|
Comes Sacrae Vestis
''Protovestiarios'' (, ) was a high Byzantine court position, originally reserved for eunuchs. In the late Byzantine period (12th–15th centuries), it denoted the Empire's senior-most financial official, and was also adopted by the medieval Serbian state as protovestiyar (прото-вестијар). History and functions The title is first attested in 412, as the ''comes sacrae vestis'', an official in charge of the Byzantine emperor's "sacred wardrobe" (), coming under the ''praepositus sacri cubiculi''. In Greek, the term used was ''oikeiakon vestiarion'' (, "private wardrobe"), and by this name it remained known from the 7th century onward. As such, the office was distinct from the public or imperial wardrobe, the '' basilikon vestiarion'', which was entrusted to a state official, the ''chartoularios tou vestiariou''. The private wardrobe also included part of the Byzantine emperor's private treasury, and controlled an extensive staff. Consequently, the holders of this of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protovestiarites
The (, βεστιαρίτης, '' vestiarites'') were a corps of imperial bodyguards and fiscal officials in the Byzantine Empire, attested from the 11th to the 15th centuries. History and functions The appear in the mid-11th century, with the first known , John Iberitzes, attested in 1049.. As their name indicates, they had a connection to the imperial wardrobe and treasury, the , probably initially raised as a guard detachment for it. From circa 1080 on, they were formally distinguished into two groups: the "inner" or "household" ( or ), attached to the emperor's private treasury (the or ) under a , and the "outer" () under a , who were probably under the public or state treasury (). Gradually, they replaced various other groups of armed guards that the Byzantine emperors had employed inside Constantinople itself, such as the or the , and became the exclusive corps of the emperor's confidential agents. As the princess and historian Anna Komnene writes, they were the courtie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudo-Kodinos
George Kodinos (), also Pseudo-Kodinos or Codinus, is the conventional name of an anonymous late 15th-century author of late Byzantine literature. Their attribution to him is only traditional, and is based on the fact that all three works come in the same manuscript. The works referred to are the following: #'' Patria'' (Πάτρια Κωνσταντινουπόλεως), treating of the history, topography, and monuments of Constantinople. It is divided into five sections: (a) the foundation of the city; (b) its situation, limits and topography; (c) its statues, works of art, and other notable sights; (d) its buildings; (e) and the construction of the Hagia Sophia. It was written in the reign of Basil II (976-1025), revised and rearranged under Alexios I Komnenos (1081–1118), and perhaps copied by Codinus, whose name it bears in some (later) manuscripts. The chief sources are: the ''Patria'' of Hesychius Illustrius of Miletus, the anonymous ''Parastaseis syntomoi chronikai'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
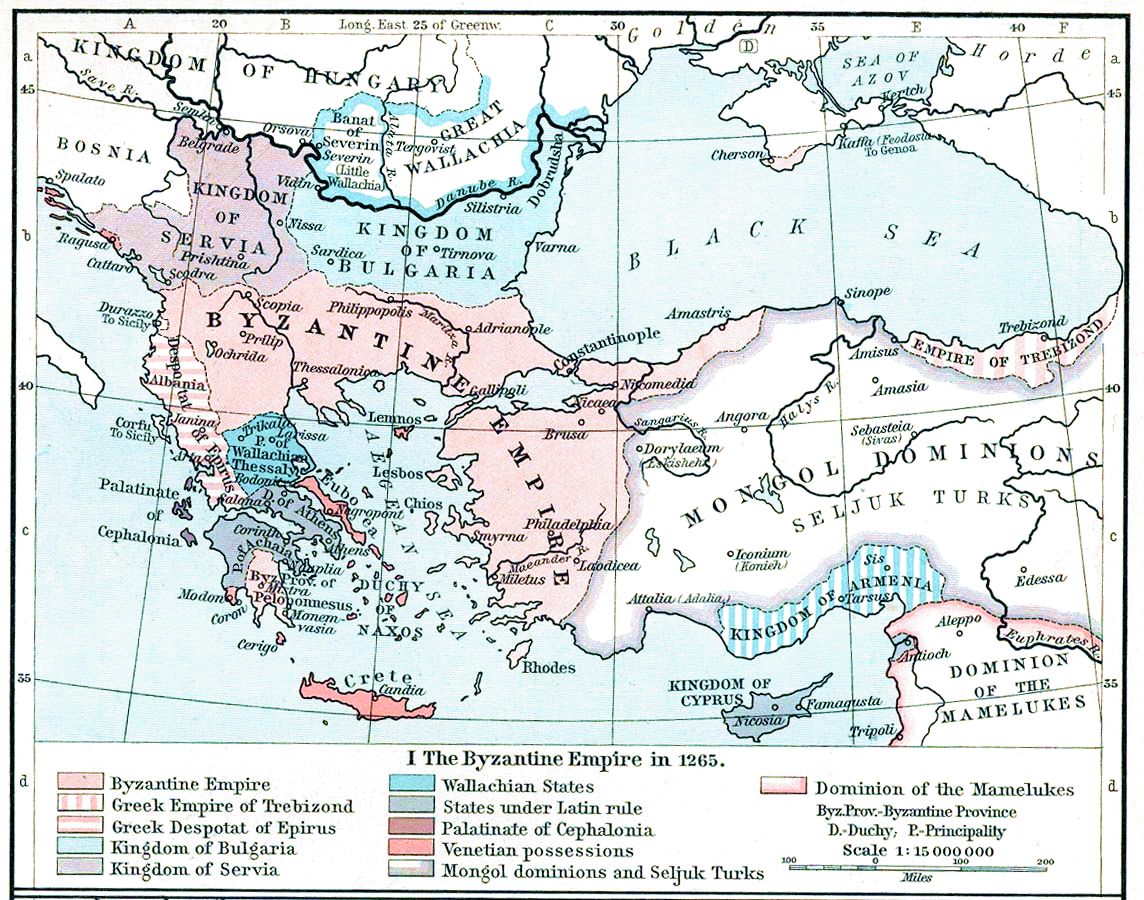
Thomas Preljubović
Thomas Preljubović (; ) was Despot of Epirus, ruler of the Despotate of Epirus in Ioannina from 1367 to his death in 1384. Thomas was an unpopular ruler and is appraised very negatively by his contemporaries. On December 23, 1384 he was stabbed to death by his guards at dawn. The conspiracy of the faction which overthrew him involved his wife Maria Angelina Doukaina Palaiologina, Maria Angelina who succeeded him. A great deal of his rule was preoccupied with fighting against the Albanians of the Despotate of Arta to his south, the Zenebishi family to his north and the Mazreku (Epirus), Mazreku and other clans to his northwest. Thomas gave himself the self-styled epithet of Albanian-slayer (Greek language, Greek: Αλβανοκτόνος/Αλβανιτόκτονος) after torturing Albanian prisoners in order to terrify his enemies. Life Early years Thomas was the son of ''caesar'' Gregorios Preljub (), the Serbian governor of Medieval Thessaly, Thessaly, who died in late 1355 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Apsaras
Michael Apsaras () was a 14th-century Greek noble from Ioannina. Apsaras came from a noble Byzantine family and one of the most influential families in the city of Ioannina. Apsaras received the title of '' protovestiarios'' and became chief minister of the Despot of Epirus, Thomas Preljubović Thomas Preljubović (; ) was Despot of Epirus, ruler of the Despotate of Epirus in Ioannina from 1367 to his death in 1384. Thomas was an unpopular ruler and is appraised very negatively by his contemporaries. On December 23, 1384 he was stabbed to ... (1366–1384). Both Apsaras and Thomas were negatively portrayed in the '' Chronicle of Ioannina'' due to the cruelty they displayed against the local population of Ioannina. Apsaras was exiled from Ioannina after the assassination of Thomas. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Apsaras, Michael 14th-century Greek people People from the Despotate of Epirus People from Ioannina Protovestiarioi Medieval Ioannina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael VIII Palaiologos
Michael VIII Palaiologos or Palaeologus (; 1224 – 11 December 1282) reigned as Byzantine emperor from 1261 until his death in 1282, and previously as the co-emperor of the Empire of Nicaea from 1259 to 1261. Michael VIII was the founder of the Palaiologos, Palaiologan dynasty that would rule the Byzantine Empire until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. He Reconquest of Constantinople, recovered Constantinople from the Latin Empire in 1261 and transformed the Empire of Nicaea into a Byzantine Empire under the Palaiologos dynasty, restored Byzantine Empire. His reign saw considerable recovery of Byzantine power, including the enlargement of the Byzantine army and Byzantine navy, navy. It also included the reconstruction of the city of Constantinople, and the increase of its population. His re-establishment of the University of Constantinople contributed to the Palaeologan Renaissance, a cultural flowering between the 13th and 15th centuries. It was also at this time that the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Tarchaneiotes
Michael Palaiologos Tarchaneiotes () was a Byzantine aristocrat and general, active against the Turks in Asia Minor and against the Angevins in the Balkans from 1278 until his death from disease in 1284. Biography Michael Tarchaneiotes was the son of Nikephoros Tarchaneiotes, ''megas domestikos'' to John III Vatatzes (r. 1221–1254), and Maria-Martha Palaiologina, the eldest sister of Michael VIII Palaiologos (r. 1259–1261)... His family supported the rise of Palaiologos to the throne in 1259, and the new emperor rewarded Michael and his brothers: they came to live in the imperial palace, while eventually Michael and his younger brother Andronikos received the high offices of ''protovestiarios'' and '' megas konostaulos'' respectively, and the third brother, John, became a general. He first appears in the sources taking part in the 1262 campaign against the Despotate of Epirus under his uncle, John Palaiologos. In 1278, having risen to the post of ''megas domestikos'', Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios V Doukas
Alexios V Doukas (; died December 1204), Latinized as Alexius V Ducas, was Byzantine emperor from February to April 1204, just prior to the sack of Constantinople by the participants of the Fourth Crusade. His family name was Doukas, but he was also known by the nickname Mourtzouphlos or Murtzuphlus (), referring to either bushy, overhanging eyebrows or a sullen, gloomy character. He achieved power through a palace coup, killing his predecessors in the process. Though he made vigorous attempts to defend Constantinople from the crusader army, his military efforts proved ineffective. His actions won the support of the mass of the populace, but he alienated the elite of the city. Following the fall, sack, and occupation of the city, Alexios V was blinded by his father-in-law, the ex-emperor Alexios III, and later executed by the new Latin regime. He was the last Byzantine emperor to rule in Constantinople until the Byzantine recapture of Constantinople in 1261. Origins and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodore II Laskaris
Theodore II Laskaris or Ducas Lascaris (; November 1221/1222 – 16 August 1258) was Emperor of Nicaea from 1254 to 1258. He was the only child of Emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes and Empress Irene Laskarina. His mother was the eldest daughter of Theodore I Laskaris, who had established the Empire of Nicaea as a successor state to the Byzantine Empire in Asia Minor after the crusaders captured the Byzantine capital, Constantinople, during the Fourth Crusade in 1204. Theodore received an excellent education from two renowned scholars, Nikephoros Blemmydes and George Akropolites. He made friends with young intellectuals, especially with a page of low birth, George Mouzalon. Theodore began to write treatises on theological, historical and philosophical themes in his youth. Emperor John III arranged for Theodore to marry Elena Asenina in 1235, to forge an alliance with her father, Ivan Asen II, Emperor of Bulgaria, against the Latin Empire of Constantin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Mouzalon
George Mouzalon (; – 25 August 1258) was a high official of the Empire of Nicaea under Theodore II Laskaris (). Of humble origin, he became Theodore's companion in childhood and was raised to high state office upon the latter's assumption of power. This caused great resentment from the aristocracy, which had monopolized high offices and opposed Theodore's policies. Shortly before Theodore's death in 1258, he was appointed regent of Theodore's under-age son John IV Laskaris (). He was assassinated only a few days later by soldiers, as the result of a conspiracy led by the nobles under the soon-to-be emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos (). Biography Early life and service under Theodore II The Mouzalon family is first attested in the 11th century, but produced few notable members until the mid-13th century, with exception of Nicholas IV Mouzalon, Patriarch of Constantinople in 1147–1151.. George Mouzalon was born at Adramyttium on the western Anatolian coast in . His fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John III Vatatzes
John III Doukas Vatatzes, Latinized as Ducas Vatatzes (; 1192 – 3 November 1254), was Emperor of Nicaea from 1221 to 1254. He was succeeded by his son, known as Theodore II Doukas Laskaris. Life John Doukas Vatatzes, born in about 1192 in Didymoteicho, was probably the son of the general Basil Vatatzes, who was killed in battle in 1194, and his wife, a cousin of the Emperors Isaac II Angelos and Alexios III Angelos. John Doukas Vatatzes had two older brothers. The eldest was Isaac Doukas Vatatzes (1188-1261), while his younger brother died young. Through his marriage to Eudokia Angelina he fathered Theodora Doukaina Vatatzaina, who later married Michael VIII Palaiologos. The middle brother's name is unknown, but his daughter married the ''protovestiarios'' Alexios Raoul. A successful soldier from a military family, John had risen to the position of protovestiarites when he was chosen in about 1216 by Emperor Theodore I Komnenos Laskaris as the second husband for his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexios Raoul (protovestiarios)
Alexios Raoul (; died c. 1258) was a Byzantine aristocrat and general of the Empire of Nicaea. He attained the rank of ''protovestiarios'' during the reign of Emperor John III Vatatzes (r. 1221–1254). Biography Alexios Raoul was the scion of a wealthy aristocratic family with large landholdings around Smyrna, and possibly the son of the ''sebastos'' Constantine Raoul, who had played a role in the usurpation of Alexios III Angelos (r. 1195–1203). He became the son-in-law of Emperor John III Vatatzes (r. 1221–1254), having married a niece of his... Alexios and Vatatzes's niece together had four sons, three of whom are known by name, John, Manuel and Isaac, and one daughter. Under Vatatzes, Alexios was raised to the rank of ''protovestiarios'', and was given command of troops in Macedonia. In 1242, he accompanied the emperor in his campaign against the ruler of Thessalonica, John Komnenos Doukas (r. 1237–1244).. He appears again in 1252, during Vatatzes's wars against the Des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos Doukas (cousin Of Michael VII)
Andronikos Doukas, Latinized as Andronicus Ducas (; died 14 October 1077), was a ''protovestiarios'' and '' protoproedros'' of the Byzantine Empire. Life Andronikos Doukas was son of the ''Caesar'' John Doukas and Eirene Pegonitissa. His father was a brother of Emperor Constantine X Doukas. His maternal grandfather was Niketas Pegonites. Andronikos himself was a first cousin of Michael VII Doukas. In 1071 Andronikos was the commander of a section of the Byzantine army in the campaign of Romanos IV Diogenes against the Seljuk Turks of Alp Arslan. Commanding the rearguard of the army during the Battle of Manzikert, Andronikos announced that the emperor had been cut down and deserted from the battlefield. He was widely blamed for causing the crushing defeat of the Byzantine forces and the subsequent capture of Romanos IV by the enemy. In 1072, after Romanos had been released by Alp Arslan, Andronikos and his brother Constantine were sent out by Michael VII and their father the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |