|
Common Water-plantain
''Alisma plantago-aquatica'', also known as European water-plantain, common water-plantain or mad-dog weed, is a perennial flowering aquatic plant widespread across most of Europe and Asia, and apparently spread elsewhere in both the Old and New World. Description ''Alisma plantago-aquatica'' is a hairless plant that grows in shallow water, consists of a fibrous root, several basal long stemmed leaves long, and a triangular stem up to tall. It has branched inflorescence bearing numerous small flowers, across, with three round or slightly jagged, white or pale purple petals. The flowers open in the afternoon. There are three blunt green sepals and six stamens per flower. The carpels often exist as a flat single whorl. It flowers from June until August. The fruits appear as a ring of seeds inside each flower. Chemistry Chemical constituents of —rhizomes of ''Alisma orientale'' (syn. ''Alisma '' var. ''orientale'') as a traditional Chinese medicine—include alisol A 24-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
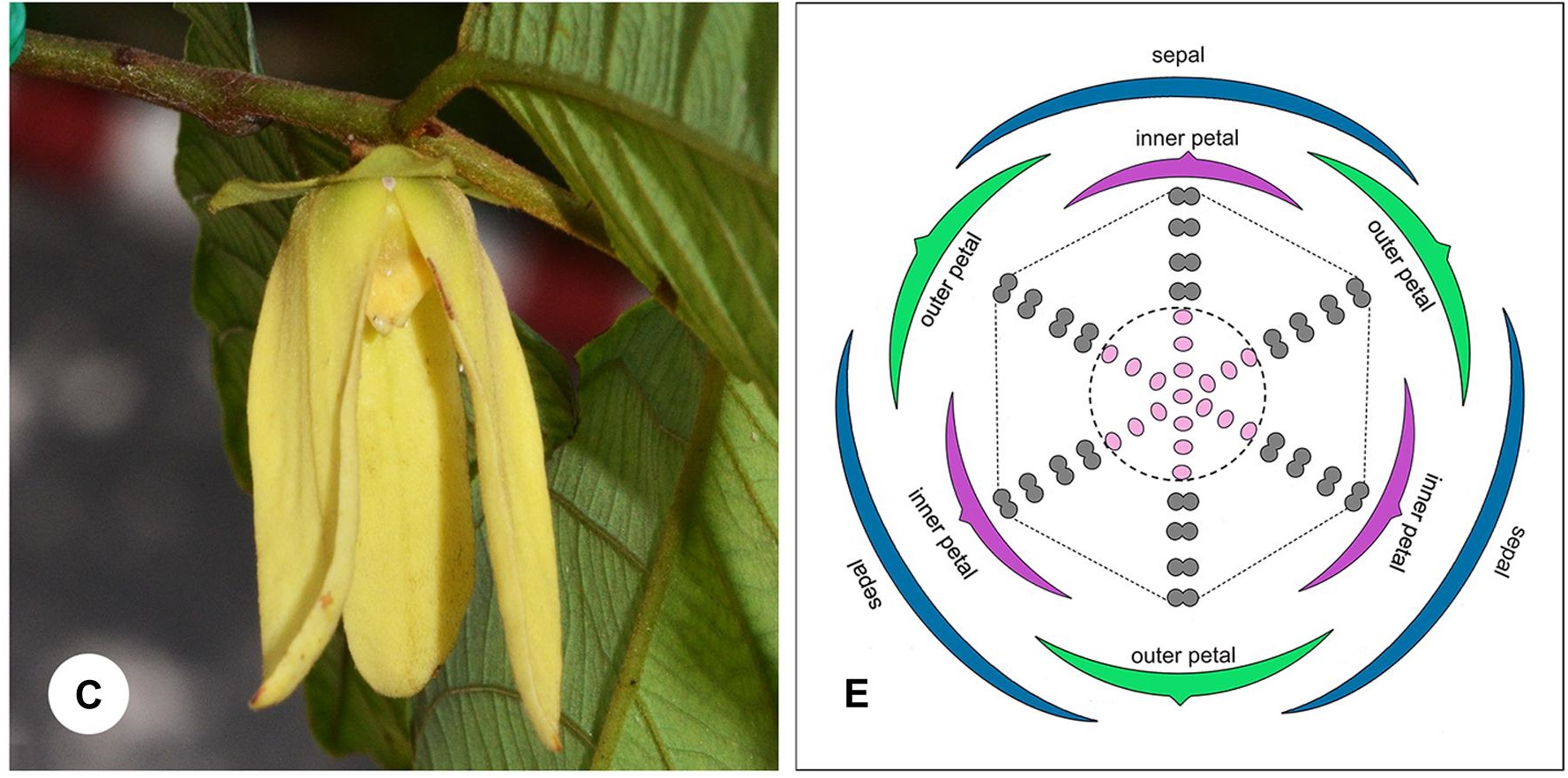
Whorl (botany)
In botany, a whorl or verticil is a whorled arrangement of Leaf, leaves, sepals, petals, stamens, or Gynoecium#Carpels, carpels that radiate from a single point and surround or wrap around the stem or stalk. A leaf whorl consists of at least three elements; a pair of opposite leaves is not called a whorl. For leaves to grow in whorls is fairly rare except in plant species with very short Plant stem, internodes and some other genera (''Galium'', ''Nerium'', ''Elodea'' etc.). Leaf whorls occur in some trees such as ''Brabejum stellatifolium'' and other species in the family Proteaceae (e.g., in the genus ''Banksia''). In plants such as these, crowded internodes within the leaf whorls alternate with long internodes between the whorls. The Morphology (biology), morphology of most flowers (called cyclic flowers) is based on four types of whorls: # The Sepal, calyx: zero or more whorls of sepals at the base # The Petal, corolla: zero or more whorls of petals above the calyx # The Stam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morocco
Morocco, officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It has coastlines on the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria to Algeria–Morocco border, the east, and the disputed territory of Western Sahara to Morocco–Western Sahara border, the south. Morocco also claims the Spain, Spanish Enclave and exclave, exclaves of Ceuta, Melilla and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera, and several small Plazas de soberanía, Spanish-controlled islands off its coast. It has a population of approximately 37 million. Islam is both the official and predominant religion, while Arabic and Berber are the official languages. Additionally, French and the Moroccan dialect of Arabic are widely spoken. The culture of Morocco is a mix of Arab culture, Arab, Berbers, Berber, Culture of Africa, African and Culture of Europe, European cultures. Its capital is Rabat, while its largest city is Casablanca. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic, is a country on the Iberian Peninsula in Southwestern Europe. Featuring Cabo da Roca, the westernmost point in continental Europe, Portugal borders Spain to its north and east, with which it shares Portugal-Spain border, the longest uninterrupted border in the European Union; to the south and the west is the North Atlantic Ocean; and to the west and southwest lie the Macaronesia, Macaronesian archipelagos of the Azores and Madeira, which are the two Autonomous Regions of Portugal, autonomous regions of Portugal. Lisbon is the Capital city, capital and List of largest cities in Portugal, largest city, followed by Porto, which is the only other Metropolitan areas in Portugal, metropolitan area. The western Iberian Peninsula has been continuously inhabited since Prehistoric Iberia, prehistoric times, with the earliest signs of Human settlement, settlement dating to 5500 BC. Celts, Celtic and List of the Pre-Roman peoples of the Iberia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plantago
''Plantago'' is a genus of about 200 species of flowering plants in the family Plantaginaceae, commonly called plantains or fleaworts. The common name plantain is shared with the unrelated cooking plantain. Most are herbaceous plants, though a few are subshrubs growing to tall. Description The leaves are sessile or have a poorly defined petiole. They have three or five parallel veins that diverge in the wider part of the leaf. Leaves are broad or narrow, depending on the species. The inflorescences are borne on stalks typically tall, and can be a short cone or a long spike, with numerous tiny wind-pollinated flowers. Species The boundaries of the genus ''Plantago'' have been fairly stable, with the main question being whether to include '' Bougueria'' (one species from the Andes) and '' Littorella'' (2–3 species of aquatic plants).Albach, D. C., Meudt, H. M. & Oxelman, B. 2005Piecing together the "new" Plantaginaceae ''American Journal of Botany'' 92: 297–315. There a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celtic Languages
The Celtic languages ( ) are a branch of the Indo-European language family, descended from the hypothetical Proto-Celtic language. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward Lhuyd in 1707, following Paul-Yves Pezron, who made the explicit link between the Celts described by classical writers and the Welsh and Breton languages. During the first millennium BC, Celtic languages were spoken across much of Europe and central Anatolia. Today, they are restricted to the northwestern fringe of Europe and a few diaspora communities. There are six living languages: the four continuously living languages Breton, Irish, Scottish Gaelic and Welsh, and the two revived languages Cornish and Manx. All are minority languages in their respective countries, though there are continuing efforts at revitalisation. Welsh is an official language in Wales and Irish is an official language across the island of Ireland and of the European Union. Welsh is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alisma Triviale
''Alisma triviale'', the northern water plantain, is a perennial semi-aquatic or aquatic plant in the water-plantain family (Alismataceae). Description It is a perennial herb that ranges in height from 1-3 ft. Each plant has long-petioled, lanceolate and linear leaves that grow in a clump. A flowering stem rises between them. The flowers have 3 green sepals and 3 white or pink-tinged petals. Distribution and habitat The plant is native to Canada (including the Northwest Territories), the United States (including Alaska), and Northern Mexico Mexico, officially the United Mexican States, is a country in North America. It is the northernmost country in Latin America, and borders the United States to the north, and Guatemala and Belize to the southeast; while having maritime boundar .... It grows in shallow water or mud. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alisma Subcordatum
''Alisma subcordatum'', the American water plantain, is a perennial aquatic plant in the water-plantain family (Alismataceae). This plant grows to about in height with lance to oval shaped leaves rising from bulbous corms with fibrous roots. Any leaves that form underwater are weak and quick to rot; they rarely remain on adult plants. A branched inflorescence with white to pink 3-petaled flowers blooms from June to September. The seeds are eaten by waterfowl and upland birds.USDA NRCS Plant Fact Sheet Retrieved 2010-03-18. Native Americans dried and ate the submerged rootlike structures. The species name ''subcordatum'' means "almost heart-shaped". Distribution and habitat< ...
|
North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere, Northern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres. North America is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and the Caribbean Sea, and to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean. The region includes Middle America (Americas), Middle America (comprising the Caribbean, Central America, and Mexico) and Northern America. North America covers an area of about , representing approximately 16.5% of Earth's land area and 4.8% of its total surface area. It is the third-largest continent by size after Asia and Africa, and the list of continents and continental subregions by population, fourth-largest continent by population after Asia, Africa, and Europe. , North America's population was estimated as over 592 million people in list of sovereign states and dependent territories in North America, 23 independent states, or about 7.5% of the world's popula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alisma Plantago-aquatica (Water Plantain) - Theodore Green - 26 1931 10
''Alisma plantago-aquatica'', also known as European water-plantain, common water-plantain or mad-dog weed, is a perennial flowering aquatic plant widespread across most of Europe and Asia, and apparently spread elsewhere in both the Old and New World. Description ''Alisma plantago-aquatica'' is a hairless plant that grows in shallow water, consists of a fibrous root, several basal long stemmed leaves long, and a triangular stem up to tall. It has branched inflorescence bearing numerous small flowers, across, with three round or slightly jagged, white or pale purple petals. The flowers open in the afternoon. There are three blunt green sepals and six stamens per flower. The carpels often exist as a flat single whorl. It flowers from June until August. The fruits appear as a ring of seeds inside each flower. Chemistry Chemical constituents of —rhizomes of ''Alisma orientale'' (syn. ''Alisma '' var. ''orientale'') as a traditional Chinese medicine—include alisol A 24-a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lanceolate
The following terms are used to describe leaf plant morphology, morphology in the description and taxonomy (biology), taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (that is, the leaf blade or 'lamina' is undivided) or compound (that is, the leaf blade is divided into two or more leaflet (botany), leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, and may be smooth or have hair, bristles, or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf#Terminology, leaf article. The terms listed here all are supported by technical and professional usage, but they cannot be represented as mandatory or undebatable; readers must use their judgement. Authors often use terms arbitrarily, or coin them to taste, possibly in ignorance of established terms, and it is not always clear whether because of ignorance, or personal preference, or because usages change with time or context, or because of variation between specimens, even specimens from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |