|
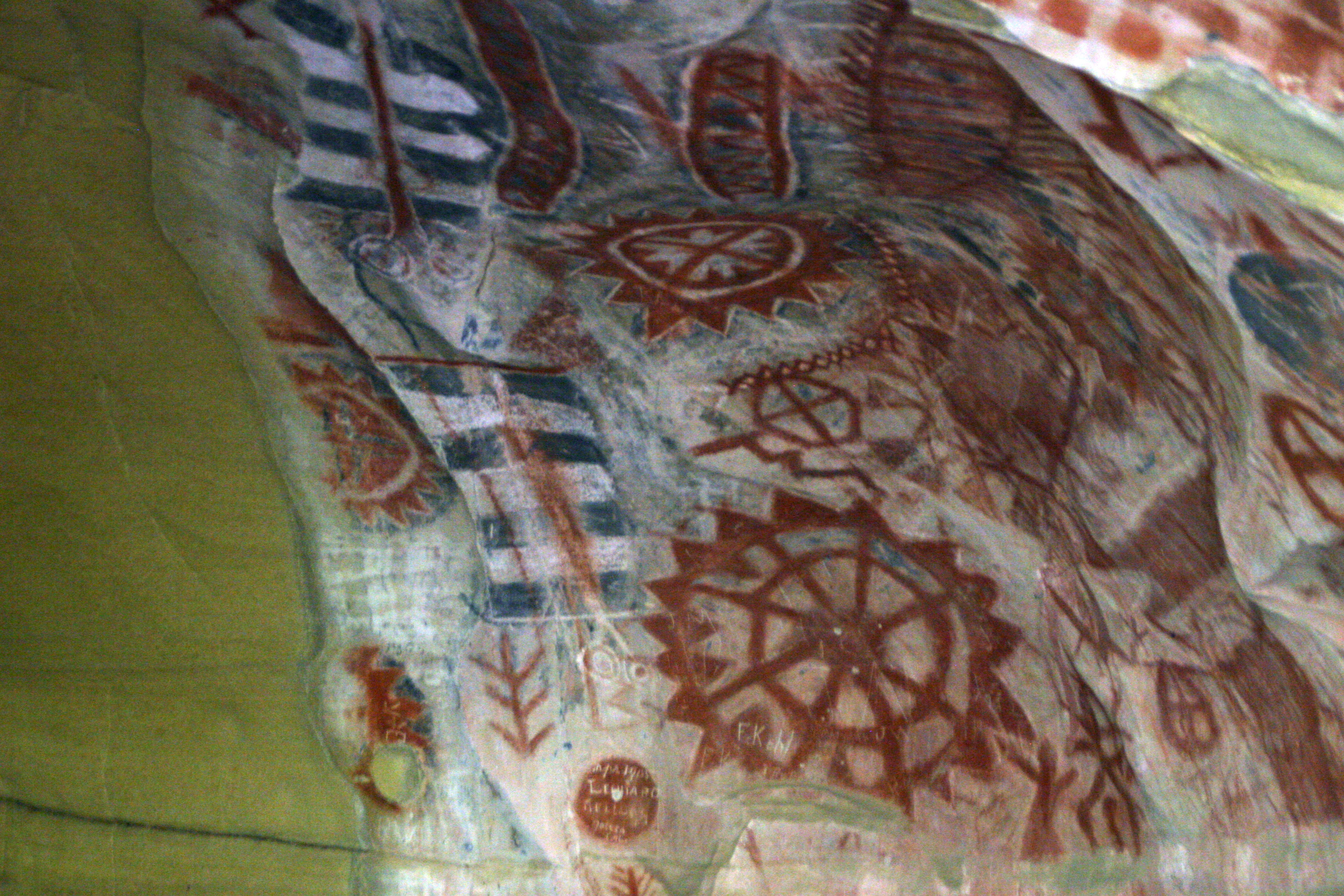
Compass Rose Network
A rhumbline network (or windrose network) is a navigational aid consisting in lines drawn from multiple vertices in different directions forming a web-like mesh. They were featured on portolan charts and other early nautical charts used in the medieval age and age of exploration in marine navigation. Since the invention of the Mercator projection , the term ''rhumb line'' (or ''loxodrome'') has been redefined to mean a mathematically precise curve of constant bearing on the Earth's surface. To avoid confusion, the lines on earlier sailing charts can be unambiguously called ''windrose lines'' (after wind roses), since they are not true rhumb lines by the modern definition. A rhumb line in the modern sense is only straight on a chart drawn with the Mercator projection, but not on charts from the 13th–16th centuries. Older windrose lines were a close approximation on charts of the Mediterranean Sea and surrounding areas, but the rhumb lines on small-scale maps such as the T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another. Tide tables can be used for any given locale to find the predicted times and amplitude (or " tidal range"). The predictions are influenced by many factors including the alignment of the Sun and Moon, the phase and amplitude of the tide (pattern of tides in the deep ocean), the amphidromic systems of the oceans, and the shape of the coastline and near-shore bathymetry (see '' Timing''). They are however only predictions, the actual time and height of the tide is affected by wind and atmospheric pressure. Many shorelines experience semi-diurnal tides—two nearly equal high and low tides each day. Other locations have a diurnal tide—one high and low tide each day. A "mixed tide"—two uneven magnitude tides a day—is a third regular category. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hexadecagon
In mathematics, a hexadecagon (sometimes called a hexakaidecagon or 16-gon) is a sixteen-sided polygon. Regular hexadecagon A ''regular polygon, regular hexadecagon'' is a hexadecagon in which all angles are equal and all sides are congruent. Its Schläfli symbol is and can be constructed as a Truncation (geometry), truncated octagon, t, and a twice-truncated square tt. A truncated hexadecagon, t, is a triacontadigon, . Construction As 16 = 24 (a power of two), a regular hexadecagon is constructible polygon, constructible using compass and straightedge: this was already known to ancient Greek mathematicians. Measurements Each angle of a regular hexadecagon is 157.5 Degree (angle), degrees, and the total angle measure of any hexadecagon is 2520 degrees. The area of a regular hexadecagon with edge length ''t'' is :\begin A = 4t^2 \cot \frac =& 4t^2 \left(1+\sqrt+\sqrt\right)\\ =& 4t^2 (\sqrt+1)(\sqrt+1) .\end Because the hexadecagon has a number of sides that is a power of tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is called the radius. The length of a line segment connecting two points on the circle and passing through the centre is called the diameter. A circle bounds a region of the plane called a Disk (mathematics), disc. The circle has been known since before the beginning of recorded history. Natural circles are common, such as the full moon or a slice of round fruit. The circle is the basis for the wheel, which, with related inventions such as gears, makes much of modern machinery possible. In mathematics, the study of the circle has helped inspire the development of geometry, astronomy and calculus. Terminology * Annulus (mathematics), Annulus: a ring-shaped object, the region bounded by two concentric circles. * Circular arc, Arc: any Connected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portolan
Portolan charts are nautical charts, first made in the 13th century in the Mediterranean basin and later expanded to include other regions. The word ''portolan'' comes from the Italian ''portolano'', meaning "related to ports or harbors", and which since at least the 17th century designates "a collection of sailing directions". Definition The term "portolan chart" was coined in the 1890s because at the time it was assumed that these maps were related to portolani, medieval or early modern books of sailing directions. Other names that have been proposed include rhumb line charts, compass charts or loxodromic charts whereas modern French scholars prefer to call them nautical charts to avoid any relationship with portolani. Several definitions of portolan chart coexist in the literature. A narrow definition includes only medieval or, at the latest, early modern sea charts (i.e. maps that primarily cover maritime rather than inland regions) that include a network of rhumb line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrus Vesconte
Pietro Vesconte (fl. 1310–1330) was a Genoese cartographer and geographer. A pioneer of the field of the portolan chart, he influenced Italian and Catalan mapmaking throughout the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries. He appears to have been the first professional mapmaker to sign and date his works regularly. Although Vesconte was born in Genoa, he produced much of his work in Venice. He was active between 1310 and 1330, producing numerous maps. His nautical charts are among the earliest to map the Mediterranean and Black Sea regions accurately. He also produced progressively more accurate depictions of the coastlines of northern Europe, in particular that of Britain and, to a lesser extent, Ireland. Pietro Vesconte's 1311 portolan chart of the east Mediterranean is the oldest signed and dated nautical chart that survives from the medieval period. He is also the author of at least four signed multi-sheet atlases (1313, 1318a, 1318b, c. 1321), where the various sheets can be co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Map From Pietro Vesconte 1325 Atlas
The Atlantic Ocean is the second largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, with an area of about . It covers approximately 17% of Earth's surface and about 24% of its water surface area. During the Age of Discovery, it was known for separating the New World of the Americas (North America and South America) from the Old World of Afro-Eurasia (Africa, Asia, and Europe). Through its separation of Afro-Eurasia from the Americas, the Atlantic Ocean has played a central role in the development of human society, globalization, and the histories of many nations. While the Norse were the first known humans to cross the Atlantic, it was the expedition of Christopher Columbus in 1492 that proved to be the most consequential. Columbus's expedition ushered in an age of exploration and colonization of the Americas by European powers, most notably Portugal, Spain, France, and the United Kingdom. From the 16th to 19th centuries, the Atlantic Ocean was the center of both an eponymous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralised authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued into the Early Middle Ages. The large-scale movements of the Migration Period, including various Germanic peoples, formed new kingdoms in what remained of the Western Roman Empire. In the 7th century, North Africa and the Middle East—once part of the Byzantine Empire� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leo Bagrow
Leo Bagrow (born Lev Semenovich Bagrov; 6 July 1881 – 10 August 1957) was a Russian-born historian of cartography, founder of the journal ''Imago Mundi''. He grew up in Russia, and initially pursued a career within the Imperial Russian Navy. In naval service, he traveled extensively to conduct surveying work. During this time, he encountered the historical map collection of Arctic explorer Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld in Helsinki and became interested in the history of mapmaking. Following the outbreak of World War I, he taught navigation and what may have been the world's first academic course on the history of geodesy and cartography in Saint Petersburg. By this time he had also begun publishing scholarly articles and receiving international recognition within his field. Following the Russian Revolution, he fled the country, never to return. He settled in Berlin, where he began working as a dealer in antique maps. There he met Hans Wertheim, with whom he founded the world's first i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loxodrome
In navigation, a rhumb line, rhumb (), or loxodrome is an arc crossing all meridians of longitude at the same angle, that is, a path with constant azimuth ( bearing as measured relative to true north). Navigation on a fixed course (i.e., steering the vessel to follow a constant cardinal direction) would result in a rhumb-line track. Introduction The effect of following a rhumb line course on the surface of a globe was first discussed by the Portuguese mathematician Pedro Nunes in 1537, in his ''Treatise in Defense of the Marine Chart'', with further mathematical development by Thomas Harriot in the 1590s. A rhumb line can be contrasted with a great circle, which is the path of shortest distance between two points on the surface of a sphere. On a great circle, the bearing to the destination point does not remain constant. If one were to drive a car along a great circle one would hold the steering wheel fixed, but to follow a rhumb line one would have to turn the wheel, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Projection
In cartography, a map projection is any of a broad set of Transformation (function) , transformations employed to represent the curved two-dimensional Surface (mathematics), surface of a globe on a Plane (mathematics), plane. In a map projection, coordinates, often expressed as latitude and longitude, of locations from the surface of the globe are transformed to coordinates on a plane. Projection is a necessary step in creating a two-dimensional map and is one of the essential elements of cartography. All projections of a sphere on a plane necessarily distort the surface in some way. Depending on the purpose of the map, some distortions are acceptable and others are not; therefore, different map projections exist in order to preserve some properties of the sphere-like body at the expense of other properties. The study of map projections is primarily about the characterization of their distortions. There is no limit to the number of possible map projections. More generally, proje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
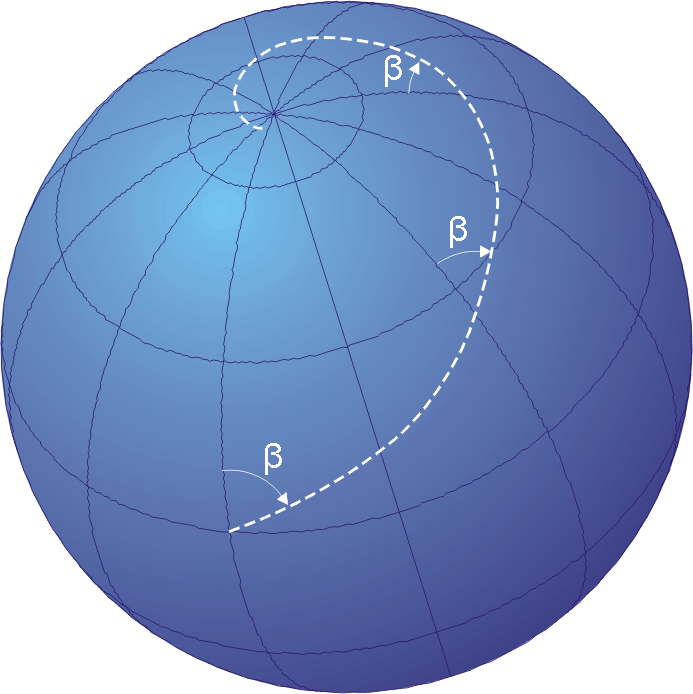
Isoazimuthal
The isoazimuth is the locus of the points on the Earth's surface whose initial orthodromic course with respect to a fixed point is constant. That is, if the initial orthodromic course Z from the starting point ''S'' to the fixed point ''X'' is 80 degrees, the associated isoazimuth is formed by all points whose initial orthodromic course with respect to point ''X'' is 80° (with respect to true north). The isoazimuth is written using the notation ''isoz(X, Z)'' . The isoazimuth is of use when navigating with respect to an object of known location, such as a radio beacon. A straight line called the ''azimuth line of position'' is drawn on a map, and on most common map projections this is a close enough approximation to the isoazimuth. On the Littrow projection, the correspondence is exact. This line is then crossed with an astronomical observation called a Sumner line, and the result gives an estimate of the navigator's position. Isoazimutal on the spherical Earth Let ''X'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |