|
Compulsive Eating
Disordered eating describes a variety of abnormal eating behaviors that, by themselves, do not warrant diagnosis of an eating disorder. Disordered eating includes behaviors that are common features of eating disorders, such as: * Chronic restrained eating. * Compulsive eating. * Binge eating, with associated loss of control. * Self-induced vomiting. Disordered eating also includes behaviors that are not characteristic of a specific eating disorder, such as: * Irregular, chaotic eating patterns. * Ignoring physical feelings of hunger and satiety (fullness). * Use of diet pills. * Emotional eating. * Night eating. * Secretive food concocting: the consumption of embarrassing food combinations, such as mashed potatoes mixed with sandwich cookies. See also Food craving § Pregnancy and Nocturnal sleep-related eating disorder § Symptoms and behaviors. Potential causes of disordered eating Disordered eating can represent a change in eating patterns caused by other mental disord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eating Disorder
An eating disorder is a mental disorder defined by abnormal eating behaviors that adversely affect a person's health, physical or mental health, mental health. These behaviors may include eating too much food or too little food. Types of eating disorders include binge eating disorder, where the person suffering keeps eating large amounts in a short period of time typically while not being hungry; anorexia nervosa, where the person has an intense fear of gaining weight and restricts food or overexercises to manage this fear; bulimia nervosa, where individuals eat a large quantity (binging) then try to rid themselves of the food (purging); pica (disorder), pica, where the patient eats non-food items; rumination syndrome, where the patient regurgitation (digestion), regurgitates undigested or minimally digested food; avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder (ARFID), where people have a reduced or selective food intake due to some psychological reasons; and a group of other specifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasting
Fasting is the act of refraining from eating, and sometimes drinking. However, from a purely physiological context, "fasting" may refer to the metabolic status of a person who has not eaten overnight (before "breakfast"), or to the metabolic state achieved after complete digestion and absorption of a meal. Metabolic changes in the fasting state begin after absorption of a meal (typically 3–5 hours after eating). A '' diagnostic fast'' refers to prolonged fasting from 1–100 hours (depending on age), conducted under observation, to facilitate the investigation of a health complication (usually hypoglycemia). Many people may also fast as part of a medical procedure or a check-up, such as preceding a colonoscopy or surgery, or before certain medical tests. '' Intermittent fasting'' is a technique sometimes used for weight loss or other health benefits that incorporates regular fasting into a person's dietary schedule. Fasting may also be part of a religious ritual, often asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overeaters Anonymous
Overeaters Anonymous (OA) is a twelve-step program founded by Rozanne S. Its first meeting was held in Hollywood, California, Hollywood, California, USA on January 19, 1960, after Rozanne attended a Gamblers Anonymous meeting and realized that the Twelve Steps could potentially help her with her own addictive behaviors relating to food. OA has since grown, with groups in over 75 countries meeting in person, over the phone, and through the internet. OA is for people with problems related to food including, but not limited to, compulsive overeaters, those with binge eating disorder, Bulimia nervosa, bulimics and Anorexia nervosa, anorexics. Anyone with a problematic relationship with food is welcomed; OA's Third Tradition states that the only requirement for memberships is a desire to stop eating compulsively. OA's headquarters, or World Service Office, is located in Rio Rancho, New Mexico. Overeaters Anonymous estimates its membership at over 60,000 people in about 6,500 groups meeti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Night Eating Syndrome
Night eating syndrome (NES) is classified as an Other Specified Feeding or Eating Disorder (OSFED) under the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition (DSM-5).American Psychiatric Association. (2013). ''Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders ''(5th ed.).'' ''Washington, DC: Author. It involves recurrent episodes of night eating after awakening from sleep or after the evening meal. Awareness and recall of the eating is present, which is a key characteristic that differentiates the disorder from Sleep-Related Eating Disorder (SRED). Although there is some degree of comorbidity with binge eating disorder (BED), it differs from binge eating in that the amount of food consumed in the night is not necessarily objectively large nor is a loss of control over food intake required. The syndrome causes significant distress or functional impairment and cannot be better explained by external influences such as changes in the sleep-wake cycle, social norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demineralization (physiology)
Demineralization is the opposite process of mineralization; it is a process of reduction in the mineral content in tissue or an organism. Examples include bone demineralization or tooth demineralization. Demineralization can lead to serious diseases such as osteoporosis, rickets, or tooth decay. Usually, treatment involves administration of appropriate dietary supplements to help restore the remineralization of human tissues and their physiological state. See also * Bone resorption * Bone remodeling 300 px, Bone tissue is removed by osteoclasts, and then new bone tissue is formed by osteoblasts. Both processes utilize cytokine ( Insulin-like_growth_factor.html" ;"title="TGF-β, Insulin-like growth factor">IGF) signalling. In osteology, bone ... References Physiology {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amenorrhoea
Amenorrhea or amenorrhoea is the absence of a menstrual period in a female organism who has reached reproductive age. Physiological states of amenorrhoea are most commonly seen during pregnancy and lactation (breastfeeding). In humans, it is where a woman or girl who has reached reproductive age who is not on birth control does not menstruate. Amenorrhoea is a symptom with many potential causes. Primary amenorrhea is defined as an absence of secondary sexual characteristics by age 13 with no menarche or normal secondary sexual characteristics but no menarche by 15 years of age. It may be caused by developmental problems, such as the congenital absence of the uterus, failure of the ovary to receive or maintain egg cells, or delay in pubertal development. Secondary amenorrhoea, ceasing of menstrual cycles after menarche, is defined as the absence of menses for three months in a woman with previously normal menstruation, or six months for women with a history of oligomenorrhoea. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minority Group
The term "minority group" has different meanings, depending on the context. According to common usage, it can be defined simply as a group in society with the least number of individuals, or less than half of a population. Usually a minority group is disempowered relative to the majority, and that characteristic lends itself to different applications of the term minority. In terms of sociology, economics, and politics, a demographic that takes up the smallest fraction of the population is not necessarily labelled the "minority" if it wields dominant power. In the academic context, the terms "minority" and "majority" are used in terms of hierarchical power structures. For example, in South Africa, during Apartheid, white Europeans held virtually all social, economic, and political power over black Africans. For this reason, black Africans are the "minority group", despite the fact that they outnumber white Europeans in South Africa. This is why academics more frequently use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
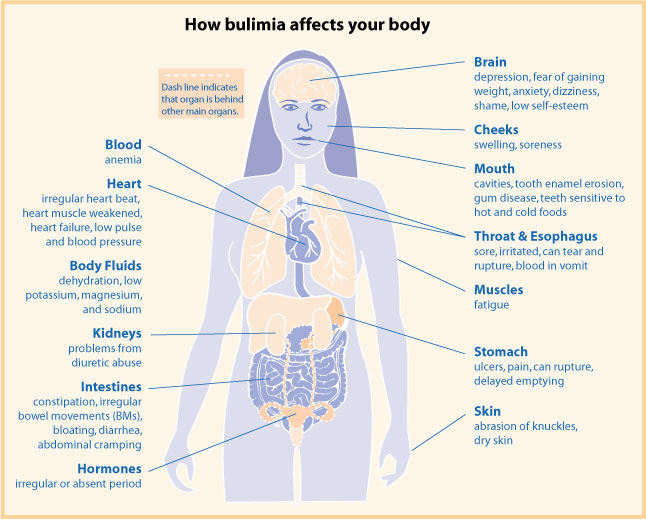
Bulimia Nervosa
Bulimia nervosa, also known simply as bulimia, is an eating disorder characterized by binge eating (eating large quantities of food in a short period of time, often feeling out of control) followed by compensatory behaviors, such as self-induced vomiting or fasting, to prevent weight gain. Other efforts to lose weight may include the use of diuretics, laxatives, stimulants, water fasting, or excessive exercise. Most people with bulimia are at normal weight and have higher risk for other mental disorders, such as depression, anxiety, borderline personality disorder, bipolar disorder, and problems with drugs to alcohol. There is also a higher risk of suicide and self-harm. Bulimia is more common among those who have a close relative with the condition. The percentage risk that is estimated to be due to genetics is between 30% and 80%. Other risk factors for the disease include psychological stress, cultural pressure to attain a certain body type, poor self-esteem, and obes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binge Eating
Binge eating is a pattern of disordered eating which consists of episodes of uncontrollable eating. It is a common symptom of eating disorders such as binge eating disorder and bulimia nervosa. During such binges, a person rapidly consumes an excessive quantity of food. A Medical diagnosis, diagnosis of binge eating is associated with feelings of loss of control. Binge eating disorder is also linked with being overweight and obesity. Diagnosis The DSM-5 includes a disorder diagnosis criterion for Binge eating disorder, Binge Eating Disorder (BED). It is as follows: * Recurrent and persistent episodes of binge eating * Binge eating episodes are associated with three (or more) of the following: ** Eating much more rapidly than normal ** Eating until feeling uncomfortably full ** Eating large amounts of food when not physically hungry ** Eating alone because of being embarrassed by how much one is eating ** Feeling disgusted with oneself, depressed, or very guilty after overeat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LGBT
LGBTQ people are individuals who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer, or questioning. Many variants of the initialism are used; LGBTQIA+ people incorporates intersex, asexual, aromantic, agender, and other individuals. The group is generally conceived as broadly encompassing all individuals who are part of a sexual or gender minority, including all sexual orientations, romantic orientations, gender identities, and sex characteristics that are not heterosexual, heteroromantic, cisgender, or endosex, respectively. Scope and terminology A broad array of sexual and gender minority identities are usually included in who is considered LGBTQ. The term ''gender, sexual, and romantic minorities'' is sometimes used as an alternative umbrella term for this group. Groups that make up the larger group of LGBTQ people include: * People with a sexual orientation that is non-heterosexual, including lesbians, gay men, bisexual people, and asexual people * People ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology Of Women Quarterly
''Psychology of Women Quarterly'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal that covers the fields of psychology and women's studies, focusing on the psychological health of women. The journal's editor is Dawn M. Szymanski, PhD (University of Tennessee, Knoxville, TN, United States). It was established in 1976 and is published by SAGE Publications on behalf of thSociety for the Psychology of Women a division of the American Psychological Association. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2017 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a type of journal ranking. Journals with higher impact factor values are considered more prestigious or important within their field. The Impact Factor of a journa ... of 2.973, ranking it 1st out of 42 journals in the category "Women's Studies" and 23rd out of 135 journals in the category "Psychol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Stress
Social stress is stress that stems from one's relationships with others and from the social environment in general. Based on the appraisal theory of emotion, stress arises when a person evaluates a situation as personally relevant and perceives that they do not have the resources to cope or handle the specific situation. The activation of social stress does not necessarily have to occur linked to a specific event, the mere idea that the event may occur could trigger it. This means that any element that takes a subject out of their personal and intimate environment could become a stressful experience. This situation makes them socially incompetent individuals. There are three main categories of social stressors. Life events are defined as abrupt, severe life changes that require an individual to adapt quickly (ex. sexual assault, sudden injury). Chronic strains are defined as persistent events which require an individual to make adaptations over an extended period of time (ex. d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |