|
Compound Heterozygotes
In medical genetics, compound heterozygosity is the condition of having two or more heterogeneous recessive alleles at a particular locus that can cause genetic disease in a heterozygous state; that is, an organism is a compound heterozygote when it has two recessive alleles for the same gene, but with those two alleles being different from each other (for example, both alleles might be mutated but at different locations). Compound heterozygosity reflects the diversity of the mutation base for many autosomal recessive genetic disorders; mutations in most disease-causing genes have arisen many times. This means that many cases of disease arise in individuals who have two unrelated alleles, who technically are heterozygotes, but both the alleles are defective. These disorders are often best known in some classic form, such as the homozygous recessive case of a particular mutation that is widespread in some population. In its compound heterozygous forms, the disease may have lower pene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch of medicine that involves the diagnosis and management of hereditary disorders. Medical genetics differs from human genetics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metabolism
Metabolism (, from ''metabolē'', "change") is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. The three main functions of metabolism are: the conversion of the energy in food to energy available to run cellular processes; the conversion of food to building blocks of proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and some carbohydrates; and the elimination of metabolic wastes. These enzyme-catalyzed reactions allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their Structures#Biological, structures, and respond to their environments. The word ''metabolism'' can also refer to the sum of all chemical reactions that occur in living organisms, including digestion and the transportation of substances into and between different cells, in which case the above described set of reactions within the cells is called intermediary (or intermediate) metabolism. Metabolic reactions may be categorized as ''catabolic''—the ''breaking down'' of compounds (for example, of glucose to pyruvate by c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin C
Hemoglobin C (abbreviated as HbC) is an abnormal hemoglobin in which glutamic acid residue at the 6th position of the β-globin chain is replaced with a glycine residue due to a point mutation in the '' HBB'' gene. People with one copy of the gene for hemoglobin C do not experience symptoms, but can pass the abnormal gene on to their children. Those with two copies of the gene are said to have hemoglobin C disease and can experience mild anemia. It is possible for a person to have both the gene for hemoglobin S (the form associated with sickle cell anemia) and the gene for hemoglobin C; this state is called hemoglobin SC disease, and is generally more severe than hemoglobin C disease, but milder than sickle cell anemia. HbC was discovered by Harvey Itano and James V. Neel in 1950 in two African-American families. It has since been established that it is most common among people in West Africa. It confers survival benefits as individuals with HbC are naturally resistant to malar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allele
An allele is a variant of the sequence of nucleotides at a particular location, or Locus (genetics), locus, on a DNA molecule. Alleles can differ at a single position through Single-nucleotide polymorphism, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), but they can also have insertions and deletions of up to several thousand base pairs. Most alleles observed result in little or no change in the function or amount of the gene product(s) they code or regulate for. However, sometimes different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation. A notable example of this is Gregor Mendel's discovery that the white and purple flower colors in pea plants were the result of a single gene with two alleles. Nearly all multicellular organisms have two sets of chromosomes at some point in their biological life cycle; that is, they are diploid. For a given locus, if the two chromosomes contain the same allele, they, and the organism, are homozygous with re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin, Hb or Hgb) is a protein containing iron that facilitates the transportation of oxygen in red blood cells. Almost all vertebrates contain hemoglobin, with the sole exception of the fish family Channichthyidae. Hemoglobin in the blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (lungs or gills) to the other tissues of the body, where it releases the oxygen to enable aerobic respiration which powers an animal's metabolism. A healthy human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. Hemoglobin is a metalloprotein, a chromoprotein, and a globulin. In mammals, hemoglobin makes up about 96% of a red blood cell's dry matter, dry weight (excluding water), and around 35% of the total weight (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL of O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen capacity seventy-fold compared to dissolved oxygen in blood plasma alone. The mammalian hemoglobin molecule can bind and transport up to four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle Cell-beta Thalassemia
A sickle, bagging hook, reaping-hook or grasshook is a single-handed agricultural tool designed with variously curved blades and typically used for harvesting or reaping grain crops, or cutting succulent forage chiefly for feeding livestock. Falx was a synonym, but was later used to mean any of a number of tools that had a curved blade that was sharp on the inside edge. Since the beginning of the Iron Age hundreds of region-specific variants of the sickle have evolved, initially of iron and later steel. This great diversity of sickle types across many cultures can be divided into smooth or serrated blades, both of which can be used for cutting either green grass or mature cereals using slightly different techniques. The serrated blade that originated in prehistoric sickles still dominates in the reaping of grain and is even found in modern grain-harvesting machines and in some kitchen knives. History Pre-Neolithic The development of the sickle in Mesopotamia can be traced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sickle Cell
Sickle cell disease (SCD), also simply called sickle cell, is a group of inherited Hemoglobinopathy, haemoglobin-related blood disorders. The most common type is known as sickle cell anemia. Sickle cell anemia results in an abnormality in the oxygen-carrying protein haemoglobin found in red blood cells. This leads to the red blood cells adopting an abnormal sickle-like shape under certain circumstances; with this shape, they are unable to deform as they pass through Capillary, capillaries, causing blockages. Problems in sickle cell disease typically begin around 5 to 6 months of age. A number of health problems may develop, such as attacks of pain (known as a sickle cell crisis) in joints, anemia, swelling in the hands and feet, bacterial infections, dizziness and stroke. The probability of severe symptoms, including long-term pain, increases with age. Without treatment, people with SCD rarely reach adulthood but with good healthcare, median life expectancy is between 58 and 66 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylketonuria
Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism that results in decreased metabolism of the amino acid phenylalanine. Untreated PKU can lead to intellectual disability, seizures, behavioral problems, and mental disorders. It may also result in a musty smell and lighter skin. A baby born to a mother who has poorly treated PKU may have heart problems, a small head, and low birth weight. Phenylketonuria is an inherited genetic disorder. It is caused by mutations in the '' PAH'' gene, which can result in inefficient or nonfunctional phenylalanine hydroxylase, an enzyme responsible for the metabolism of excess phenylalanine. This results in the buildup of dietary phenylalanine to potentially toxic levels. It is autosomal recessive, meaning that both copies of the gene must be mutated for the condition to develop. The two main types are classic PKU and variant PKU, depending on whether any enzyme function remains. Those with one copy of a mutated gene typically do not ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandhoff Disease
Sandhoff disease is a lysosomal genetic, lipid storage disorder caused by the inherited deficiency to create functional beta-hexosaminidases A and B. These catabolic enzymes are needed to degrade the neuronal membrane components, ganglioside GM2, its derivative GA2, the glycolipid globoside in visceral tissues, and some oligosaccharides. Accumulation of these metabolites leads to a progressive destruction of the central nervous system and eventually to death. The rare autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder is clinically almost indistinguishable from Tay–Sachs disease, another genetic disorder that disrupts beta-hexosaminidases A and S. There are three subsets of Sandhoff disease based on when first symptoms appear: classic infantile, juvenile and adult late onset. Symptoms and signs Sandhoff disease symptoms are clinically indeterminable from Tay–Sachs disease. The classic infantile form of the disease has the most severe symptoms and is incredibly hard to diagnose at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GM2-gangliosidosis, AB Variant
GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant is a rare, autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that causes progressive destruction of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. It has a similar pathology to Sandhoff disease and Tay–Sachs disease. The three diseases are classified together as the GM2 gangliosidoses, because each disease represents a distinct molecular point of failure in the activation of the same enzyme, beta-hexosaminidase. AB variant is caused by a failure in the gene that makes an enzyme cofactor for beta-hexosaminidase, called the GM2 activator. Symptoms and signs Signs and symptoms of GM2-gangliosidosis, AB variant are identical with those of infantile Tay–Sachs disease, except that enzyme assay testing shows normal levels of hexosaminidase A. Infantile Sandhoff disease has similar symptoms and prognosis, except that there is deficiency of both hexosaminidase A and hexosaminidase B. Infants with this disorder typically appear normal until the age of 3 to 6 month ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tay–Sachs Disease
Tay–Sachs disease is an Genetic disorder, inherited fatal lysosomal storage disease that results in the destruction of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. The most common form is infantile Tay–Sachs disease, which becomes apparent around the age of three to six months of age, with the infant losing the ability to turn over, sit, or crawl. This is then followed by seizures, hearing loss, and paralysis, inability to move, with death usually occurring by the age of three to five. Less commonly, the disease may occur later in childhood, adolescence, or adulthood (juvenile or late-onset). These forms tend to be less severe, but the juvenile form typically results in death by the age of 15. Tay–Sachs disease is caused by a genetic mutation in the ''HEXA'' gene on chromosome 15, which codes a Protein subunit, subunit of the hexosaminidase enzyme known as hexosaminidase A. It is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. The mutation disrupts the activity of the enzyme, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
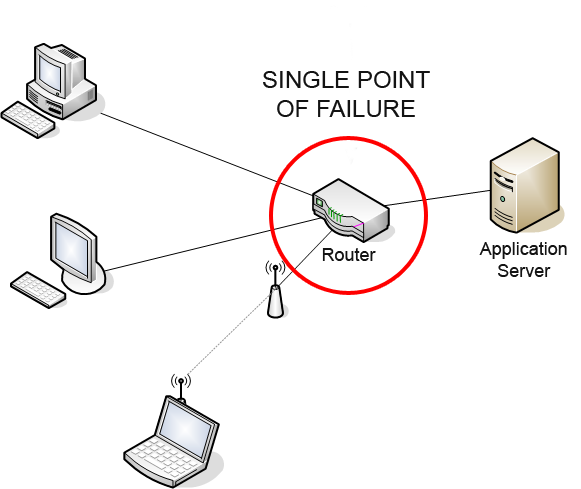
Single Point Of Failure
A single point of failure (SPOF) is a part of a system that would Cascading failure, stop the entire system from working if it were to fail. The term single point of failure implies that there is not a backup or redundant option that would enable the system to continue to function without it. SPOFs are undesirable in any system with a goal of high availability or Reliability engineering, reliability, be it a business practice, software application, or other industrial system. If there is a SPOF present in a system, it produces a potential interruption to the system that is substantially more disruptive than an error would elsewhere in the system. Overview Systems can be made robust by adding Redundancy (engineering), redundancy in all potential SPOFs. Redundancy can be achieved at various levels. The assessment of a potential SPOF involves identifying the critical components of a complex system that would provoke a total systems failure in case of wikt:malfunction, malfunction. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |