circus arts * "The Tissue (Tomaranai Seishun)", a 2011 song by Shiritsu Ebisu Chugaku * ''Tissue'', a 2017 poem by Imtiaz Dharker {{Disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Exercise Physiology
Exercise physiology is the physiology of physical exercise. It is one of the allied health professions, and involves the study of the acute responses and chronic adaptations to exercise. Exercise physiologists are the highest qualified exercise professionals and utilise education, lifestyle intervention and specific forms of exercise to rehabilitate and manage acute and chronic injuries and conditions. Understanding the effect of exercise involves studying specific changes in muscular, cardiovascular, and Neuro-hormonal, neurohormonal Biological system, systems that lead to changes in functional capacity and Physical strength, strength due to endurance training or strength training. The effect of training on the body has been defined as the reaction to the adaptive responses of the body arising from exercise or as "an elevation of metabolism produced by exercise". Exercise physiologists study the effect of exercise on pathology, and the mechanisms by which exercise can reduce or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Physical Exercise
Exercise or workout is physical activity that enhances or maintains fitness and overall health. It is performed for various reasons, including weight loss or maintenance, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, prevent injuries, hone athletic skills, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many people choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, usually, 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week is recommended for reducing the risk of health problems. At the same time, even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Only doing an hour and a quarter (11 minutes/day) of exercise could reduce the risk of early death, cardiovascular disease, stroke, and cancer. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the huma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Anatomical Pathology
Anatomical pathology (''Commonwealth'') or anatomic pathology (''U.S.'') is a medical specialty that is concerned with the diagnosis of disease based on the macroscopic, microscopic, biochemical, immunologic and molecular examination of organs and tissues. Over the 20th century, surgical pathology has evolved tremendously: from historical examination of whole bodies (autopsy) to a more modernized practice, centered on the diagnosis and prognosis of cancer to guide treatment decision-making in oncology. Its modern founder was the Italian scientist Giovanni Battista Morgagni from Forlì. Anatomical pathology is one of two branches of pathology, the other being clinical pathology, the diagnosis of disease through the laboratory analysis of bodily fluids or tissues. Often, pathologists practice both anatomical and clinical pathology, a combination known as general pathology. Similar specialties exist in veterinary pathology. Differences with clinical pathology Anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
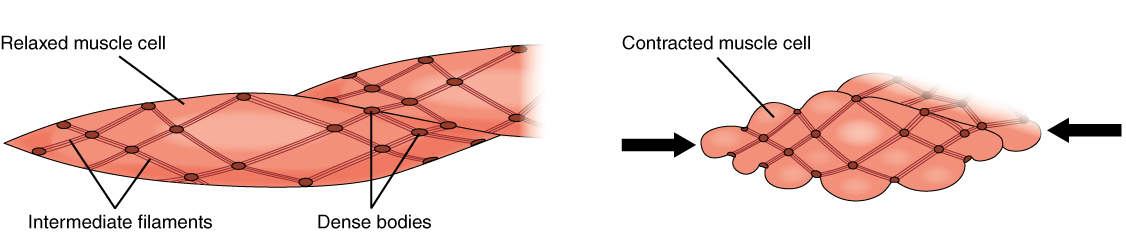 |
Smooth Muscle
Smooth muscle is one of the three major types of vertebrate muscle tissue, the others being skeletal and cardiac muscle. It can also be found in invertebrates and is controlled by the autonomic nervous system. It is non- striated, so-called because it has no sarcomeres and therefore no striations (''bands'' or ''stripes''). It can be divided into two subgroups, ''single-unit'' and ''multi-unit'' smooth muscle. Within single-unit muscle, the whole bundle or sheet of smooth muscle cells contracts as a syncytium. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of hollow organs, including the stomach, intestines, bladder and uterus. In the walls of blood vessels, and lymph vessels, (excluding blood and lymph capillaries) it is known as vascular smooth muscle. There is smooth muscle in the tracts of the respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems. In the eyes, the ciliary muscles, iris dilator muscle, and iris sphincter muscle are types of smooth muscles. The iris dilator and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
Young–Laplace Equation
In physics, the Young–Laplace equation () is an equation that describes the capillary pressure difference sustained across the interface between two static fluids, such as water and air, due to the phenomenon of surface tension or wall tension, although use of the latter is only applicable if assuming that the wall is very thin. The Young–Laplace equation relates the pressure difference to the shape of the surface or wall and it is fundamentally important in the study of static capillary surfaces. It is a statement of normal stress balance for static fluids meeting at an interface, where the interface is treated as a surface (zero thickness): \begin \Delta p &= -\gamma \nabla \cdot \hat n \\ &= -2\gamma H_f \\ &= -\gamma \left(\frac + \frac\right) \end where \Delta p is the Laplace pressure, the pressure difference across the fluid interface (the exterior pressure minus the interior pressure), \gamma is the surface tension (or wall tension), \hat n is the unit normal poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
|
 |
Systolic Dysfunction
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome caused by an impairment in the heart's ability to fill with and pump blood. Although symptoms vary based on which side of the heart is affected, HF typically presents with shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, and bilateral leg swelling. The severity of the heart failure is mainly decided based on ejection fraction and also measured by the severity of symptoms. Other conditions that have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver disease, anemia, and thyroid disease. Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease, heart attack, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excessive alcohol consumption, infection, and cardiomyopathy. These cause heart failure by altering the structure or the function of the heart or in some cases both. There are different types of heart failure: right-sided heart failure, which affects the righ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Diastolic Dysfunction
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the left ventricle is maximally filled – is normal, defined as greater than 50%; this may be measured by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. Approximately half of people with heart failure have preserved ejection fraction, while the other half have a reduction in ejection fraction, called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF). Risk factors for HFpEF include hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, smoking, and obstructive sleep apnea. Those with HFpEF have a higher prevalence of obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, atrial fibrillation and chronic kidney disease than those with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. The prevalence of HFpEF is expected to increase as more people develop obesity and other medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Organ (anatomy)
In a multicellular organism, an organ is a collection of Tissue (biology), tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the biological organization, hierarchy of life, an organ lies between Tissue (biology), tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type Cell (biology), cells to act together in a function. Tissues of different types combine to form an organ which has a specific function. The Gastrointestinal tract, intestinal wall for example is formed by epithelial tissue and smooth muscle tissue. Two or more organs working together in the execution of a specific body function form an organ system, also called a biological system or body system. An organ's tissues can be broadly categorized as parenchyma, the functional tissue, and stroma (tissue), stroma, the structural tissue with supportive, connective, or ancillary functions. For example, the gland's tissue that makes the hormones is the parenchyma, whereas the stroma includes the nerve t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
 |
Ventricle (heart)
A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles (for example the interventricular septum), while intraventricular means within one ventricle (for example an intraventricular block). In a four-chambered heart, such as that in humans, there are two ventricles that operate in a double circulatory system: the right ventricle pumps blood into the pulmonary circulation to the lungs, and the left ventricle pumps blood into the systemic circulation through the aorta. Structure Ventricles have thicker walls than atria and generate higher blood pressures. The physiological load on the ventricles requiring pumping of blood throughout the body and lungs is much greater than the pressure generated by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |