 |
Comb Filter
In signal processing, a comb filter is a Filter (signal processing), filter implemented by adding a delayed version of a signal processing, signal to itself, causing constructive and destructive Interference (wave propagation), interference. The frequency response of a comb filter consists of a series of regularly spaced notches in between regularly spaced ''peaks'' (sometimes called ''teeth'') giving the appearance of a comb. Comb filters exist in two forms, ''feedforward'' and ''feedback''; which refer to the direction in which signals are delayed before they are added to the input. Comb filters may be implemented in discrete time or continuous time forms which are very similar. Applications Comb filters are employed in a variety of signal processing applications, including: * Cascaded integrator–comb filter, Cascaded integrator–comb (CIC) filters, commonly used for anti-aliasing filter, anti-aliasing during interpolation and decimation (signal processing), decimation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Comb Filter Feedforward
A comb is a tool consisting of a shaft that holds a row of teeth for pulling through the hair to clean, untangle, or style it. Combs have been used since Prehistory, prehistoric times, having been discovered in very refined forms from settlements dating back to 5,000 years ago in Persia. Weaving combs made of whalebone dating to the middle and late Iron Age Europe, Iron Age have been found on archaeological digs in Orkney and Somerset. Description Combs are made of a shaft and teeth that are placed at a perpendicular angle to the shaft. Combs can be made out of a number of materials, most commonly plastic, metal, or wood. In antiquity, horn and whalebone was sometimes used. Combs made from ivory and tortoiseshell were once common but concerns for the animals that produce them have reduced their usage. Wooden combs are largely made of boxwood (genus), boxwood, cherry wood, or other fine-grained wood. Good quality wooden combs are usually handmade and polished. Combs come in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Audio Signal Processing
Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. Audio signals are electronic representations of sound waves—longitudinal waves which travel through air, consisting of compressions and rarefactions. The energy contained in audio signals or sound power level is typically measured in decibels. As audio signals may be represented in either Digital signal (signal processing), digital or analog signal, analog format, processing may occur in either domain. Analog processors operate directly on the electrical signal, while digital processors operate mathematically on its digital representation. History The motivation for audio signal processing began at the beginning of the 20th century with inventions like the telephone, phonograph, and radio that allowed for the transmission and storage of audio signals. Audio processing was necessary for early radio broadcasting, as there were many problems with stud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Difference Equation
In mathematics, a recurrence relation is an equation according to which the nth term of a sequence of numbers is equal to some combination of the previous terms. Often, only k previous terms of the sequence appear in the equation, for a parameter k that is independent of n; this number k is called the ''order'' of the relation. If the values of the first k numbers in the sequence have been given, the rest of the sequence can be calculated by repeatedly applying the equation. In ''linear recurrences'', the th term is equated to a linear function of the k previous terms. A famous example is the recurrence for the Fibonacci numbers, F_n=F_+F_ where the order k is two and the linear function merely adds the two previous terms. This example is a linear recurrence with constant coefficients, because the coefficients of the linear function (1 and 1) are constants that do not depend on n. For these recurrences, one can express the general term of the sequence as a closed-form expression o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Rule Of Thumb
In English language, English, the phrase ''rule of thumb'' refers to an approximate method for doing something, based on practical experience rather than theory. This usage of the phrase can be traced back to the 17th century and has been associated with various Trade (occupation), trades where quantities were measured by comparison to the width or length of a thumb. An erroneous folk etymology began circulating in the 1970s falsely connecting the origins of the phrase "rule of thumb" to legal doctrine on Domestic violence, domestic abuse. The error appeared in a number of law journals, and the United States Commission on Civil Rights published a report on domestic abuse titled "Under the Rule of Thumb" in 1982. Some efforts were made to discourage the phrase, which was seen as taboo owing to this false origin. During the 1990s, several authors correctly identified the spurious folk etymology; however, the connection to domestic violence was still being cited in some legal sources ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Loudspeakers
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or, more fully, a speaker system) is a combination of one or more speaker drivers, an enclosure, and electrical connections (possibly including a crossover network). The speaker driver is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. The driver is a linear motor connected to a diaphragm, which transmits the motor's movement to produce sound by moving air. An audio signal, typically originating from a microphone, recording, or radio broadcast, is electronically amplified to a power level sufficient to drive the motor, reproducing the sound corresponding to the original unamplified signal. This process functions as the inverse of a microphone. In fact, the ''dynamic speaker'' driver—the most common type—shares the same basic configuration as a dynamic microphone, which operates in reverse as a generator. The dynamic speaker was invented in 1925 by Edward W. Kello ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an Acoustical engineering, acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing (sense), Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Spectrograph
An optical spectrometer (spectrophotometer, spectrograph or spectroscope) is an instrument used to measure properties of light over a specific portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, typically used in spectroscopic analysis to identify materials. The variable measured is most often the irradiance of the light but could also, for instance, be the polarization state. The independent variable is usually the wavelength of the light or a closely derived physical quantity, such as the corresponding wavenumber or the photon energy, in units of measurement such as centimeters, reciprocal centimeters, or electron volts, respectively. A spectrometer is used in spectroscopy for producing spectral lines and measuring their wavelengths and intensities. Spectrometers may operate over a wide range of non-optical wavelengths, from gamma rays and X-rays into the far infrared. If the instrument is designed to measure the spectrum on an absolute scale rather than a relative one, then it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Astro-comb
An astro-comb is a type of frequency comb used in observational astronomy to increase the accuracy of wavelength calibration in spectrographs. The increased accuracy reduces systematic errors and enhances detection of small variations in stellar radial velocities caused by smaller orbiting exoplanets (e.g. Earth-mass planets), among other applications. Astro-combs are distinguished from conventional frequency combs by their focus on high repetition frequencies (with mode spacings of ≥10 GHz). A green astro-comb was installed in January 2013 in the high accuracy radial velocity planet searcher in the northern hemisphere (HARPS-N) spectrograph at the Telescopio Nazionale Galileo on the Canary Islands. The device was developed by a team led by Chih-Hao Li of Harvard University. This astro-comb uses a pulsed laser to filter starlight before feeding the signal into a spectrograph. As of December 2016, it is gathering data from Venus to demonstrate its ability to discover exoplanet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
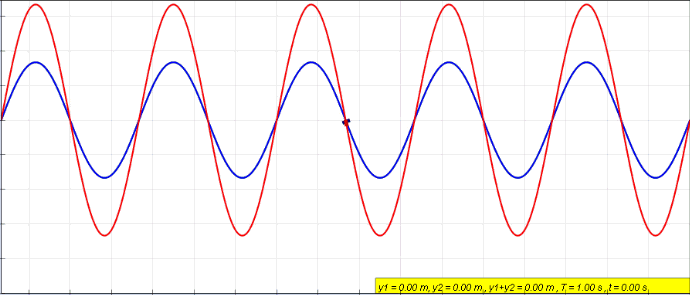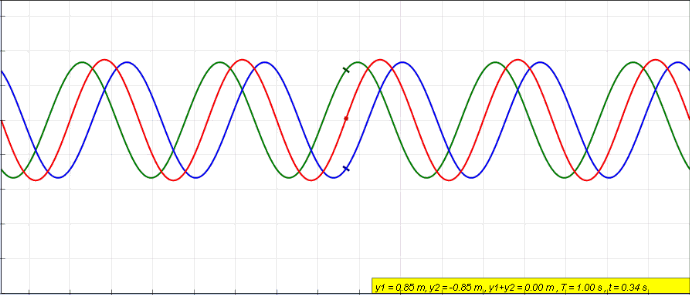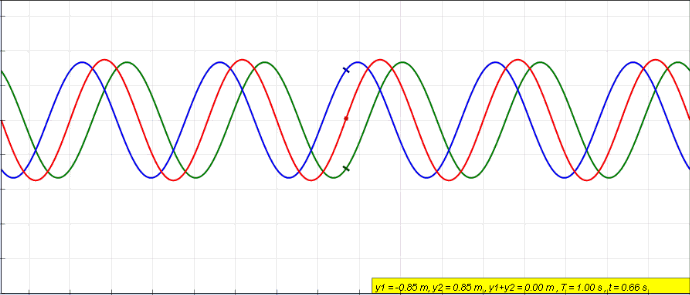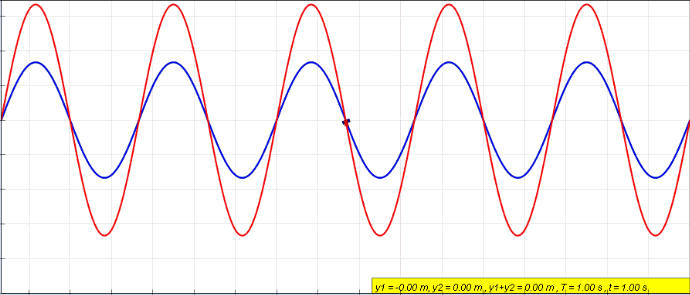 |
Standing Waves
In physics, a standing wave, also known as a stationary wave, is a wave that oscillates in time but whose peak amplitude profile does not move in space. The peak amplitude of the wave oscillations at any point in space is constant with respect to time, and the oscillations at different points throughout the wave are in phase. The locations at which the absolute value of the amplitude is minimum are called nodes, and the locations where the absolute value of the amplitude is maximum are called antinodes. Standing waves were first described scientifically by Michael Faraday in 1831. Faraday observed standing waves on the surface of a liquid in a vibrating container. Franz Melde coined the term "standing wave" (German: ''stehende Welle'' or ''Stehwelle'') around 1860 and demonstrated the phenomenon in his classic experiment with vibrating strings. This phenomenon can occur because the medium is moving in the direction opposite to the movement of the wave, or it can arise in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Acoustics
Acoustics is a branch of physics that deals with the study of mechanical waves in gases, liquids, and solids including topics such as vibration, sound, ultrasound and infrasound. A scientist who works in the field of acoustics is an acoustician while someone working in the field of acoustics technology may be called an Acoustical engineering, acoustical engineer. The application of acoustics is present in almost all aspects of modern society with the most obvious being the audio and noise control industries. Hearing (sense), Hearing is one of the most crucial means of survival in the animal world and speech is one of the most distinctive characteristics of human development and culture. Accordingly, the science of acoustics spreads across many facets of human society—music, medicine, architecture, industrial production, warfare and more. Likewise, animal species such as songbirds and frogs use sound and hearing as a key element of mating rituals or for marking territories. Art, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Digital Waveguide Synthesis
Digital waveguide synthesis is the synthesis of audio using a digital waveguide. Digital waveguides are efficient computational models for physical media through which acoustic waves propagate. For this reason, digital waveguides constitute a major part of most modern physical modeling synthesizers. A lossless digital waveguide realizes the discrete form of d'Alembert's solution of the one-dimensional wave equation as the superposition of a right-going and a left-going waves, : y(m, n) = y^+(m - n) + y^-(m + n), where y^+ is the right-going wave, and y^- is the left-going wave. It can be seen from this representation that sampling the function y at a given position m and time n merely involves summing two delayed copies of its traveling waves. These traveling waves will reflect at boundaries such as the suspension points of vibrating strings or the open or closed ends of tubes. Hence the waves travel along closed loops. Digital waveguide models therefore comprise digit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |