|
Color Palette
In color theory, a color scheme is a combination of 2 or more colors used in aesthetic or practical design. Aesthetic color schemes are used to create style and appeal. Colors that create a color harmony, harmonious feeling when viewed together are often used together in aesthetic color schemes. Practical color schemes are used to inhibit or facilitate color tasks, such as camouflage color schemes or high-visibility clothing, high visibility color schemes. Qualitative and quantitative color schemes are used to encode unordered categorical data and ordered data, respectively. Color schemes are often described in terms of logical combinations of colors on a color wheel or within a color space. Harmonious schemes Harmonious color schemes are designed to accomplish an Color task#Aesthetic, aesthetic color task and enhance color harmony. They do not represent any underlying variable. The color scheme of a logo is typically purely aesthetic. A color scheme in marketing is referred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Theory
Color theory, or more specifically traditional color theory, is a historical body of knowledge describing the behavior of colors, namely in color mixing, color contrast effects, color harmony, color schemes and color symbolism. Modern color theory is generally referred to as color science. While there is no clear distinction in scope, traditional color theory tends to be more subjective and have artistic applications, while color science tends to be more objective and have functional applications, such as in chemistry, astronomy or color reproduction. Color theory dates back at least as far as Aristotle's treatise ''On Colors'' and Bharata_(sage), Bharata's Natya_Shastra, Nāṭya Shāstra. A formalization of "color theory" began in the 18th century, initially within a partisan controversy over Isaac Newton's theory of color (''Opticks'', 1704) and the nature of primary colors. By the end of the 19th century, a schism had formed between traditional color theory and color science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Code
A color code is a system for encoding and representing non-color information with colors to facilitate communication. This information tends to be categorical (representing unordered/qualitative categories) though may also be sequential (representing an ordered/quantitative variable). History The earliest examples of color codes in use are for long-distance communication by use of flags, as in semaphore communication. The United Kingdom adopted a color code scheme for such communication wherein red signified danger and white signified safety, with other colors having similar assignments of meaning. As chemistry and other technologies advanced, it became expedient to use coloration as a signal for telling apart things that would otherwise be confusingly similar, such as wiring in electrical and electronic devices, and pharmaceutical pills. Encoded Variable A color code encodes a variable, which may have different representations, where the color code type should match th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Categorical Variable
In statistics, a categorical variable (also called qualitative variable) is a variable that can take on one of a limited, and usually fixed, number of possible values, assigning each individual or other unit of observation to a particular group or nominal category on the basis of some qualitative property. In computer science and some branches of mathematics, categorical variables are referred to as enumerations or enumerated types. Commonly (though not in this article), each of the possible values of a categorical variable is referred to as a level. The probability distribution associated with a random categorical variable is called a categorical distribution. Categorical data is the statistical data type consisting of categorical variables or of data that has been converted into that form, for example as grouped data. More specifically, categorical data may derive from observations made of qualitative data that are summarised as counts or cross tabulations, or from observat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prison Uniform
A prison uniform is a set of standardized clothing worn by prisoners. It usually includes visually distinct clothes worn to indicate the wearer is a prisoner, in clear distinction from civil clothing. Prison uniforms are intended to make prisoners instantly identifiable, limit risks through concealed objects and prevent injuries through undesignated clothing objects. A prison uniform can also spoil attempts of prison escape, escape, as prison uniforms typically use a design and color scheme that is easily noticed and identified even at a greater distance. Wearing a prison uniform is typically done only reluctantly and is often perceived as badge of shame, stigmatizing, and as an invasion into the autonomy of decision. The Standard Minimum Rules for the Treatment of Prisoners, United Nations Standard Minimum Rules for the Treatment of Prisoners (The Mandela Rules) first adopted in 1955 and amended in 2015, prohibit degrading or humiliating clothing, requiring in Rule 19 that: #Eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-and-white
Black-and-white (B&W or B/W) images combine black and white to produce a range of achromatic brightnesses of grey. It is also known as greyscale in technical settings. Media The history of various visual media began with black and white, and as technology improved, altered to color. However, there are exceptions to this rule, including black-and-white fine art photography, as well as many film motion pictures and art film(s). Early photographs in the late 19th and early to mid 20th centuries were often developed in black and white, as an alternative to sepia due to limitations in film available at the time. Black and white was also prevalent in early television broadcasts, which were displayed by changing the intensity of monochrome phosphurs on the inside of the screen, before the introduction of colour from the 1950s onwards. Black and white continues to be used in certain sections of the modern arts field, either stylistically or to invoke the perception of a hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
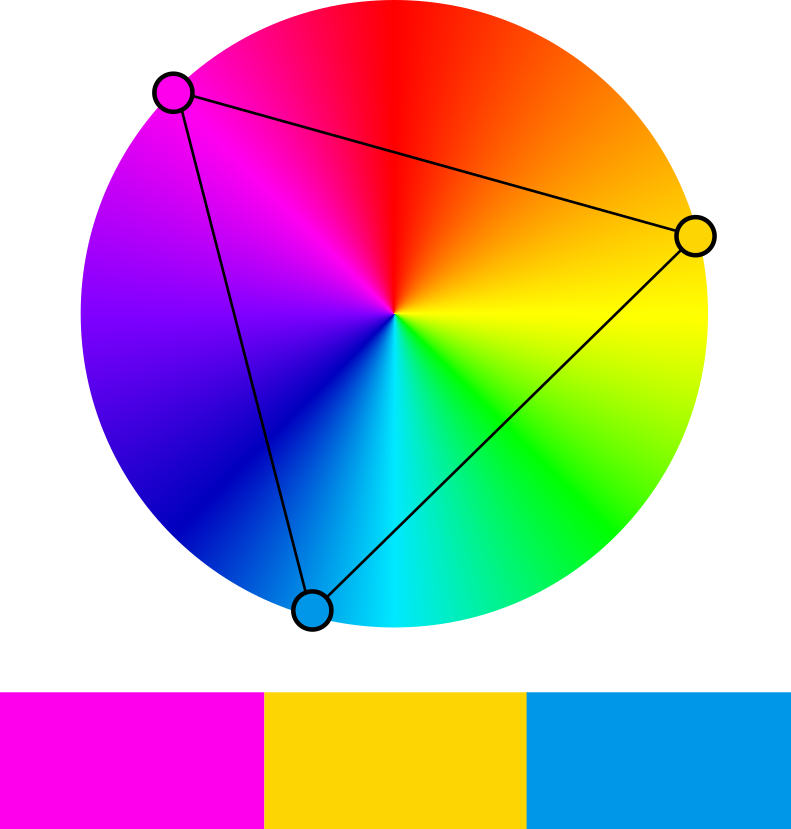
Triadic Colors
In color theory, a color scheme is a combination of 2 or more colors used in aesthetic or practical design. Aesthetic color schemes are used to create style and appeal. Colors that create a harmonious feeling when viewed together are often used together in aesthetic color schemes. Practical color schemes are used to inhibit or facilitate color tasks, such as camouflage color schemes or high visibility color schemes. Qualitative and quantitative color schemes are used to encode unordered categorical data and ordered data, respectively. Color schemes are often described in terms of logical combinations of colors on a color wheel or within a color space. Harmonious schemes Harmonious color schemes are designed to accomplish an aesthetic color task and enhance color harmony. They do not represent any underlying variable. The color scheme of a logo is typically purely aesthetic. A color scheme in marketing is referred to as a trade dress and can sometimes be protected by trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complementary Colors
Complementary colors are pairs of colors which, when combined or mixed, cancel each other out (lose chroma) by producing a grayscale color like white or black. When placed next to each other, they create the strongest contrast for those two colors. Complementary colors may also be called "opposite colors". Which pairs of colors are considered complementary depends on the color model that one uses: * Modern color theory uses either the RGB additive color model or the CMY subtractive color model, and in these, the complementary pairs are red–cyan, green–magenta (one of the purples), and blue–yellow. * In the traditional RYB color model, the complementary color pairs are red–green, yellow– purple, and blue– orange. * Opponent process theory suggests that the most contrasting color pairs are red–green and blue–yellow. * The black–white color pair is common to all the above theories. These contradictions stem in part from the fact that traditional color ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monochromatic Color
A monochrome or monochromatic image, object or palette is composed of one color (or values of one color). Images using only shades of grey are called grayscale (typically digital) or black-and-white (typically analog). In physics, monochromatic light refers to electromagnetic radiation that contains a narrow band of wavelengths, which is a distinct concept. Application Of an image, the term monochrome is usually taken to mean the same as black and white or, more likely, grayscale, but may also be used to refer to other combinations containing only tones of a single color, such as green-and-white or green-and-red. It may also refer to sepia displaying tones from light tan to dark brown or cyanotype ("blueprint") images, and early photographic methods such as daguerreotypes, ambrotypes, and tintypes, each of which may be used to produce a monochromatic image. In computing, monochrome has two meanings: * it may mean having only one color which is either on or off (als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Temperature
Color temperature is a parameter describing the color of a visible light source by comparing it to the color of light emitted by an idealized opaque, non-reflective body. The temperature of the ideal emitter that matches the color most closely is defined as the color temperature of the original visible light source. The color temperature scale describes only the ''color'' of light emitted by a light source, which may actually be at a different (and often much lower) temperature. Color temperature has applications in lighting, photography, videography, publishing, manufacturing, astrophysics, and other fields. In practice, color temperature is most meaningful for light sources that correspond somewhat closely to the color of some black body, i.e., light in a range going from red to orange to yellow to white to bluish white. Although the concept of correlated color temperature extends the definition to any visible light, the color temperature of a green or a purple light rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Color
A secondary color is a color made by mixing two primary colors of a given color model in even proportions. Combining two secondary colors in the same manner produces a tertiary color. Secondary colors are special in traditional color theory, but have no special meaning in color science. Overview Primary color In traditional color theory, it is believed that all colors can be mixed from 3 universal primary - or pure - colors, which were originally believed to be red, yellow and blue pigments (representing the RYB color model). However, modern color science does not recognize universal primary colors and only defines primary colors for a given color model or color space. RGB and CMYK color models are popular color models in modern color science, but are only chosen as efficient primaries, in that their combination leads to a large gamut. However, any three primaries can produce a viable color gamut. The RYB model continues to be used and taught as a color model for practical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Color
A secondary color is a color made by color mixing, mixing two primary colors of a given color model in even proportions. Combining two secondary colors in the same manner produces a tertiary color. Secondary colors are special in traditional color theory, but have no special meaning in color science. Overview Primary color In traditional color theory, it is believed that all colors can be mixed from 3 universal primary - or pure - colors, which were originally believed to be red, yellow and blue pigments (representing the RYB color model). However, modern color science does not recognize universal primary colors and only defines primary colors for a given color model or color space. RGB color model, RGB and CMYK color model, CMYK color models are popular color models in modern color science, but are only chosen as efficient primaries, in that their combination leads to a large gamut. However, any three primaries can produce a viable color gamut. The RYB model continues to be us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |